ASN.1编解码:asn1c的基本使用
Posted rtoax
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ASN.1编解码:asn1c的基本使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上篇主要讲了ASN.1编码《ASN.1编解码与编程》
本文主要介绍 ASN.1 编码的C语言实现,asn1c。ASN.1 在通信领域非常关键。
1. ASN.1 基础
如果你想在计算机之间传输一个标准数据格式,这个数据格式中包含字符串tag,整形,浮点型,那么这个结构就可以用 ASN.1 来描述,如下:
CertainStructure ::= SEQUENCE {
tag VisibleString,
val1 INTEGER,
val2 INTEGER OPTIONAL,
reals SET OF REAL
}
用 asn1c 进行编译,即可生成 C语言代码:
typedef struct CertainStructure {
VisibleString_t tag;
long val1;
long *val2; /* OPTIONAL */
A_SET_OF(double) reals;
} CertainStructure_t;
上述变量可能被直接修改。
重要的是,这个复杂的数据格式与二进制格式之间的相互转化是比较复杂的。(快照snap)
下面展示上面的数据结构通过网络接收、编辑和转化编码的过程:
CertainStructure_t *cs = 0;
ber_decode(0, &asn_DEF_CertainStructure, &cs, buffer, buffer_length);
cs->val1 = 123; /* Modify the contents */
der_encode(&asn_DEF_CertainStructure, cs, write_handle, 0);
write_handle的意思是asn1c编译器的使用提示。
下面就可以直接转化为 xml格式:
xer_fprint(stdout, &asn_DEF_CertainStructure, cs);
上面的代码的输出结果为:
<CertainStructure>
<tag>This is a random tag</tag>
<val1>123</val1>
<reals>
<REAL>3.14159265</REAL>
<REAL><MINUS-INFINITY/></REAL>
<REAL>2.7182818284</REAL>
</reals>
</CertainStructure>
ASN.1 被用作 通信行业,如果需要使用 SSL(HTTPS)来访问银行和邮件账号,确保 ASN.1 也参与其中。
2. ASN.1 编译器
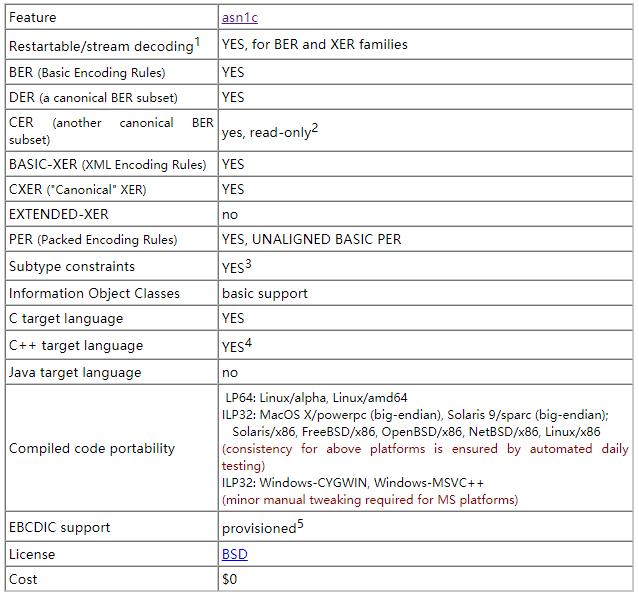
asn1c 是一个免费的将 ASN.1 结构转化为C语言格式的编译器。它支持 ASN.1 语法,包括: ISO/IEC/ITU ASN.1 1988, '94, '97, 2002 以及更新的版本。支持的编码规则为:
- BER: ITU-T Rec. X.690 | ISO/IEC 8825-1 (2002) (BER/DER/CER)
- PER: X.691|8825-2 (2002) (PER).
- XER: X.693|8825-3 (2001) (BASIC-XER/CXER).
License:
/*-
* Copyright (c) 2003-2013 Lev Walkin <vlm@lionet.info>
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND
* ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
* FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
* DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS
* OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
* HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY
* OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
* SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
3. 文档
http://lionet.info/asn1c/documentation.html
文档请按需下载:

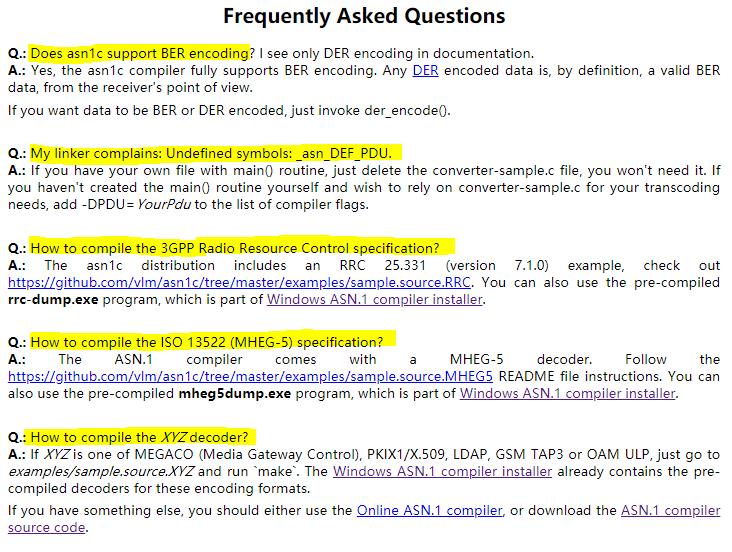
4. F&Q
http://lionet.info/asn1c/faq.html
5. 示例
这一章节,给出一个简单的编码示例,从 ASN.1 格式到 C语言代码,然后,再生成xml格式。
5.1. 编写 ASN.1 文件
假定我们已经有了MyModule.asn1文件:
MyModule DEFINITIONS ::=
BEGIN
MyTypes ::= SEQUENCE {
myObjectId OBJECT IDENTIFIER,
mySeqOf SEQUENCE OF MyInt,
myBitString BIT STRING {
muxToken(0),
modemToken(1)
}
}
MyInt ::= INTEGER (0..65535)
END
5.2. 用asn1c指令进行编译
asn1c MyModule.asn1
期间会生成几个文件,同时,会拷贝一些文件
[rongtao@localhost demo]$ asn1c MyModule.asn1
Compiled MyTypes.c
Compiled MyTypes.h
Compiled MyInt.c
Compiled MyInt.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/INTEGER.h -> INTEGER.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/NativeEnumerated.h -> NativeEnumerated.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/INTEGER.c -> INTEGER.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/NativeEnumerated.c -> NativeEnumerated.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/NativeInteger.h -> NativeInteger.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/NativeInteger.c -> NativeInteger.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/OBJECT_IDENTIFIER.h -> OBJECT_IDENTIFIER.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/OBJECT_IDENTIFIER.c -> OBJECT_IDENTIFIER.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_SEQUENCE_OF.h -> asn_SEQUENCE_OF.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_SEQUENCE_OF.c -> asn_SEQUENCE_OF.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_SET_OF.h -> asn_SET_OF.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_SET_OF.c -> asn_SET_OF.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SEQUENCE.h -> constr_SEQUENCE.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SEQUENCE.c -> constr_SEQUENCE.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SEQUENCE_OF.h -> constr_SEQUENCE_OF.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SEQUENCE_OF.c -> constr_SEQUENCE_OF.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SET_OF.h -> constr_SET_OF.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_SET_OF.c -> constr_SET_OF.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_application.h -> asn_application.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_system.h -> asn_system.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_codecs.h -> asn_codecs.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_internal.h -> asn_internal.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/OCTET_STRING.h -> OCTET_STRING.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/OCTET_STRING.c -> OCTET_STRING.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/BIT_STRING.h -> BIT_STRING.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/BIT_STRING.c -> BIT_STRING.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_codecs_prim.c -> asn_codecs_prim.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/asn_codecs_prim.h -> asn_codecs_prim.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_tlv_length.h -> ber_tlv_length.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_tlv_length.c -> ber_tlv_length.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_tlv_tag.h -> ber_tlv_tag.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_tlv_tag.c -> ber_tlv_tag.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_decoder.h -> ber_decoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/ber_decoder.c -> ber_decoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/der_encoder.h -> der_encoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/der_encoder.c -> der_encoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_TYPE.h -> constr_TYPE.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constr_TYPE.c -> constr_TYPE.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constraints.h -> constraints.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/constraints.c -> constraints.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_support.h -> xer_support.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_support.c -> xer_support.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_decoder.h -> xer_decoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_decoder.c -> xer_decoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_encoder.h -> xer_encoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/xer_encoder.c -> xer_encoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_support.h -> per_support.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_support.c -> per_support.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_decoder.h -> per_decoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_decoder.c -> per_decoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_encoder.h -> per_encoder.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_encoder.c -> per_encoder.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_opentype.h -> per_opentype.h
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_opentype.c -> per_opentype.c
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/converter-sample.c -> converter-sample.c
Generated Makefile.am.sample
从上面的输出结果可以看出,生成了一些文件:
Compiled MyTypes.c
Compiled MyTypes.h
Compiled MyInt.c
Compiled MyInt.h
Generated Makefile.am.sample
同时,也会拷贝一些文件:
Copied /usr/local/share/asn1c/per_encoder.c -> per_encoder.c
asn1c 为啥做成这种拷贝文件的格式,我不知道,我感觉可以做成 asn1c-devel 形式,编译成动态库来做,可能相对来说对项目代码量没有那么大。
5.3. 分析数据结构
5.3.1. MyInt
首先从简单的开始看:
MyInt ::= INTEGER (0..65535)
然我们查看 MyInt.h 头文件,看下数据类型:
/* MyInt */
typedef long MyInt_t;
此外,还有一些函数指针:
/* Implementation */
extern asn_TYPE_descriptor_t asn_DEF_MyInt;
asn_struct_free_f MyInt_free;
asn_struct_print_f MyInt_print;
asn_constr_check_f MyInt_constraint;
ber_type_decoder_f MyInt_decode_ber;
der_type_encoder_f MyInt_encode_der;
xer_type_decoder_f MyInt_decode_xer;
xer_type_encoder_f MyInt_encode_xer;
到这里,是不是和net-snmp 的使用很像,我觉得有异曲同工之妙。
然后,我们看c文件,该文件中实现了上述中头文件的 方法,截取一部分:
asn_enc_rval_t
MyInt_encode_der(asn_TYPE_descriptor_t *td,
void *structure, int tag_mode, ber_tlv_tag_t tag,
asn_app_consume_bytes_f *cb, void *app_key) {
MyInt_1_inherit_TYPE_descriptor(td);
return td->der_encoder(td, structure, tag_mode, tag, cb, app_key);
}
asn_dec_rval_t
MyInt_decode_xer(asn_codec_ctx_t *opt_codec_ctx, asn_TYPE_descriptor_t *td,
void **structure, const char *opt_mname, const void *bufptr, size_t size) {
MyInt_1_inherit_TYPE_descriptor(td);
return td->xer_decoder(opt_codec_ctx, td, structure, opt_mname, bufptr, size);
}
asn_enc_rval_t
MyInt_encode_xer(asn_TYPE_descriptor_t *td, void *structure,
int ilevel, enum xer_encoder_flags_e flags,
asn_app_consume_bytes_f *cb, void *app_key) {
MyInt_1_inherit_TYPE_descriptor(td);
return td->xer_encoder(td, structure, ilevel, flags, cb, app_key);
}
一个正向还是比较简单的,下面看比较复杂的是数据结构。
5.3.2. MyTypes
MyType 的 ASN.1 定义为:
MyTypes ::= SEQUENCE {
myObjectId OBJECT IDENTIFIER,
mySeqOf SEQUENCE OF MyInt,
myBitString BIT STRING {
muxToken(0),
modemToken(1)
}
}
首先看一下C语言结构定义:
/* Dependencies */
typedef enum myBitString {
myBitString_muxToken = 0,
myBitString_modemToken = 1
} e_myBitString;
/* MyTypes */
typedef struct MyTypes {
OBJECT_IDENTIFIER_t myObjectId;
struct mySeqOf {
A_SEQUENCE_OF(MyInt_t) list;
/* Context for parsing across buffer boundaries */
asn_struct_ctx_t _asn_ctx;
} mySeqOf;
BIT_STRING_t myBitString;
/* Context for parsing across buffer boundaries */
asn_struct_ctx_t _asn_ctx;
} MyTypes_t;
上述数据结构中,_asn_ctx用来管理,我们在编写过程中不能显式对其进行修改。其他标签,均和ASN.1 格式匹配。
5.4. 编写asn程序
#include <stdio.h> /* for stdout */
#include <stdlib.h> /* for malloc() */
#include <assert.h> /* for run-time control */
#include "MyTypes.h" /* Include MyTypes definition */
int main() {
/* Define an OBJECT IDENTIFIER value */
int oid[] = { 1, 3, 6, 1, 4, 1, 9363, 1, 5, 0 }; /* or whatever */
/* Declare a pointer to a new instance of MyTypes type */
MyTypes_t *myType;
/* Declare a pointer to a MyInt type */
MyInt_t *myInt;
/* Temporary return value */
int ret;
/* Allocate an instance of MyTypes */
myType = calloc(1, sizeof *myType);
assert(myType); /* Assume infinite memory */
/*
* Fill in myObjectId
*/
ret = OBJECT_IDENTIFIER_set_arcs(&myType->myObjectId,
oid, sizeof(oid[0]), sizeof(oid) / sizeof(oid[0]));
assert(ret == 0);
/*
* Fill in mySeqOf with a couple of integers.
*/
/* Prepare a certain INTEGER */
myInt = calloc(1, sizeof *myInt);
assert(myInt);
*myInt = 123; /* Set integer value */
/* Fill in mySeqOf with the prepared INTEGER */
ret = ASN_SEQUENCE_ADD(&myType->mySeqOf, myInt);
assert(ret == 0);
/* Prepare another integer */
myInt = calloc(1, sizeof *myInt);
assert(myInt);
*myInt = 111222333; /* Set integer value */
/* Append another INTEGER into mySeqOf */
ret = ASN_SEQUENCE_ADD(&myType->mySeqOf, myInt);
assert(ret == 0);
/*
* Fill in myBitString
*/
/* Allocate some space for bitmask */
myType->myBitString.buf = calloc(1, 1);
assert(myType->myBitString.buf);
myType->myBitString.size = 1; /* 1 byte */
/* Set the value of muxToken */
myType->myBitString.buf[0] |= 1 << (7 - myBitString_muxToken);
/* Also set the value of modemToken */
myType->myBitString.buf[0] |= 1 << (7 - myBitString_modemToken);
/* Trim unused bits (optional) */
myType->myBitString.bits_unused = 6;
/*
* Print the resulting structure as XER (XML)
*/
xer_fprint(stdout, &asn_DEF_MyTypes, myType);
return 0;
}
因为上面的编译 ASN.1 语法的时候,生成了一个 Makefile.am.sample 文件,实际上,main主程序在拷贝的文件 converter-sample.c中 ,为了编译方便,我把上面的文件内容放入了文件converter-sample.c中,并进行编译执行:
[rongtao@localhost demo]$ make -f Makefile.am.sample
[rongtao@localhost demo]$ ./progname
<MyTypes>
<myObjectId>1.3.6.1.4.1.9363.1.5.0</myObjectId>
<mySeqOf>
<MyInt>123</MyInt>
<MyInt>111222333</MyInt>
</mySeqOf>
<myBitString>
11
</myBitString>
</MyTypes>
5.5. 从xer文件中取数据
我将上面的文本保存到文件MyType.xer中:
[rongtao@localhost demo]$ cat MyType.xer
<MyTypes>
<myObjectId>1.3.6.1.4.1.9363.1.5.0</myObjectId>
<mySeqOf>
<MyInt>123</MyInt>
<MyInt>111222333</MyInt>
</mySeqOf>
<myBitString>
11
</myBitString>
</MyTypes>
采用上面的编译步骤,运行下面的程序,源代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> /* for stdout */
#include <stdlib.h> /* for malloc() */
#include <assert.h> /* for run-time control */
#include "MyTypes.h" /* Include MyTypes definition */
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char buf[1024]; /* Hope, sufficiently large buffer */
MyTypes_t *myType = 0;
asn_dec_rval_t rval;
char *filename;
size_t size;
FILE *f;
/*
* Target variables.
*/
int *oid_array; /* holds myObjectId */
int oid_size;
int *int_array; /* holds mySeqOf */
int int_size;
int muxToken_set; /* holds single bit */
int modemToken_set; /* holds single bit */
/*
* Read in the input file.
*/
assert(argc == 2);
filename = argv[1];
f = fopen(filename, "r");
assert(f);
size = fread(buf, 1, sizeof buf, f);
if(size == 0 || size == sizeof buf) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Too large input\\n", filename);
exit(1);
}
/*
* Decode the XER buffer.
*/
rval = xer_decode(0, &asn_DEF_MyTypes, &myType, buf, size);
assert(rval.code == RC_OK);
/*
* Convert the OBJECT IDENTIFIER into oid_array/oid_size pair.
*/
/* Figure out the number of arcs inside OBJECT IDENTIFIER */
oid_size = OBJECT_IDENTIFIER_get_arcs(&myType->myObjectId,
0, sizeof(oid_array[0]), 0);
assert(oid_size >= 0);
/* Create the array of arcs and fill it in */
oid_array = malloc(oid_size * sizeof(oid_array[0]));
assert(oid_array);
(void)OBJECT_IDENTIFIER_get_arcs(&myType->myObjectId,
oid_array, sizeof(oid_array[0]), oid_size);
/*
* Convert the sequence of integers into array of integers.
*/
int_size = myType->mySeqOf.list.count;
int_array = malloc(int_size * sizeof(int_array[0]));
assert(int_array);
for(int_size = 0; int_size < myType->mySeqOf.list.count; int_size++)
int_array[int_size] = *myType->mySeqOf.list.array[int_size];
if(myType->myBitString.buf) {
muxToken_set = myType->myBitString.buf[0]
& (1 << (7 - myBitString_muxToken));
modemToken_set = myType->myBitString.buf[0]
& (1 << (7 - myBitString_modemToken));
} else {
muxToken_set = modemToken_set = 0; /* Nothing is set */
}
/*
* Print the resulting structure as XER (XML)
*/
xer_fprint(stdout, &asn_DEF_MyTypes, myType);
return 0;
}
和原网址的唯一区别在于,我在 main 程序的末尾添加了 打印的代码:
/*
* Print the resulting structure as XER (XML)
*/
xer_fprint(stdout, &asn_DEF_MyTypes, myType);
我们运行上述程序,得出:
[rongtao@localhost demo]$ ./progname MyType.xer
<MyTypes>
<myObjectId>1.3.6.1.4.1.9363.1.5.0</myObjectId>
<mySeqOf>
<MyInt>123</MyInt>
<MyInt>111222333</MyInt>
</mySeqOf>
<myBitString>
11
</myBitString>
</MyTypes>
6. 参考链接
以上是关于ASN.1编解码:asn1c的基本使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章