JUC并发编程 多线程设计模式 -- 同步模式之保护性暂停(join方法原理 & 保护性暂停-扩展-解耦等待和生产)
Posted Z && Y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC并发编程 多线程设计模式 -- 同步模式之保护性暂停(join方法原理 & 保护性暂停-扩展-解耦等待和生产)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. join方法原理
调用join方法,默认调用了join(0):
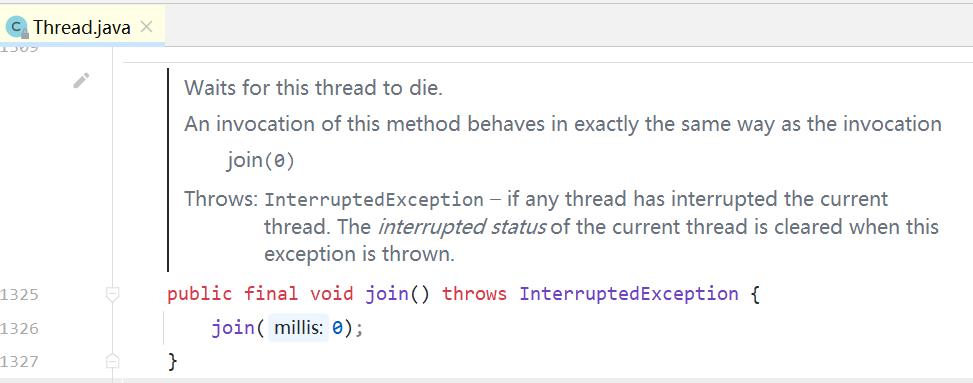
join() 方法源码:
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
// 开始时间
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 经历的时间
long now = 0;
// 如果最大的时间小于0 则抛出异常
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
// 如果参数为 0 则一直等待下去 直到线程运行结束
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
// 最大超时时间-去经历的时间
long delay = millis - now;
// 如果超时就退出循环
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
// 如果没有超时就继续等待
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
2. 保护性暂停-扩展-解耦等待和生产
1个邮递员对应一个居民
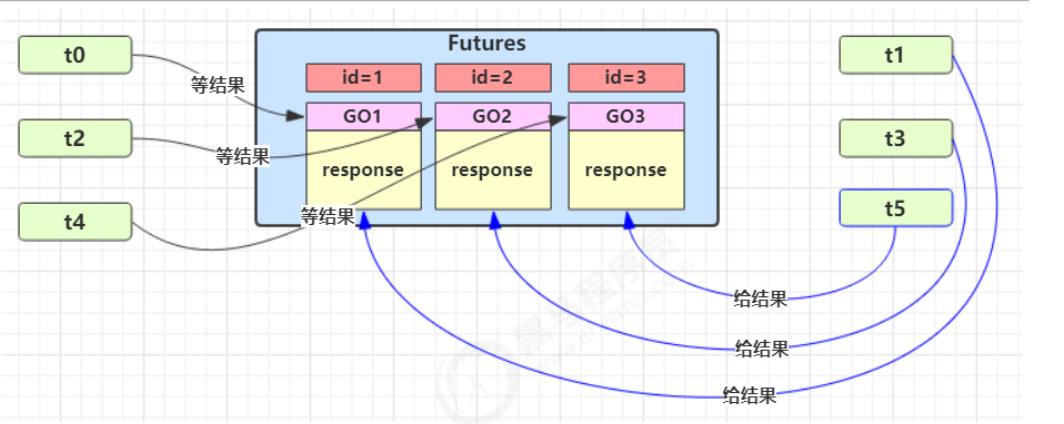
- 图中 Futures 就好比居民楼一层的信箱(每个信箱有房间编号),左侧的 t0,t2,t4 就好比等待邮件的居民,右侧的 t1,t3,t5 就好比邮递员
- 如果需要在多个类之间使用 GuardedObject 对象,作为参数传递不是很方便,因此设计一个用来解耦的中间类,这样不仅能够解耦【结果等待者】和【结果生产者】,还能够同时支持多个任务的管理
GuardedObject 类,里面增加了一个ID作为GuardedObject 的唯一标识:
// 增加超时效果
class GuardedObject {
// 标识 Guarded Object
private int id;
public GuardedObject(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
// 结果
private Object response;
// 获取结果
// timeout 表示要等待多久 2000
public Object get(long timeout) {
synchronized (this) {
// 开始时间 15:00:00
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 经历的时间
long passedTime = 0;
while (response == null) {
// 这一轮循环应该等待的时间
long waitTime = timeout - passedTime;
// 经历的时间超过了最大等待时间时,退出循环
if (timeout - passedTime <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
this.wait(waitTime); // 虚假唤醒 15:00:01
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 求得经历时间
passedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin; // 15:00:02 1s
}
return response;
}
}
// 产生结果
public void complete(Object response) {
synchronized (this) {
// 给结果成员变量赋值
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
邮箱: Mailboxes类
class Mailboxes {
// Hashtable是一个线程安全的集合类
private static Map<Integer, GuardedObject> boxes = new Hashtable<>();
private static int id = 1;
// 产生唯一 id
private static synchronized int generateId() {
return id++;
}
// 根据id返回GuardedObject 对象 因为是邮递员送信
public static GuardedObject getGuardedObject(int id) {
return boxes.remove(id);
}
public static GuardedObject createGuardedObject() {
GuardedObject go = new GuardedObject(generateId());
boxes.put(go.getId(), go);
return go;
}
public static Set<Integer> getIds() {
return boxes.keySet();
}
}
居民类:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.People")
class People extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// 收信
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.createGuardedObject();
log.debug("开始收信 id:{}", guardedObject.getId());
Object mail = guardedObject.get(5000);
log.debug("收到信 id:{}, 内容:{}", guardedObject.getId(), mail);
}
}
邮递员类:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Postman")
class Postman extends Thread {
// 邮件编号(GuardedObject ID)
private int id;
// 新建的内容
private String mail;
public Postman(int id, String mail) {
this.id = id;
this.mail = mail;
}
@Override
public void run() {
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.getGuardedObject(id);
log.debug("送信 id:{}, 内容:{}", id, mail);
guardedObject.complete(mail);
}
}
测试代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test20")
public class Test20 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new People().start();
}
// 睡眠1s后开始送信
Thread.sleep(1000);
for (Integer id : Mailboxes.getIds()) {
new Postman(id, "内容" + id).start();
}
}
}
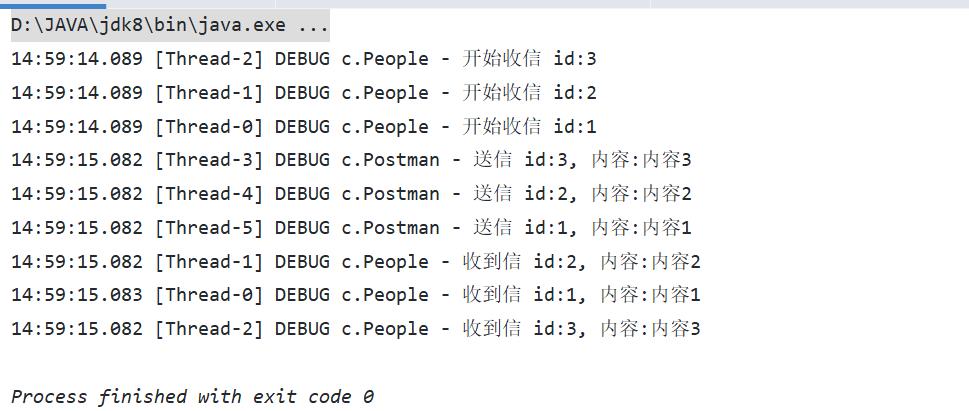
运行结果:
以上是关于JUC并发编程 多线程设计模式 -- 同步模式之保护性暂停(join方法原理 & 保护性暂停-扩展-解耦等待和生产)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章