map与set
Posted 蚍蜉撼树谈何易
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了map与set相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
map、set简介



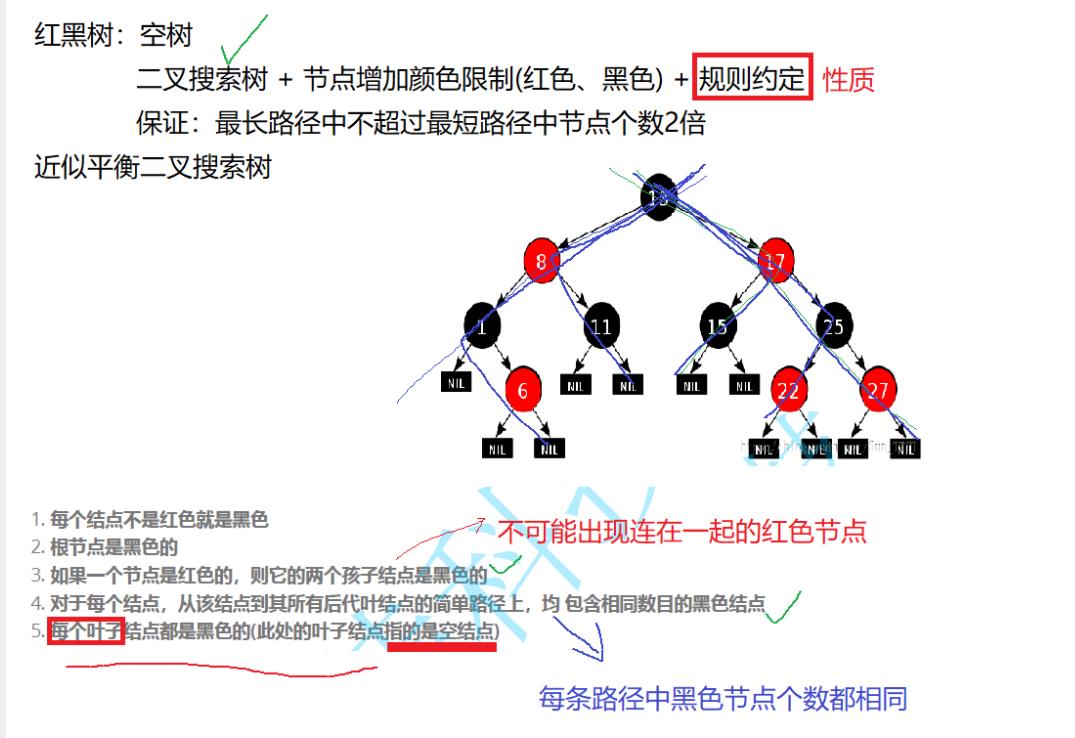
常见接口使用
map构造
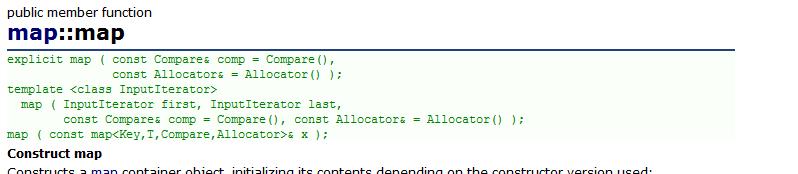
void testmap1()
{
map<string, string> m1;
map<string, string>m2{ {"apple","苹果"},{"orange","橘子"} };
cout << m1.size() << endl;
cout << m2.size() << endl;
m1 = m2;
cout << m1.size() << endl;
cout << m2.size() << endl;
map<string, string>m3(m2.begin(), m2.end());
cout << m3.size() << endl;
}
map的insert操作
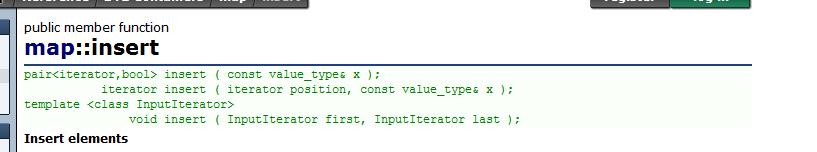
void testmap2()
{
map<string, string> m;
// 通过insert直接往map中插入键值对
pair<string, string> p("orange", "橙子");
m.insert(p);
m.insert(pair<string, string>("banana", "香蕉"));
m.insert(make_pair("apple", "苹果"));
cout << m.size() << endl;
// m[key]--->表明:返回key对应的value
cout << m["orange"] << endl;
// m[key] = newvalue; 使用newvalue给map中key对应的value进行赋值
m["orange"] = "橘子";
// 如果通过m[key]访问key对应的value时,如果key不存子?
// m会使用当前key与一个默认的value构成一个键值对<key, 默认value>插入到m中
// 然后将key对应的默认的value返回来
cout << m["peach"] << endl;
m["pair"] = "梨";
// map中已经存在orange,在插入一个orange看能否成功
m.insert(make_pair("orange", "橙子"));
cout << m.size() << endl;
// 对map中的元素进行遍历
//std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = m.begin();
auto it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// e 就是m中所存在的键值对的别名
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << "<" << e.first << "," << e.second << ">" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
m.erase("apple");
it = m.find("orange");
if (it != m.end())
{
m.erase(it);
}
}
map中的元素访问的操作

map中的删除操作
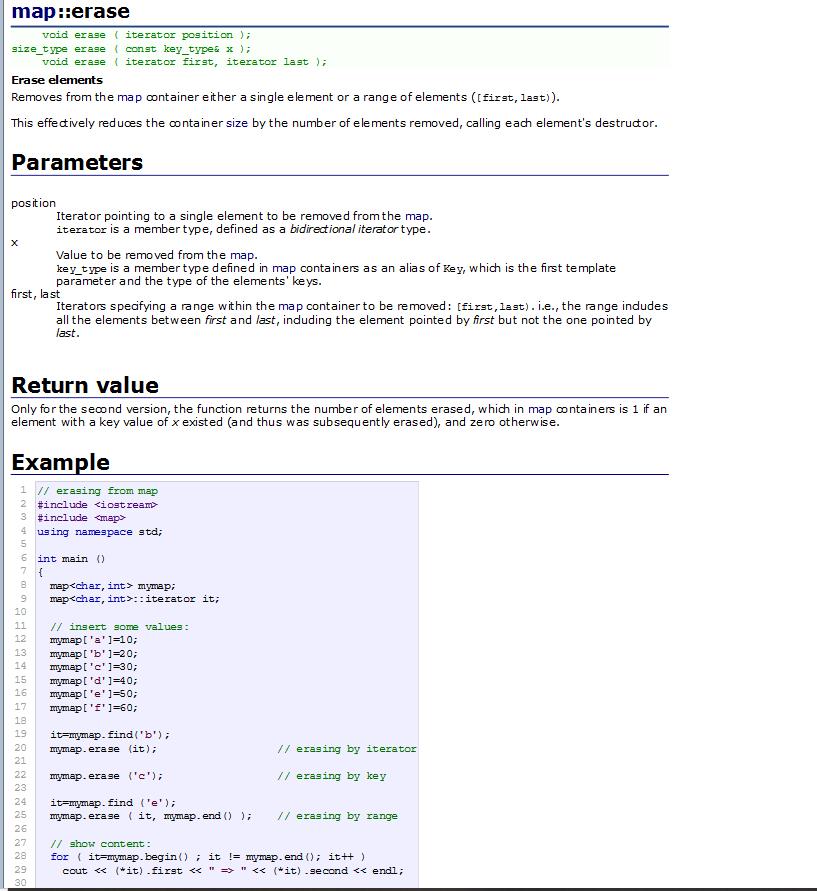
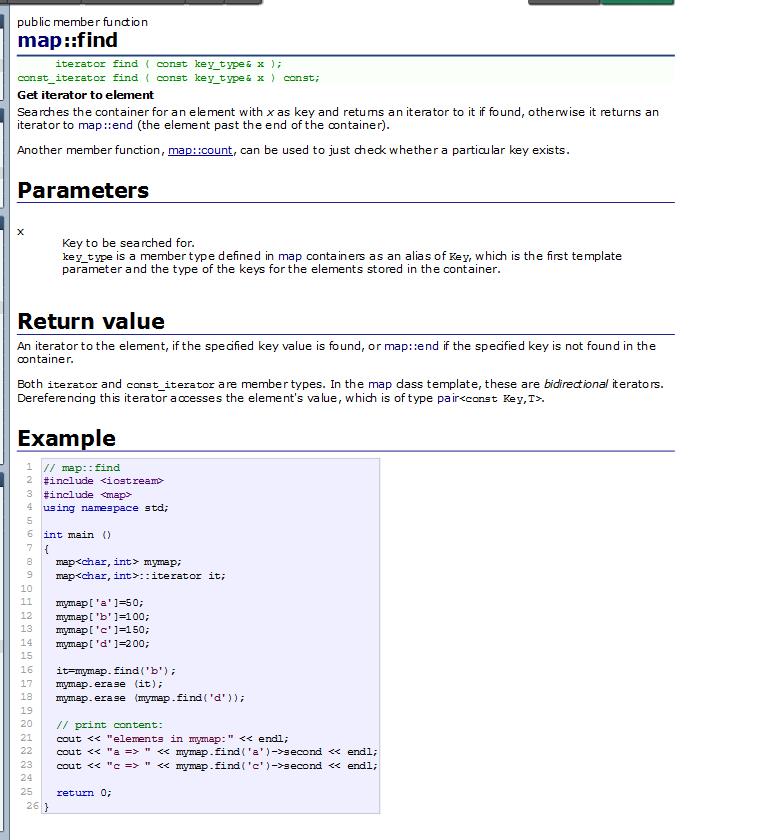
map中的find操作
set

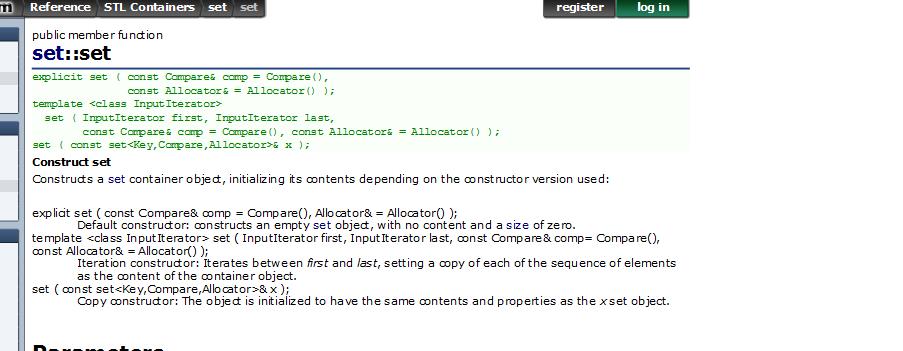
set构造
void TestSet()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
set<int> s(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
set<int>m{ 1,2,3,4,2,1,3,4 };
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : m)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
mulity_map与mulity_set()相对于map与set来说允许重复的元素,操作与其类似,不赘述。
以上是关于map与set的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章