Semaphore源码分析
Posted 醉酒的小男人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Semaphore源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Semaphore是什么
Semaphore用来控制同时操作某个资源的操作数量。Semaphore管理着permits,每当一个线程来获取许可时,permits数减1,当permits数小于0时,再来获取许可的资源就需要阻塞。
Semaphore对信号量的控制是基于AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)。Semaphore有一个内部类Sync继承了AQS。而且Semaphore中还有两个内部类FairSync和NonfairSync继承Sync,也就是说Semaphore有公平锁和非公平锁之分。以下是Semaphore中内部类的结构:
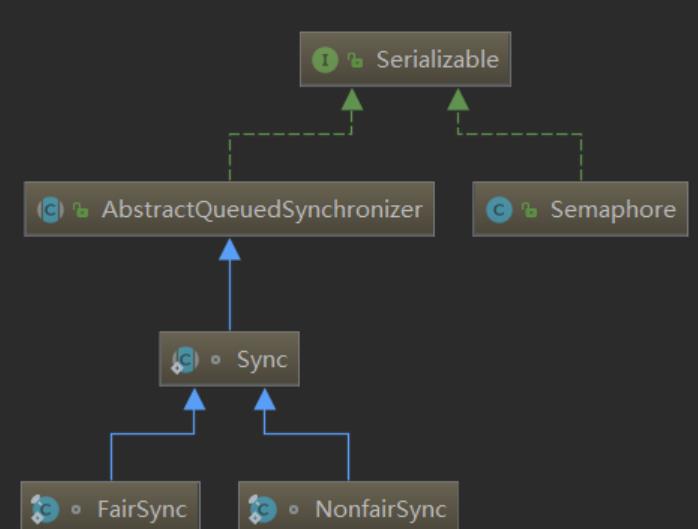
源码分析
package com;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class SemaphoreTest {
//停车场同时容纳的车辆10
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("===="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"来");
if(semaphore.availablePermits()==0){
System.out.println("车位不足,请耐心等待");
}
semaphore.acquire();//获取令牌尝试进入停车场
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"成功进入停车场");
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10000));//模拟车辆在停车产停留
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"驶出停车场");
semaphore.release();//释放令牌,腾出停车场车位
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},i+"号车");
}
}
}
acquire
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
//state的值小于0的时候添加到AQS队列堵塞挂起
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
tryAcquireShared
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
//主要功能就是对state值减一,非公平锁
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
//自旋+CAS,可以保证原子性,这种方式生成的字节码指令少
for (;;) {
//获取许可数state值
int available = getState();
//计算剩余许可数
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
//比较并替换CAS
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
//创建共享节点添加AQS队列尾部
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
//获取node节点前一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//是否是头节点
if (p == head) {
//再次对state的值减一,判断是否大于0,这么做也是为了提高效率,因为存在临界区,有一定的代码冗余
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
//有助于GC
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//挂起当前线程LockSupport.park(this);
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
setHeadAndPropagate
//propagate>0时唤醒下一个节点释放锁
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
//node节点前一个节点的state值,如果等于-1,直接返回,状态值为-1时,说明这个节点有义务去唤醒它后继节点
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
//如果前一节点已取消,则往前找,直到找到第一个状态正常的节点,其实就是从队列删除取消状态的节点
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
//第一个不为取消状态的节点和这个node节点相连
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
release
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryReleaseShared
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
//自旋
for (;;) {
//获取state的值
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
//CAS把state的值修改成next,当内存值state和current相等时
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
doReleaseShared
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
unparkSuccessor
//把首节点的状态改为0,唤醒下一个节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
//如果节点为空或者被取消了,则从队列尾部开始查找,找到离node最近的非null且状态正常的节点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
//唤醒后从acquire的LockSupport.park(this)开始执行,判断是不是首节点等
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
以上是关于Semaphore源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章