Netty学习笔记:Netty核心模块组件
Posted 邋遢的流浪剑客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Netty学习笔记:Netty核心模块组件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二、Netty核心模块组件
1、Bootstrap、ServerBootstrap
- 一个Netty应用通常由一个Bootstrap开始,主要作用是配置整个Netty程序,串联各个组件,Netty中Bootstrap类是客户端程序的启动引导类,ServerBootstrap是服务端启动引导类
- 常用方法:
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup):该方法用于服务器端,用来设置两个EventLooppublic B group(EventLoopGroup group):该方法用于客户端,用来设置一个EventLooppublic B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass):该方法用来设置一个服务器端的通道实现public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value):用来给ServerChannel添加配置public <T> ServerBootstrap childOption(ChannelOption<T> childOption, T value):用来给接收到的通道添加配置public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler):该方法用来设置业务处理类(自定义的handler)public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort):该方法用于服务器端,用来设置占用的端口号public ChannelFuture connect(String inetHost, int inetPort):该方法用于客户端,用来连接服务器端
2、Future、ChannelFuture
Netty中所有的IO操作都是异步的,不能立刻得知消息是否被正确处理。但是可以过一会等它执行完成或者直接注册一个监听,具体的实现就是通过Future和ChannelFutures,可以注册一个监听,当操作执行成功或失败时监听会自动触发注册的监听事件
常用方法:
Channel channel():返回当前正在进行IO操作的通道ChannelFuture sync():等待异步操作执行完毕
3、Channel
- Netty网络通信的组件,能够用于执行网络I/O操作
- 通过Channel可获得当前网络连接的通道的状态
- 通过Channel可获得网络连接的配置参数(例如接收缓冲区大小)
- Channel提供异步的网络I/O操作(如建立连接、读写、绑定端口),异步调用意味着任何I/O调用都将立即返回,并且不保证在调用结束时所请求的I/O操作已完成
- 调用立即返回一个ChannelFuture实例,通过注册监听器到ChannelFuture上,可以I/O操作成功、失败或取消时回调通知调用方
- 支持关联I/O操作与对应的处理程序
- 不同协议、不同的阻塞类型的连接都有不同的Channel类型与之对应,常用的Channel类型:
- NiosocketChannel:异步的客户端TCP Socket连接
- NioServerSocketChannel:异步的服务器端TCP Socket连接
- NioDatagramChannel:异步的UDP连接
- NioSctpChannel:异步的客户端Sctp连接
- NioSctpServerChannel:异步的Sctp服务器端连接
4、Selector
- Netty基于Selector对象实现I/O多路复用,通过Selector一个线程可以监听多个连接的Channel事件
- 当向一个Selector中注册Channel后,Selector内部的机制就可以自动不断地查询(Select)这些注册的Channel是否有已就绪的I/O事件(例如可读、可写、网络连接完成等),这样程序就可以很简单地使用一个线程高效地管理多个Channel
5、ChannelHandler及其实现类
- ChannelHandler是一个接口,处理I/O事件或拦截I/O操作,并将其转发到其ChannelPipeline(业务处理链)中的下一个处理程序
- ChannelHandler本身并没有提供很多方法,因为这个接口有许多的方法需要实现,方便使用期间,可以继承它的子类
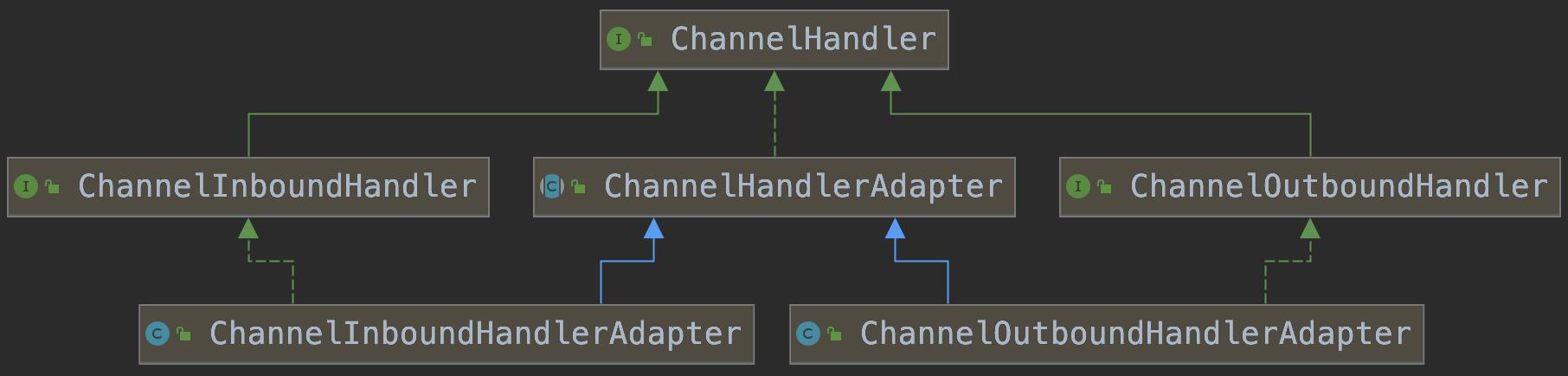
- ChannelInboundHandler:用于处理入站I/O事件
- ChannelOutboundHandler:用于处理出站I/O事件
适配器:
- ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter:用于处理入站I/O事件
- ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter:用于处理出站I/O事件
- ChannelDuplexHandler:用于处理入站和出站事件
public class ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter extends ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelUnregistered();
}
// 通道就绪事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelInactive();
}
// 通道读取数据事件
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
// 通道读取完毕事件
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelReadComplete();
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(evt);
}
@Override
public void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelWritabilityChanged();
}
// 通道发生异常事件
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
6、Pipeline和ChannelPipeline
- ChannelPipeline是一个Handler的集合,它负责处理和拦截inbound或者outbound的事件和操作,相当于一个贯穿Netty的链(也可以这样理解:ChannelPipeline是保存ChannelHandler的List,用于处理或拦截Channel的入站事件和出站操作)
- ChannelPipeline实现了一种高级形式的拦截过滤器模式,使用户可以完全控制事件的处理方式,以及Channel中各个的ChannelHandler如何相互交互
- 在Netty中每个Channel都有且仅有一个ChannelPipeline与之对应,它们的组成关系如下:
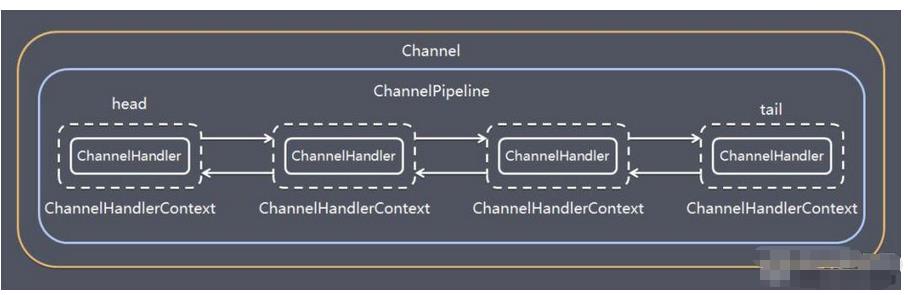
一个Channel包含了一个ChannelPipeline,而ChannelPipeline中又维护了一个由ChannelHandlerContext组成的双向链表,并且每个ChannelHandlerContext中又关联着一个ChannelHandler
入站事件和出站事件在一个双向链表中,入站事件从链表head往后传递到最后一个入站的handler,出站事件会从链表tail往前传递到最前一个出站的handler,两种类型的handler互不干扰
常用方法:
ChannelPipeline addFirst(ChannelHandler... handlers):把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的第一个位置ChannelPipeline addLast(ChannelHandler... handlers):把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的最后一个位置
7、ChannelHandlerContext
- 保存Channel相关的所有上下文信息,同时关联一个ChannelHandler对象
- 即ChannelHandlerContext中包含一个具体的事件处理器ChannelHandler,同时ChannelHandlerContext中也绑定了对应的pipeline和Channel的信息,方便对ChannelHandler进行调用
- 常用方法:
ChannelFuture close():关闭通道ChannelOutboundInvoker flush():刷新ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg):将数据写到ChannelPipeline中当前ChannelHandler的下一个ChannelHandler开始处理(出站)
8、ChannelOption
Netty在创建Channel实例后,一般都需要设置ChannelOption参数,ChannelOption参数如下:
ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG:对应TCP/IP协议listen函数中的backlog参数,用来初始化服务器可连接队列大小。服务端处理客户端连接请求是顺序处理的,所以同一时间只能处理一个客户端连接。多个客户端来的时候,服务端将不能处理的客户端连接请求放在队列中等待处理,backlog参数指定了队列的大小ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE:一直保持连接活动状态
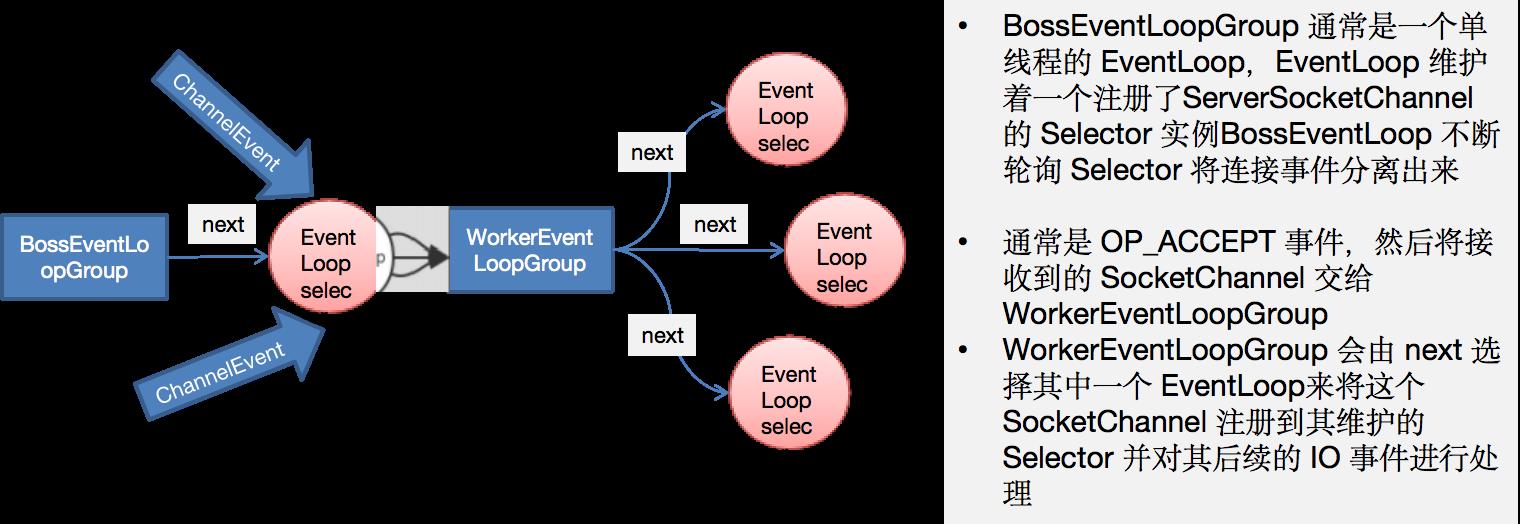
9、EventLoopGroup和其实现类NioEventLoopGroup
- EventLoopGroup是一组EventLoop的抽象,Netty为了更好的利用多核CPU资源,一般会有多个EventLoop同时工作,每个EventLoop维护着一个Selector实例
- EventLoopGroup提供next接口,可以从组里面按照一定规则获取其中一个EventLoop来处理任务。在Netty服务器端编程中,我们一般都需要提供两个EventLoopGroup:BossEventLoopGroup和WorkerEventLoopGroup
- 通常一个服务端口即一个ServerSocketChannel对应一个Selector和一个EventLoop线程。BossEventLoop负责接收客户端的连接并将SocketChannel交给WorkerEventLoopGroup来进行IO处理
10、Unpooled类
public class NettyByteBuf01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个ByteBuf
// 1.创建ByteBuf对象,该对象包含一个数组arr,是一个byte[10]
// 2.在ByteBuf中,不需要使用flip进行反转
// 底层维护了readerIndex和writerIndex
// 3.通过readerIndex和writerIndex和capacity,将ByteBuf分成三个区域
// 0--readerIndex,已经读取的区域
// readerIndex--writerIndex,可读的区域
// writerIndex--capacity,可写的区域
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
buffer.writeByte(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
}
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes |
| | (CONTENT) | |
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| | | |
0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity
public class NettyByteBuf02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello world", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
if (byteBuf.hasArray()) {
byte[] context = byteBuf.array();
System.out.println(new String(context, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println(byteBuf.arrayOffset()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.readerIndex()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.writerIndex()); // 11
System.out.println(byteBuf.capacity()); // 33
System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(0)); // 104
int len = byteBuf.readableBytes(); //可读的字节数11
System.out.println("len=" + len);
// 使用for取出各个字节
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuf.getByte(i));
}
// 按照某个范围读取
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(0, 4, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(4, 6, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
}
ByteBuf使用模式:
-
堆缓存区HEAP BUFFER
优点:存储在JVM的堆空间中,可以快速的分配和释放
缺点:每次使用前会拷贝到直接缓存区(也叫堆外内存)
-
直接缓存区DIRECR BUFFER
优点:存储在堆外内存上,堆外分配的直接内存,不会占用堆空间
缺点:内存的分配和释放,比在堆缓冲区更复杂
-
复合缓冲区COMPOSITE BUFFER
可以创建多个不同的ByteBuf,然后放在一起,但是只是一个视图
选择:大量IO数据读写,用直接缓存区;业务消息编解码用堆缓存区
11、Netty应用实例-群聊系统
需求:
- 服务器端:可以监测用户上线、离线,并实现消息转发功能
- 客户端:通过channel可以无阻塞发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息(由服务器转发得到)
1)、服务端实现
public class GroupChartServer {
private final int port;
public GroupChartServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() {
EventLoopGroup boosGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.group(boosGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChartServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boosGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new GroupChartServer(7000).run();
}
}
public class GroupChartServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
// 定义一个Channel组,管理所有的Channel
// GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE是全局的事件执行器 是一个单例
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
private DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* handlerAdded表示连接建立,一旦连接,第一个被执行
* 将当前channel加入到channelGroup
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
// 将该客户端加入聊天的信息推送给其他在线的客户端
// 该方法会将channelGroup中所有的channel遍历,并发送消息
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("时间:" + dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + ",[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "加入聊天\\n");
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
/**
* 断开连接,将xxx客户离开信息推送给当前在线的客户
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("时间:" + dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + ",[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "离开了\\n");
}
/**
* 表示channel处于活动状态,提示xxx上线
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("时间:" + dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "," + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "上线了~");
}
/**
* 表示channel处于不活动状态,提示xxx离线了
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("时间:" + dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "," + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "离线了~");
}
/**
* 读取数据
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.forEach(ch -> {
if (channel != ch) {
ch.writeAndFlush("时间:" + dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + ",[客户]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "发送了消息:" + msg + "\\n");
}
});
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
2)、客户端实现
public class GroupChartClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public GroupChartClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void run() {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
channel.writeAndFlush(msg + "\\n");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
group