Day383.注解编程 -Spring5
Posted 阿昌喜欢吃黄桃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Day383.注解编程 -Spring5相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
注解编程
⼀、注解基础概念
1. 什么是注解编程
指的是在类或者⽅法上加特定的注解(@XXX),完成特定功能的开发。
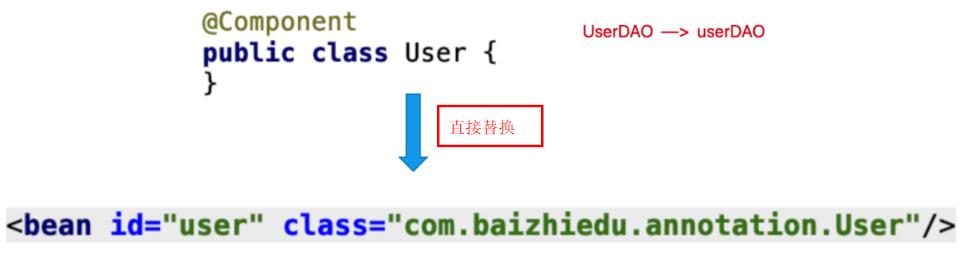
@Component
public class XXX{}
2. 为什么要讲解注解编程
-
注解开发⽅便
代码简洁 开发速度⼤⼤提⾼ -
Spring开发潮流
Spring2.x引⼊注解 Spring3.x完善注解 SpringBoot普及 推⼴注解编程
3. 注解的作⽤
- 替换XML这种配置形式,简化配置
- 替换接⼝,实现调⽤双⽅的契约性
通过注解的⽅式,在功能调⽤者和功能提供者之间达成约定,进⽽进⾏功能的调⽤。
因为注解应⽤更为⽅便灵活,所以在现在的开发中,更推荐通过注解的形式,完成

4. Spring注解的发展历程
-
Spring2.x开始⽀持注解编程 @Component @Service @Scope…
⽬的:提供的这些注解只是为了在某些情况下简化XML的配置,作为XML开发的有益补充。 -
Spring3.x @Configuration @Bean…
⽬的:彻底替换XML,基于纯注解编程 -
Spring4.x SpringBoot
提倡使⽤注解常⻅开发
5. Spring注解开发的⼀个问题
Spring基于注解进⾏配置后,还能否解耦合呢?
在Spring框架应⽤注解时,如果对注解配置的内容不满意,可以通过Spring配置⽂件进⾏覆盖的。
⼆、Spring的基础注解(Spring2.x)
这个阶段的注解,仅仅是简化XML的配置,并不能完全替代XML
1. 对象创建相关注解
- 搭建开发环境
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang"/>
作⽤:让Spring框架在设置包及其⼦包中扫描对应的注解,使其⽣效。
-
对象创建相关注解
-
@Component
-
作⽤:
- 替换原有spring配置⽂件中的<bean标签
-
注意:
- id属性 component注解 提供了默认的设置⽅式
⾸单词⾸字⺟⼩写class属性通过反射获得class内容

-
-
@Component 细节
-
如何显示指定⼯⼚创建对象的id值
@Component("achang") -
Spring配置⽂件覆盖注解配置内容
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="u" class="com.achang.bean.User"/>id值 class的值 要和 注解中的设置保持⼀值
-
-
@Component的衍⽣注解
@Repository ---> XXXDAO public class UserDAO{} @Service public class UserService{} @Controller public class RegAction{}-
注意:
-
本质上这些衍⽣注解就是@Component作⽤ <bean
细节 @Service(“s”) -
⽬的:
- 更加准确的表达⼀个类型的作⽤
-
注意:
- Spring整合Mybatis开发过程中 不使⽤@Repository @Component
-
-
-
-
@Scope注解
-
作⽤:控制简单对象创建次数
-
注意:不添加@Scope Spring提供
默认值 singleton<bean id="" class="" scope="singleton|prototype"/>
-
-
@Lazy注解
-
作⽤:延迟创建单实例对象
-
注意:⼀旦使⽤了@Lazy注解后,
Spring会在使⽤这个对象时候,进⾏这个对象的创建<bean id="" class="" lazy="false"/>
-
-
⽣命周期⽅法相关注解
- 初始化相关⽅法 @PostConstruct
InitializingBean
<bean init-method=""/>- 销毁⽅法 @PreDestroy
DisposableBean
<bean destory-method=""/>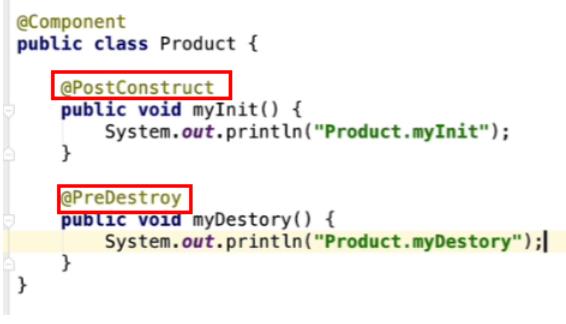
- 注意:
- 上述的2个注解并不是Spring提供的,JSR(JavaEE规范)520
- 再⼀次的验证,通过注解实现了接⼝的契约性
- 初始化相关⽅法 @PostConstruct
2. 注⼊相关注解
- ⽤户⾃定义类型 @Autowired

@Autowired细节
1. Autowired注解基于类型进⾏注⼊ [推荐]
基于类型的注⼊:注⼊对象的类型,必须与⽬标成员变量类型相同或者是其⼦类
(实现类)
2. Autowired Qualifier 基于名字进⾏注⼊ [了解]
基于名字的注⼊:注⼊对象的id值,必须与Qualifier注解中设置的名字相同
3. Autowired注解放置位置
a) 放置在对应成员变量的set⽅法上
b) 直接把这个注解放置在成员变量之上,Spring通过反射直接对成员变量进⾏注⼊(赋值)[推荐]
4. JavaEE规范中类似功能的注解
JSR250 @Resouce(name="userDAOImpl") 基于名字进⾏注⼊
@Autowired()
@Qualifier("userDAOImpl")
注意:如果在应⽤Resource注解时,名字没有配对成功,那么他会继续按照类型进⾏注⼊。
JSR330 @Inject 作⽤ @Autowired完全⼀致 基于类型进⾏注⼊ ---》EJB3.0
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
-
JDK类型
- @Value
1. 设置xxx.properties id = 10 name = achang 2. Spring的⼯⼚读取这个配置⽂件 <context:property-placeholder location=""/> 3. 代码 属性 @Value("${key}")- @PropertySource
1. 作⽤: ⽤于替换Spring配置⽂件中的<context:property-placeholder location=""/>标签 2. 开发步骤 1. 设置xxx.properties id = 10 name = achang 2. 应⽤@PropertySource 3. 代码 属性 @Value()-
@Value注解使⽤细节
- @Value注解
不能应⽤在静态成员变量上
如果应⽤,赋值(注⼊)失败@Value注解+Properties这种⽅式,不能注⼊集合类型
Spring提供新的配置形式 YAML YML (SpringBoot) - @Value注解
3. 注解扫描详解
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang"/>
当前包 及其 ⼦包
1. 排除⽅式
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang">
<context:exclude-filter type="" expression=""/>
type:
assignable:排除特定的类型 不进⾏扫描
annotation:排除特定的注解 不进⾏扫描
aspectj:切⼊点表达式
包切⼊点: com.achang.bean..*
类切⼊点: *..User
regex:正则表达式
custom:⾃定义排除策略框架底层开发
</context:component-scan>
排除策略可以叠加使⽤
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang">
<context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.achang.bean.User"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="aspectj" expression="com.achang.injection.. *"/>
</context:component-scan>
2. 包含⽅式
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="" expression=""/>
</context:component-scan>
1. use-default-filters="false"
作⽤:让Spring默认的注解扫描⽅式 失效。
2. <context:include-filter type="" expression=""/>
作⽤:指定扫描那些注解
type:assignable:排除特定的类型 不进⾏扫描
annotation:排除特定的注解 不进⾏扫描
aspectj:切⼊点表达式
包切⼊点: com.baizhiedu.bean..*
类切⼊点: *..User
regex:正则表达式
custom:⾃定义排除策略框架底层开发
包含的⽅式⽀持叠加
<context:component-scan base-package="com.achang" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>
</context:component-scan>
4. 对于注解开发的思考
- 配置互通
//Spring注解配置 配置⽂件的配置 互通
@Repository
public class UserDAOImpl{
}
public class UserServiceImpl{
private UserDAO userDAO;
set/get
}
<bean id="userService" class="com.achang.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDAO" ref="userDAOImpl"/>
</bean>
- 什么情况下使⽤注解 什么情况下使⽤配置⽂件
@Component 替换 <bean
基础注解(@Component @Autowired @Value) 程序员开发类型的配置
1. 在程序员开发的类型上 可以加⼊对应注解 进⾏对象的创建
User UserService UserDAO UserAction
2. 应⽤其他⾮程序员开发的类型时,还是需要使⽤<bean 进⾏配置的
后续使用@Configuration + @Bean
SqlSessionFactoryBean MapperScannerConfigure
5. SSM整合开发(半注解开发)
-
搭建开发环境
-
引⼊相关jar 【SSM POM】
-
引⼊相关配置⽂件
- applicationContext.xml
- struts.xml
- log4.properties
- XXXMapper.xml
-
初始化配置
- Web.xml Spring (ContextLoaderListener)
- Web.xml Struts Filter
-
-
编码
注解扫描 <context:component-scan base-package=""/>-
DAO (Spring+Mybatis)
1. 配置⽂件的配置 1. DataSource 2. SqlSessionFactory ----> SqlSessionFactoryBean 1. dataSource 2. typeAliasesPackage 3. mapperLocations 3. MapperScannerConfigur ---> DAO接⼝实现类 2. 编码 1. entity 2. table 3. DAO接⼝ 4. 实现Mapper⽂件 -
Service
1. 原始对象 ---》 注⼊DAO @Service ---> @Autowired 2. 额外功能 ---》 DataSourceTransactionManager ---> dataSource 3. 切⼊点 + 事务属性 @Transactional(propagation,readOnly...) 4. 组装切⾯ <tx:annotation-driven -
Controller (Spring+Struts2)
1. @Controller @Scope("prototype") public class RegAction implements Action{ @Autowired private UserService userServiceImpl; } 2. struts.xml <action class="spring配置⽂件中action对应的id值"/>
-
三、Spring的⾼级注解(Spring3.x 及以上)
明天继续!!!
以上是关于Day383.注解编程 -Spring5的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章