Java集合数据结构——优先级队列 (堆PriorityQueue)
Posted 爱敲代码的三毛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合数据结构——优先级队列 (堆PriorityQueue)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、二叉树的顺序存储
1. 存储方式
使用数组保存二叉树结构,方式即将二叉树用层序遍历方式放入数组中。
一般只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费。
这种方式的主要用法就是堆的表示

2. 父亲和孩子的下标关系
已知父亲(parent)的下标
- 左孩子(left)下标 = 2 * parent + 1;
- 右孩子(right)下标 = 2 * parent + 2;
已知孩子(不区分左右)(child)下标
- 父亲ji(parent)下标 = (child - 1) / 2;
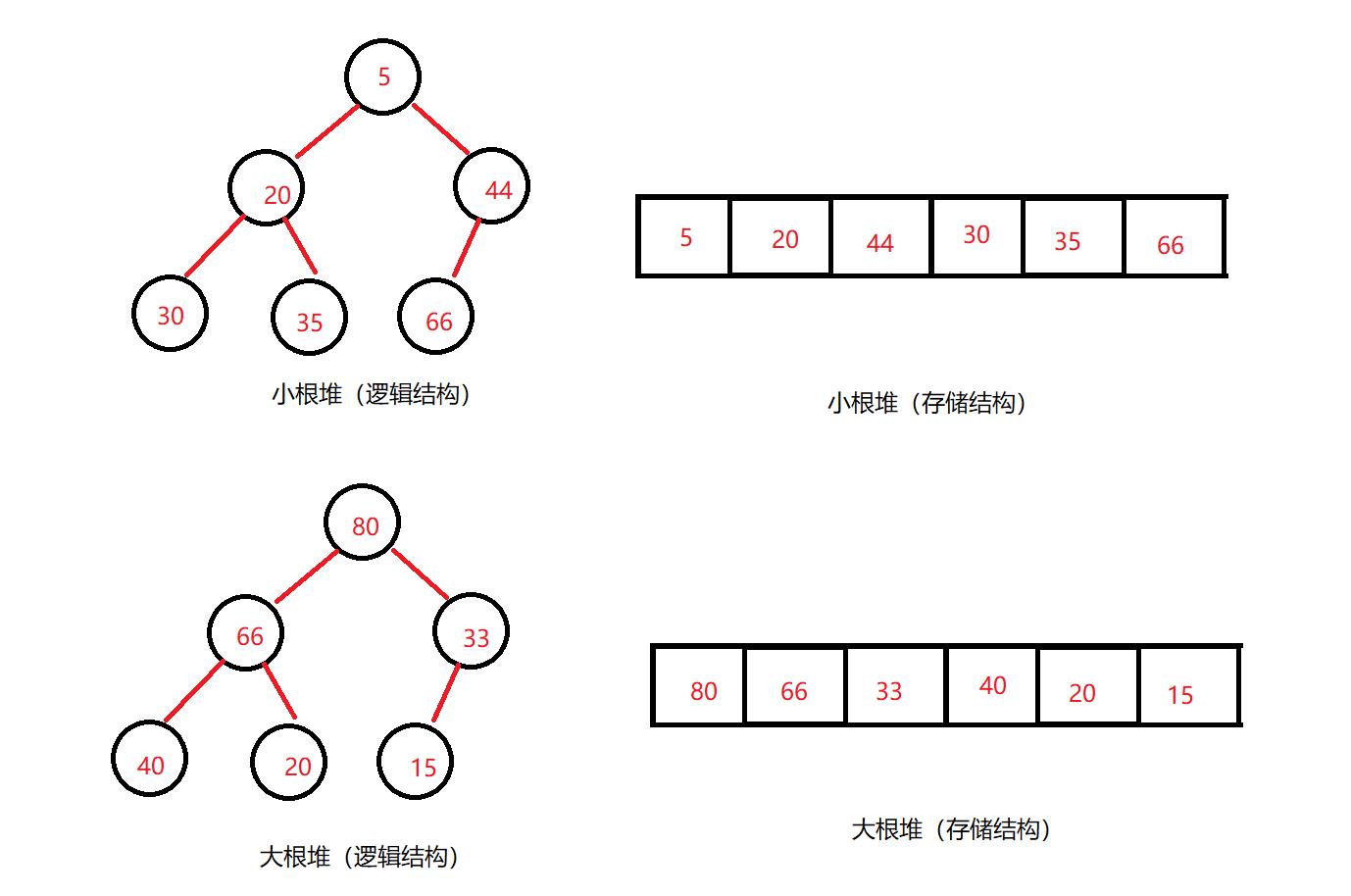
二、堆(heap)
1. 堆的基本概念
- 堆逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树
- 堆物理上是保存在数组中
- 满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆
- 反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆
- 堆的基本作用是,快速找集合中的最值
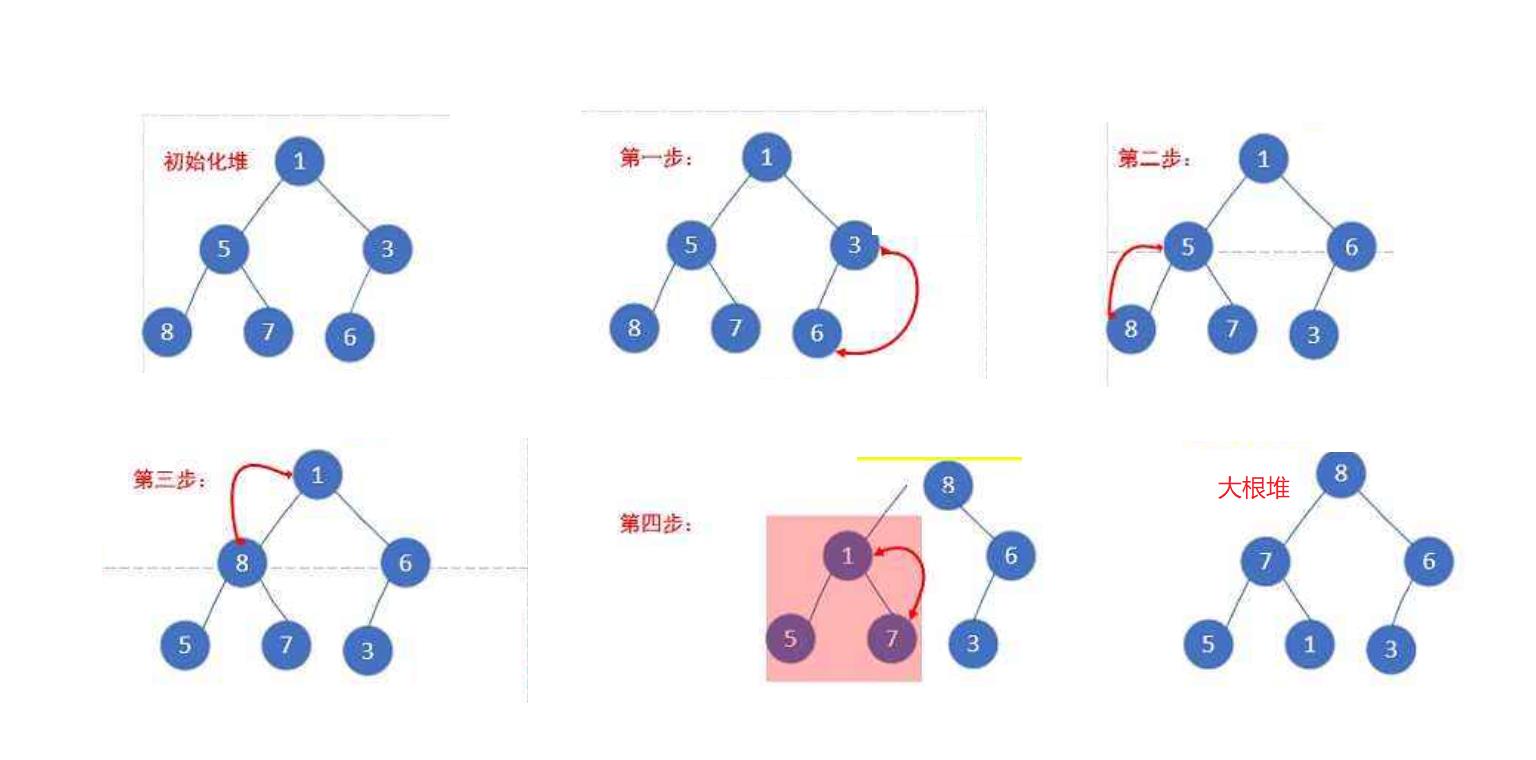
2. 堆的操作
(1) 建堆(向下调整)
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算法,把它构建成一个堆。根节点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子节点的子树开始调整,一直调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
向上调整的思路:从堆的最后一个元素的父亲。左右孩子比较大小后再和父亲比较如果大就交换。再更新父亲和孩子的下标,直到当所有孩子都没有父亲大时就是大根堆了。
代码示例:
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
TestHeap() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/**
* 建大堆
* @param array
*/
public void creteHeap(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for (int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2; parent >= 0; parent--) {
adjustDown(parent,this.usedSize);//向上调整
}
}
public void adjustDown(int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent+1;
while (child < len) {
//判断是否有右孩子
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//如果左右孩子的最大值大于父亲的值就交换
if(this.elem[parent] < this.elem[child]) {
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
}
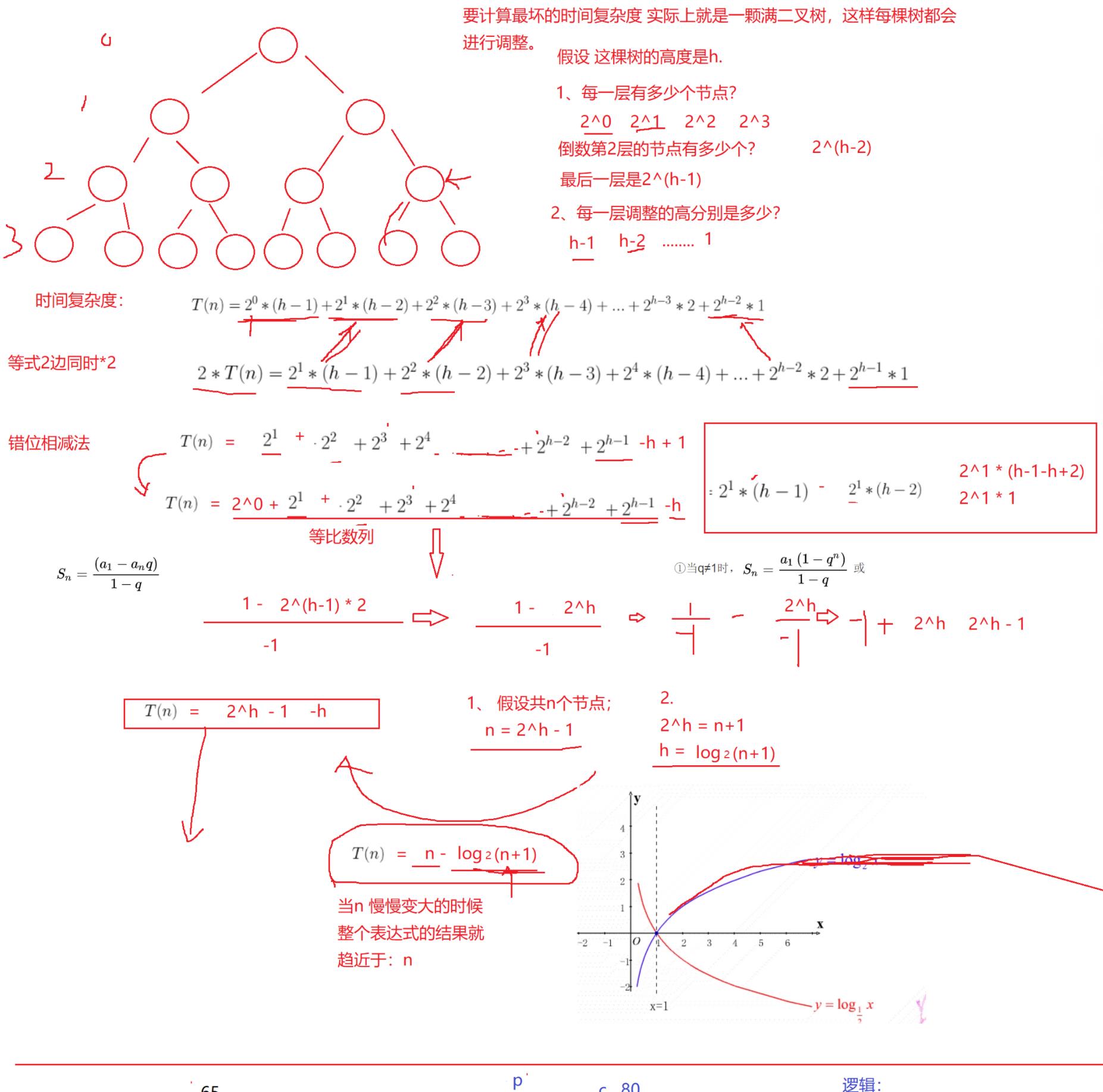
(2) 建堆的时间复杂度
通过公式一步计算得到: n - log₂(n + 1)
当n慢慢变大,时间复杂度就是 O(n)
建堆的时间复杂度
(3) 入队(向上调整)

//向上调整
public void adjustUp(int child) {
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while(parent >= 0) {
if(this.elem[parent] < this.elem[child]) {
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child-1)/2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 入队
* @param val
*/
public void push(int val) {
//扩容
if(this.isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
adjustUp(this.usedSize-1);
}
(4) 出队(向下调整)
让堆顶元素和堆的最后一个元素交换,元素个数减1。再从0下标向下调整

/**
* 出队首元素
*/
public void pop() {
if(this.isEmpty()) return;
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
this.elem[this.usedSize-1] = tmp;
this.usedSize--;
this.adjustDown(0,this.usedSize);//堆顶和堆尾下标
}
public void adjustDown(int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent+1;
while(child < len) {
//找到左右孩子的最大值
//1、前提是你得有右孩子
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//保证,child下标的数据 一定是左右孩子的最大值的下标
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
三、Java中的优先级队列(PriorityQueue)
Java中的PriorityQueue默认是一个小堆,需要指定比较规则才能改为大堆。下篇博客会讲到。
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();

四、堆排序
从大到小:建一个小堆
从小到大:建一个大堆
时间复杂度:O(n*logN)
空间复杂度:O(1)
稳定性:不稳定
这里不细说,到后面常见排序算法中还会提到。

/**
* 堆排序
* 先交换第一个和最后一个元素,再调整树
* 从小到大排序
*/
public void heapSort() {
if(this.isEmpty()) return;
int len = this.usedSize-1;
while(len > 0) {
int tmp = this.elem[len];
this.elem[len] = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = tmp;
adjustDown(0,len);
len--;
}
}
public void adjustDown(int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent+1;
while (child < len) {
//判断是否有右孩子
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//如果左右孩子的最大值大于父亲的值就交换
if(this.elem[parent] < this.elem[child]) {
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
完!
以上是关于Java集合数据结构——优先级队列 (堆PriorityQueue)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章