数据结构 Java 版玩转链表链表面试题及个人题解
Posted 吞吞吐吐大魔王
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构 Java 版玩转链表链表面试题及个人题解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- 1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
- 2. 反转一个单链表
- 3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
- 4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
- 5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
- 6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
- 7. 在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针
- 8. 链表的回文结构
- 9. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
- 10. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
- 11. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev=head;
ListNode cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
cur=cur.next;
prev.next=cur;
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
}
2. 反转一个单链表
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode newHead=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=newHead;
newHead=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
return newHead;
}
}
方法: 头插法(从第二个节点开始对第一个节点进行头插)
注意:
逆置不是只将数值反转,而是将节点本身进行逆置
如果用前一章的 diplay 方法将逆置后的打印结果不正确,因为该 diplay 方法是从一开始定义的 head 节点开始打印,而现在真正的头节点已经改变,可以将其修改一下
public void display2(Node newHead){ Node cur = newHead; while(cur!=null){ System.out.print(cur.val + " "); cur=cur.next; } System.out.println(); }
3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
方法一:通过遍历找到节点数,然后找到中间节点
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head;
int count=0;
while(cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
count=count/2+1;
ListNode node=head;
int i=0;
while(i!=count-1){
node=node.next;
i++;
}
return node;
}
}
方法二: 快慢指针法(快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步)
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
方法一:通过遍历找到节点数,然后找到倒数第 k 个节点
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur = head;
int count=0;
while(cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
if(k<1 || k>count){
return null;
}
ListNode node = head;
int i=0;
while(i!=count-k){
node=node.next;
i++;
}
return node;
}
}
方法二: 快慢指针法(先让快指针走 k-1 步,再让快慢指针同时走)
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null || k<=0){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(k-1!=0){
fast=fast.next;
if(fast==null){
return null;
}
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null && l2==null){
return null;
}
if(l1==null && l2!=null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null && l1!=null){
return l1;
}
ListNode node=new ListNode();
ListNode head=node;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
while(l1!=null && l2!=null && l1.val<=l2.val){
node.next=l1;
node=node.next;
l1=l1.next;
}
while(l1!=null && l2!=null && l1.val>l2.val){
node.next=l2;
node=node.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(l1!=null){
node.next=l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
node.next=l2;
}
return head.next;
}
}
6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=pHead;
ListNode as=null;
ListNode ae=null;
ListNode bs=null;
ListNode be=null;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<x){
if(bs==null){
bs=cur;
be=bs;
}else{
be.next=cur;
be=be.next;
}
}else{
if(as==null){
as=cur;
ae=as;
}else{
ae.next=cur;
ae=ae.next;
}
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(bs==null){
return as;
}
be.next=as;
if(as!=null){
ae.next=null;
}
return bs;
}
}
其中 bs、be、as、ae,分别为小于 x 和大于 x 的两端的头尾节点
7. 在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead==null){
return null;
}
ListNode node=new ListNode(0);
ListNode newHead=node;
ListNode cur=pHead;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.next!=null && cur.val==cur.next.val){
while(cur.next!=null && cur.val==cur.next.val){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}else{
newHead.next=cur;
newHead=newHead.next;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
newHead.next=null;
return node.next;
}
}
8. 链表的回文结构
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
if(A==null){
return true;
}
if(A.next==null){
return true;
}
ListNode left=A;
ListNode mid=A;
ListNode right=A;
while(right!=null && right.next!=null){
right=right.next.next;
mid=mid.next;
}
ListNode cur=mid.next;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=mid;
mid=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
while(mid!=left){
if(mid.val!=left.val){
return false;
}
if(left.next==mid){
return true;
}
mid=mid.next;
left=left.next;
}
return true;
}
}
方法:
- 找中间节点
- 反转中间节点之后的链表
- 将反转链表头尾进行比较
9. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
public class Solution {
public int getLength(ListNode head){
if(head==null){
return 0;
}
int count=0;
while(head!=null){
count++;
head=head.next;
}
return count;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null || headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur1=headA;
ListNode cur2=headB;
int length1=getLength(headA);
int length2=getLength(headB);
int i=0;
if(length1>=length2){
while(i!=length1-length2){
cur1=cur1.next;
i++;
}
}else{
while(i!=length2-length1){
cur2=cur2.next;
i++;
}
}
while(cur1!=cur2){
cur1=cur1.next;
cur2=cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
}
方法: 因为共同节点之后,两个链表的节点一样长。只要在共同节点之前,让两个链表移动的节点与公共节点距离相等,再一步一步移动即可
10. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return false;
}
if(head.next==null){
return false;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
方法: 快慢指针法(通过快指针追击慢指针,能追得上则有环)
11. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast==null || fast.next==null){
return null;
}
fast=head;
while(fast!=slow){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
重点: 上述题中 fast=head ,以及后面代码含义就是找到公共节点之后,从该链表的头节点,以及交点,一起一步一步移动,当两个节点相遇时,则为第一个公共节点
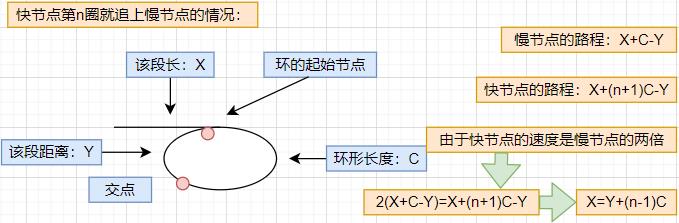
分析: 上述重点不懂点可以结合下图分析理解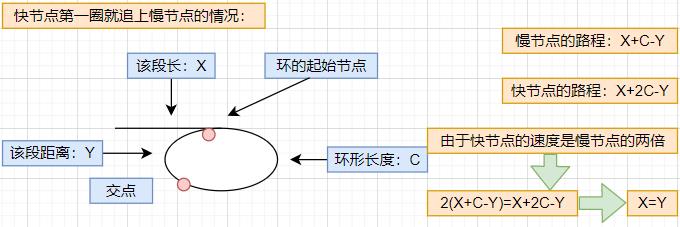
- 当第一圈就追上时: 结论为 X=Y,所以两个节点每次移动一步就可
- 当第 n 圈就追上时: 结论为 X=Y+(n-1)C。因为两个节点移动路程是一样的,并且交点那个节点移动 n-1 圈后,再要走 Y 正好到了起始节点。所以两个节点每次移动一步就可
如果你已经可以轻松应对上述题目了,可以继续去下面的链接中做题 Leetcode OJ 链接 和 牛客 OJ 链接
一起加油呀!
以上是关于数据结构 Java 版玩转链表链表面试题及个人题解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章