Java数据结构线性表之链表
Posted <一蓑烟雨任平生>
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java数据结构线性表之链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
(1)链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,其物理结构不能只管的表示数据元素的逻辑顺序,数据元 素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列的结点(链表中的每一个元素称为结点)组成, 结点可以在运行时动态生成。
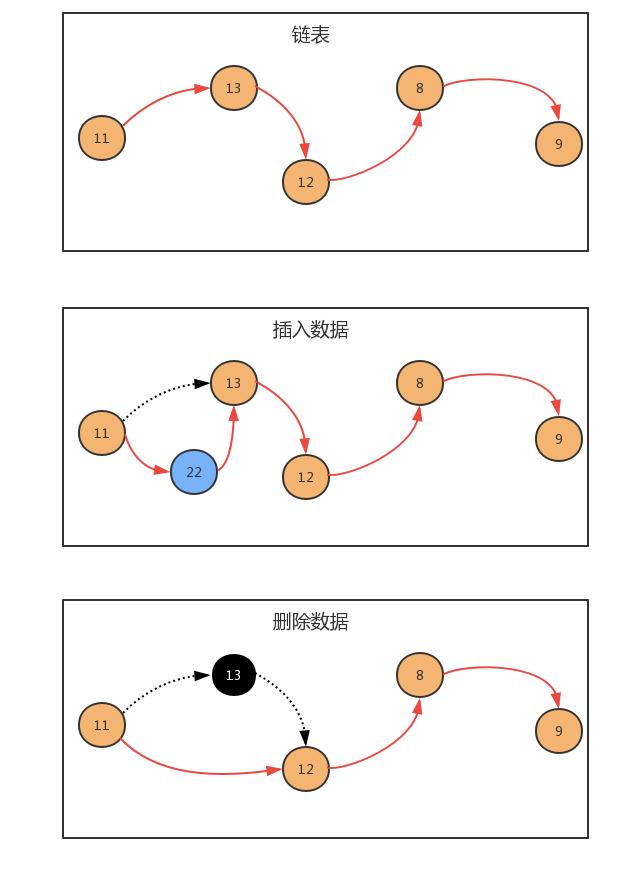
那我们如何使用链表呢?按照面向对象的思想,我们可以设计一个类,来描述结点这个事物,用一个属性描述这个 结点存储的元素,用来另外一个属性描述这个结点的下一个结点。
结点API设计:
| 类名 | Node |
|---|---|
| 构造方法 | Node(T t,Node next):创建Node对象 |
| 成员变量 | T item:存储数据 Node next:指向下一个结点 |
结点类实现:
/**
* 节点类实现
*/
public static class Node<T>{
// 存储元素
public T item;
// 指向下一个节点
public Node<T> next;
public Node(T item,Node<T> next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
生成链表:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//构建结点
Node<Integer> first = new Node<Integer>(11, null);
Node<Integer> second = new Node<Integer>(13, null);
Node<Integer> third = new Node<Integer>(12, null);
Node<Integer> fourth = new Node<Integer>(8, null);
Node<Integer> fifth = new Node<Integer>(9, null);
//生成链表
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
}
(2)单向链表
单向链表是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和一个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据, 指针域用来指向其后继结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。

(2.1)单向链表API设计

(2.2)单向链表代码实现
package cn.itcast.algorithm.linear;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author :caizhengjie
* @description:单向链表
* @date :2021/6/28 10:59 下午
*/
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
/**
* 记录头节点
*/
private Node<T> head;
/**
* 记录链表的长度
*/
private int N;
/**
* 节点类实现
*/
public static class Node<T>{
// 存储元素
public T item;
// 指向下一个节点
public Node<T> next;
public Node(T item,Node<T> next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 构造方法
*/
public LinkList() {
// 初始化头节点
this.head = new Node<>(null, null);
// 初始化元素个数
this.N = 0;
}
public LinkList(Node<T> head, int n) {
this.head = head;
N = n;
}
/**
* 置空链表
*/
public void clear(){
// 让头节点为null
head.next = null;
// 让元素个数为0
this.N = 0;
}
/**
* 判断链表是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
// 只需判断元素个数是否为0,为0就是空,不为0就不是空
return N == 0;
}
/**
* 获取链表中元素的个数
*/
public int length(){
return N;
}
/**
* 读取并返回链表中第i个元素
*/
public T get(int i){
// 通过循环从头节点开始往后找,依次找i次,就可以找到对应的元素
Node<T> n = head.next;
for (int index = 0;index < i;index++){
n = n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
/**
* 删除并返回链表中第i个元素的个数
*/
public T remove(int i){
// 找到i位置的前一个节点
Node<T> pre = head;
for (int index = 0;index <= i-1;index++){
pre = pre.next;
}
// 找到i位置的节点
Node<T> curr = pre.next;
// 找到i位置的下一个节点
Node<T> nextNode = curr.next;
// 前一个节点指向下一个节点
pre.next = nextNode;
// 元素个数-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
/**
* 往链表中添加一个元素
*/
public void insert(T t){
// 找到当前最后一个节点
Node<T> n = head;
while (n.next != null){
n = n.next;
}
// 创建新节点,保存元素t
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(t,null);
// 让当前最后一个节点指向新节点
n.next = newNode;
// 元素的个数+1
N++;
}
/**
* 在链表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素
*/
public void insert(int i,T t){
// 找到i位置前一个节点
Node<T> pre = head;
for (int index = 0;index <= i-1;index++){
pre = pre.next;
}
// 找到i位置的节点
Node<T> curr = pre.next;
// 创建新节点,并且新节点需要指向原来i位置的节点
Node<T> nowNode = new Node<>(t,curr);
// 原来i位置的前一个节点指向新节点即可
pre.next = nowNode;
// 元素个数+1
N++;
}
/**
* 返回链表中首次出现的指定的数据元素的位序号,若不存在,则 返回-1。
*/
public int indexOf(T t){
// 从头节点开始,依次找到每个节点,取出item,和t比较,如果相同,就找到了
Node<T> n = head;
for (int i = 0;n.next != null;i++){
n = n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 链表反转
* 反转整个链表
* @return
*/
public void reverse(){
// 判断当前链表是否为空链表,如果是空链表,则结束运行,如果不是,则调用重载的reverse方法完成反转
if (isEmpty()){
return;
}
reverse(head.next);
}
/**
* 反转指定的节点curr,并把反转后的节点返回
* @return
*/
public Node<T> reverse(Node<T> curr){
if (curr.next == null){
head.next = curr;
return curr;
}
// 递归的反转当前节点curr的下一个节点;返回值就是链表反转后当前节点的上一个节点
Node<T> pre = reverse(curr.next);
// 让返回的节点的下一个节点变为当前节点curr
pre.next = curr;
// 把当前节点的下一个节点变为null
curr.next = null;
return curr;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new LTterator();
}
private class LTterator implements Iterator{
private Node<T> n;
public LTterator() {
this.n = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
测试代码:
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.LinkList;
/**
* @author :caizhengjie
* @description:TODO
* @date :2021/2/2 12:11 上午
*/
public class LinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建单向链表对象
LinkList<String> l1 = new LinkList<>();
// 测试插入
l1.insert("alex");
l1.insert("lili");
l1.insert("jone");
l1.insert(1,"jack");
// 遍历
for (String s : l1) {
System.out.println(s);
}
// 测试获取
String getResult = l1.get(1);
System.out.println("获取索引1处的结果为:" + getResult);
// 测试删除
String removeResult = l1.remove(0);
System.out.println("删除的元素为:" + removeResult);
// 测试清空
l1.clear();
System.out.println("清空后线性表中的元素的个数为:" + l1.length());
}
}
alex
jack
lili
jone
获取索引1处的结果为:jack
删除的元素为:alex
清空后线性表中的元素的个数为:0
(3)双向链表
双向链表也叫双向表,是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用 来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存 储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。

按照面向对象的思想,我们需要设计一个类,来描述结点这个事物。由于结点是属于链表的,所以我们把结点类作 为链表类的一个内部类来实现
(3.1)结点API设计

(3.2)双向链表API设计

(3.3)双向链表代码实现
package cn.itcast.algorithm.linear;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author :caizhengjie
* @description:双向链表
* @date :2021/7/6 11:44 下午
*/
public class TowWayLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
/**
* 记录头节点
*/
private Node<T> head;
/**
* 记录尾节点
*/
private Node<T> last;
/**
* 记录链表的长度
*/
private int N;
/**
* 节点类实现
*/
public static class Node<T>{
// 存储元素
public T item;
// 指向下一个节点
public Node<T> next;
// 指向上一个节点
public Node<T> pre;
public Node(T item, Node<T> pre,Node<T> next){
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 构造方法
*/
public TowWayLinkList() {
// 初始化头节点和尾节点
this.head = new Node<>(null,null,null);
// 初始化元素个数
this.N = 0;
}
/**
* 置空链表
*/
public void clear(){
// 让头节点和尾节点为null
this.head.next = null;
this.head.pre = null;
this.head.item = null;
this.last = null;
// 让元素个数为0
this.N = 0;
}
/**
* 判断链表是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
// 只需判断元素个数是否为0,为0就是空,不为0就不是空
return N == 0;
}
/**
* 获取链表中元素的个数
*/
public int length(){
return N;
}
/**
* 获取第一个元素
*/
public T getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
/**
* 获取最后一个元素
*/
public T getLast(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
/**
* 插入元素t
*/
public void insert(T t){
// 如果链表为空
if (isEmpty()){
// 创建新的节点
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(t,head,null);
// 让新节点称为尾节点
last = newNode;
// 让头节点指向尾节点
head.next = last;
}
// 如果链表不为空
else {
// 当前尾节点
Node<T> oldLast = last;
// 创建新的节点
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(t,oldLast,null);
// 让当前的尾节点指向新节点
oldLast.next = newNode;
// 让新节点成为尾节点
last = newNode;
}
// 元素个数+1
N++;
}
/**
* 在链表的第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的数据元素
*/
public void insert(int i,T t){
// 找到i位置的前一个节点
Node<T> pre = head;
for (int index = 0;index < i; index++){
pre = pre.next;
}
// 找到i位置的节点
Node<T> curr = pre.next;
// 创建新节点
Node<T