细说Kotlin工具函数及使用准则-转换函数map()过滤函数filter()聚合函数
Posted LQS_Android
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了细说Kotlin工具函数及使用准则-转换函数map()过滤函数filter()聚合函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
过滤
过滤是最常用的集合处理任务之一。在Kotlin中,过滤条件由 谓词 定义——接受一个集合元素并且返回布尔值的 lambda 表达式:true 说明给定元素与谓词匹配,false 则表示不匹配。
标准库包含了一组让你能够通过单个调用就可以过滤集合的扩展函数。这些函数不会改变原始集合,因此它们既可用于可变集合也可用于只读集合。为了操作过滤结果,应该在过滤后将其赋值给变量或链接其他函数。
按谓词过滤
基本的过滤函数是 filter()。当使用一个谓词来调用时,filter() 返回与其匹配的集合元素。对于 List 和Set,过滤结果都是一个 List,对 Map 来说结果还是一个 Map。
public inline fun <T> kotlin.collections.Iterable<T>.filter(predicate: (T) -> kotlin.Boolean): kotlin.collections.List<T> {
/* compiled code */
}过滤操作使用filter函数,它可以对Collection集合、Map集合或数组元素进行过滤,Collection集合和数组返回的是一个List集合,Map集合返回的还是一个Map集合。
基本数据类型举例:
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val longerThan3 = numbers.filter { it.length > 3 }
println(longerThan3)
val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key11" to 11)
val filteredMap = numbersMap.filter { (key, value) -> key.endsWith("1") && value > 10}
println(filteredMap)输出结果:
[three, four]
{key11=11}filter() 中的谓词只能检查元素的值。如果想在过滤中使用元素在集合中的位置,应该使用 filterIndexed()。它接受一个带有两个参数的谓词:元素的索引和元素的值。
如果想使用否定条件来过滤集合,请使用 filterNot()。它返回一个让谓词产生 false 的元素列表。
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val filteredIdx = numbers.filterIndexed { index, s -> (index != 0) && (s.length < 5) }
val filteredNot = numbers.filterNot { it.length <= 3 }
println(filteredIdx)
println(filteredNot)输出结果:
[two, four]
[three, four]还有一些函数能够通过过滤给定类型的元素来缩小元素的类型:
filterIsInstance() 返回给定类型的集合元素。在一个 List<Any> 上被调用时,filterIsInstance<T>() 返回一个 List<T>,从而让你能够在集合元素上调用 T 类型的函数。
val numbers = listOf(null, 1, "two", 3.0, "four")
println("All String elements in upper case:")
numbers.filterIsInstance<String>().forEach {
println(it.toUpperCase())
}输出结果:
All String elements in upper case:
TWO
FOUR过滤非空
filterNotNull() 返回所有非空元素。在一个 List<T?> 上被调用时,filterNotNull() 返回一个 List<T: Any>,从而让你能够将所有元素视为非空对象。
val numbers = listOf(null, "one", "two", null)
numbers.filterNotNull().forEach {
println(it.length) // 对可空的 String 来说长度不可用
}输出结果:
3
3对象过滤举例:
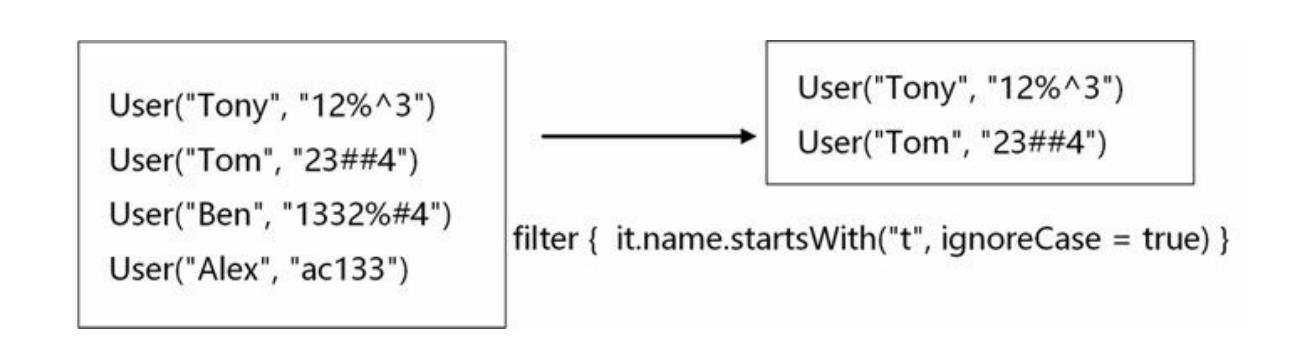
data class User(val name: String, var password: String)
val users = listOf(
User("Tony", "12%^3"),
User("Tom", "23##4"),
User("Ben", "1332%#4"),
User("Alex", "ac133")
)调用:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
users.filter { it.name.startsWith("t", ignoreCase = true) }.forEach {println(it.password) }
}输出结果:
12%^3
23##4表达式it.name.startsWith("t", ignoreCase = true)是判断集合元素的name属性是否是t字母开头的,ignoreCase = true忽略大小写比较。filter函数处理完成之后的数据,由原来的四条数据编程了现在的两条数据。
forEach函数用来遍历集合元素,它的参数也是一个Lambda表达式,所以forEach {println(it.password) }是将集合元素的password属性打印输出。
集合转换
Kotlin 标准库为集合转换提供了一组扩展函数。 这些函数根据提供的转换规则从现有集合中构建新集合。 在此页面中,我们将概述可用的集合转换函数。
映射
映射 转换从另一个集合的元素上的函数结果创建一个集合。 基本的映射函数是 map()。 它将给定的 lambda 函数应用于每个后续元素,并返回 lambda 结果列表。 结果的顺序与元素的原始顺序相同。 如需应用还要用到元素索引作为参数的转换,请使用 mapIndexed()。
public inline fun <T, R> kotlin.collections.Iterable<T>.map(transform: (T) -> R): kotlin.collections.List<R> {
/* compiled code */
}
public inline fun <T, R> kotlin.collections.Iterable<T>.mapIndexed(transform: (kotlin.Int, T) -> R): kotlin.collections.List<R> {
/* compiled code */
}
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3)
println(numbers.map { it * 3 })
println(numbers.mapIndexed { idx, value -> value * idx })输出结果:
[3, 6, 9]
[0, 2, 6] 如果转换在某些元素上产生 null 值,则可以通过调用 mapNotNull() 函数取代 map() 或 mapIndexedNotNull() 取代 mapIndexed() 来从结果集中过滤掉 null 值。
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3)
println(numbers.mapNotNull { if ( it == 2) null else it * 3 })
println(numbers.mapIndexedNotNull { idx, value -> if (idx == 0) null else value * idx })输出结果:
[3, 9]
[2, 6]映射转换时,有两个选择:转换键,使值保持不变,反之亦然。 要将指定转换应用于键,请使用 mapKeys();反过来,mapValues() 转换值。 这两个函数都使用将映射条目作为参数的转换,因此可以操作其键与值。
val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key11" to 11)
println(numbersMap.mapKeys { it.key.toUpperCase() })
println(numbersMap.mapValues { it.value + it.key.length }){KEY1=1, KEY2=2, KEY3=3, KEY11=11}
{key1=5, key2=6, key3=7, key11=16}映射操作使用map函数,它可以对Collection集合、Map集合或数组元素进行变换返回一个List集合。
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
users.filter { it.name.startsWith("t", ignoreCase = true) } .map { it.name } .forEach{ println(it)}
}上述代码使用filter函数和map函数对集合进行操作,先使用filter函数过滤,只有两元素,元素类型是User对象。再使用map函数对集合进行变换,it.name是变换表达式,将计算的结果放到一个新的List集合中,新的集合元素变成了字符串,这就是map函数变换的结果。如下图:

15个过滤函数
常用的过滤函数除了filter还有14个,如表所示:

聚合函数-归纳函数
聚合操作会将Collection集合或数组中数据聚合起来输出单个数据,聚合操作中最基础的是归纳函数reduce,reduce函数会将集合或数组的元素按照指定的算法积累叠加起来,最后输出一个数据。
data class Song(val title: String, val durationInSeconds: Int)
val songs= listOf(Song("Speak to Me", 90),
Song("Breathe", 163),
Song("On he Run", 216),
Song("Time", 421),
Song("The Great Gig in the Sky", 276),
Song("Money", 382),
Song("Us and Them", 462),
Song("Any Color You Like", 205),
Song("Brain Damage", 228),
Song("Eclipse", 123)
)调用:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
//计算所有歌曲播放时长之和
val durations = songs.map { it.durationInSeconds } .reduce { acc, i -> acc + i }
println(durations) //输出:2566
}首先声明了一个数据类Song,它是保存Song对象的List集合。 调用map函数变换songs集合数据,返回歌曲时长(durationInSeconds)的List集合,再调用reduce函数计算时长,其中acc参数是上次累积计算结果,i当前元素,acc + i表达式是进行累加,这里表达式是关键,根据自己需要这表达式是不同的。
12个聚合函数
除了上面reduce()聚合函数外,还有其他11个聚合函数,总结表如下:

合拢
合拢转换是根据两个集合中具有相同位置的元素构建配对的。 在 Kotlin 标准库中,这是通过 zip() 扩展函数完成的。 在一个集合(或数组)上以另一个集合(或数组)作为参数调用时,zip() 返回 Pair 对象的列表(List)。 接收者集合的元素是这些配对中的每一个元素。 如果集合的大小不同,则 zip() 的结果为较小集合的大小;结果中不包含较大集合的后续元素。 zip() 也可以中缀形式调用 a zip b 。
val colors = listOf("red", "brown", "grey")
val animals = listOf("fox", "bear", "wolf")
println(colors zip animals)
val twoAnimals = listOf("fox", "bear")
println(colors.zip(twoAnimals))输出结果:
[(red, fox), (brown, bear), (grey, wolf)]
[(red, fox), (brown, bear)] 也可以使用带有两个参数的转换函数来调用 zip():接收者元素和参数元素。
val colors = listOf("red", "brown", "grey")
val animals = listOf("fox", "bear", "wolf")
println(colors.zip(animals) { color, animal -> "The ${animal.capitalize()} is $color"})输出结果:
[The Fox is red, The Bear is brown, The Wolf is grey] 当拥有 Pair 的 List 时,可以进行反向转换 unzipping——从这些键值对中构建两个列表:
- 第一个列表包含原始列表中每个
Pair的键。 - 第二个列表包含原始列表中每个
Pair的值。
要分割键值对列表,请调用 unzip()。
val numberPairs = listOf("one" to 1, "two" to 2, "three" to 3, "four" to 4)
println(numberPairs.unzip())输出结果:
([one, two, three, four], [1, 2, 3, 4])关联
关联转换允许从集合元素和与其关联的某些值构建 Map。 在不同的关联类型中,元素可以是关联 Map 中的键或值。
基本的关联函数 associateWith() 创建一个 Map,其中原始集合的元素是键,并通过给定的转换函数从中产生值。 如果两个元素相等,则仅最后一个保留在 Map 中。
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
println(numbers.associateWith { it.length })输出结果:
{one=3, two=3, three=5, four=4}为了使用集合元素作为值来构建 Map,有一个函数 associateBy()。 它需要一个函数,该函数根据元素的值返回键。如果两个元素相等,则仅最后一个保留在 Map 中。 还可以使用值转换函数来调用 associateBy()。
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
//将集合numbers元素的首字母转换为大写作为Map集合的Key值,将numbers集合元素作为Map的value,生成一个新的Map集合;
println(numbers.associateBy { it.first().toUpperCase() })
//将集合numbers元素的首字母转换为大写作为Map集合的Key值,将numbers集合元素的每个字符串的长度作为Map的value,生成一个新的Map集合;
println(numbers.associateBy(keySelector = { it.first().toUpperCase() }, valueTransform = { it.length }))输出结果:
{O=one, T=three, F=four}
{O=3, T=5, F=4}另一种构建 Map 的方法是使用函数 associate(),其中 Map 键和值都是通过集合元素生成的。 它需要一个 lambda 函数,该函数返回 Pair:键和相应 Map 条目的值。
请注意,associate() 会生成临时的 Pair 对象,这可能会影响性能。 因此,当性能不是很关键或比其他选项更可取时,应使用 associate()。
后者的一个示例:从一个元素一起生成键和相应的值。
val names = listOf("Alice Adams", "Brian Brown", "Clara Campbell")
println(names.associate { name -> parseFullName(name).let { it.lastName to it.firstName } })输出结果:
{Adams=Alice, Brown=Brian, Campbell=Clara}此时,首先在一个元素上调用一个转换函数,然后根据该函数结果的属性建立 Pair。
其他更多函数的使用举例,请参见官网:
https://www.kotlincn.net/docs/reference/collections-overview.html

用知识铭记编程的岁月!遇见即是缘分,愿你我的脚步轻盈地踏过编程的花海!
完结!
以上是关于细说Kotlin工具函数及使用准则-转换函数map()过滤函数filter()聚合函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章