《剑指offer》JZ31 ~ JZ40
Posted 黑桃️
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《剑指offer》JZ31 ~ JZ40相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
《剑指offer》JZ31 ~ JZ40
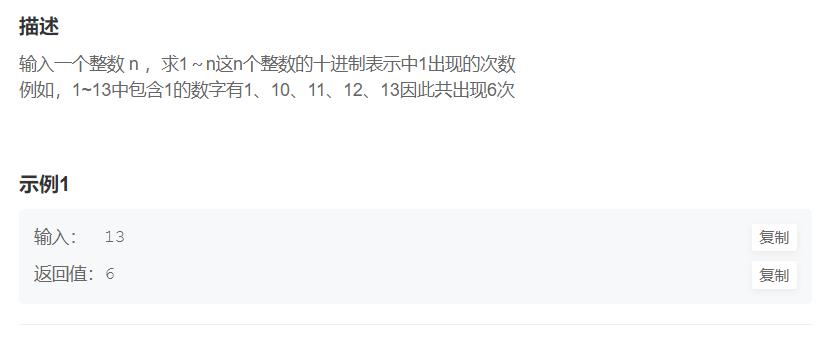
JZ31 整数中1出现的次数(从1到n整数中1出现的次数)
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans += add(i);
return ans;
}
// 取出每位
int add(int n)
{
int cnt=0;
while(n)
{
if(n%10==1) cnt++;
n/=10;
}
return cnt;
}
};
JZ32 把数组排成最小的数

一开始一直在写一个cmp,但是写的有各种问题
所以先写了一个全排列的比较暴力的写法
class Solution {
public:
string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) {
string ans;
sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end());
do{
string t;
for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();i++)
t+=to_string(numbers[i]);
ans = ans=="" ? t : min(ans,t);
}while(next_permutation(numbers.begin(), numbers.end()));
return ans;
}
};
JZ33 丑数

用优先队列实现小根堆,把丑数放进去,每个丑数的2,3,5倍同样是丑数
class Solution {
public:
int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
int f=0;
map<int,int> mp;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> p;
p.push(1);
mp[1]=1;
while(index--)
{
f = p.top();
p.pop();
// 防止越界,超过int的不要,用除法判断,乘法会爆int
if(f < (1<<31-1)/2 && !mp[f*2]) p.push(f*2),mp[f*2]=1;
if(f < (1<<31-1)/3 && !mp[f*3]) p.push(f*3),mp[f*3]=1;
if(f < (1<<31-1)/5 && !mp[f*5]) p.push(f*5),mp[f*5]=1;
}
return f;
}
};
JZ34 第一个只出现一次的字符

class Solution {
public:
int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) {
map<char,int> m;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
m[str[i]]++;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
if(m[str[i]]==1) return i;
return -1;
}
};
JZ35 数组中的逆序对

归并排序,右半部分<左半部分,就加上左半部分所有,因为左序号在前,值比右大,正是逆序对
class Solution {
public:
int ans;
int t[50005];
int InversePairs(vector<int> data) {
sort(data,0,data.size()-1);
return ans;
}
void sort(vector<int>& data,int l,int r)
{
if(l==r) return;
int mid=l+(r-l)/2;
sort(data,l,mid);
sort(data,mid+1,r);
int i=l,j=mid+1;
for(int k=l;k<=r;k++)
{
if(j>r || (i<=mid && data[i]<=data[j]) ) t[k]=data[i++];
else
{
ans = (mid-i+1+ans)%1000000007;
t[k] = data[j++];
}
}
for(int k=l;k<=r;k++) data[k]=t[k];
}
};
JZ36 两个链表的第一个公共结点

此题的公共节点是在最后面,所以可以使用以下方法,因为二者长度可能不同,所以p1+p2,和p2+p1后长度相同,且最后对应的一部分是公共节点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode* p1 = pHead1;
ListNode* p2 = pHead2;
while(p1 || p2)
{
if(p1 == p2) return p1;
p1 = p1 ? p1->next : pHead2;
p2 = p2 ? p2->next : pHead1;
}
return NULL;
}
};
JZ37 数字在升序数组中出现的次数

跑两次二分,一次找下限,一次找上限,也可以使用lower_bound和upper_bound
class Solution {
public:
int GetNumberOfK(vector<int> data ,int k) {
if(data.empty()) return 0;
int l=0,r=data.size()-1,x;
// 找下界
while(l<r)
{
int mid=l+(r-l)/2;
if(data[mid] >= k) r=mid;
else l = mid+1;
}
// 表示目标值没在数组中出现
if(data[l] != k) return 0;
x = l;
l=0,r=data.size()-1;
//找上界
while(l<r)
{
int mid=l+(r-l)/2;
if(data[mid] > k) r=mid-1;
else l = mid+1;
}
return r-x+1;
}
};
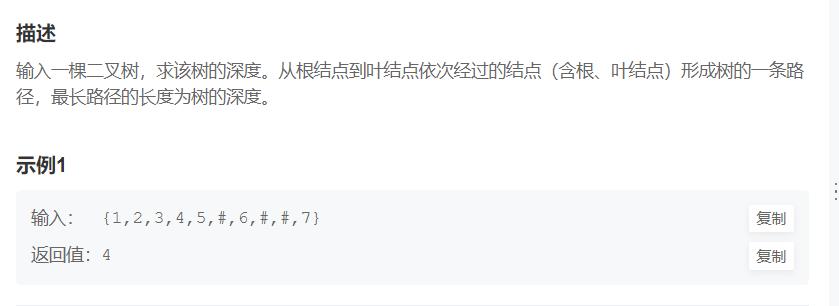
JZ38 二叉树的深度
class Solution {
public:
int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot) {
if(!pRoot) return 0;
int ans=0;
map<TreeNode*,int> m;
m[pRoot] = 1; //记录每个节点的深度
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(pRoot);
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode* f = q.front();
q.pop();
ans = max(ans, m[f]);
if(f->left)
{
q.push(f->left);
m[f->left] = m[f] + 1; // 增加深度
}
if(f->right)
{
q.push(f->right);
m[f->right] = m[f] + 1; // 增加深度
}
}
return ans;
}
};
JZ39 平衡二叉树

翻译一下平衡二叉树的特性就行
class Solution {
public:
bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot) {
if(!pRoot) return true;
return abs(deep(pRoot->left, 1)-deep(pRoot->right, 1))<=1
&& IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot->left)
&& IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot->right);
}
int deep(TreeNode* pRoot, int d)
{
if(pRoot==NULL) return d;
return max(deep(pRoot->left, d+1), deep(pRoot->right, d+1));
}
};
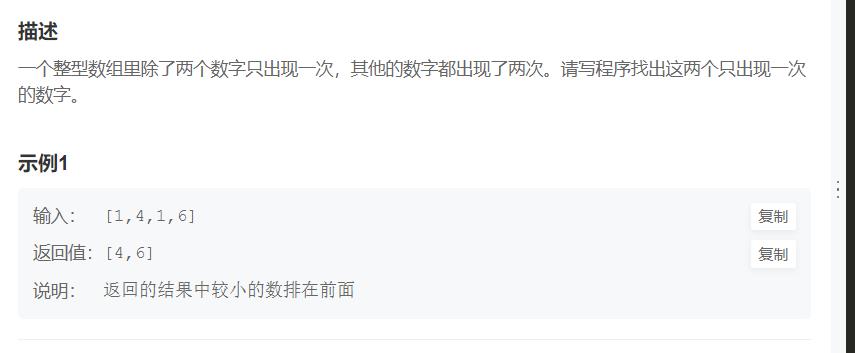
JZ40 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> FindNumsAppearOnce(vector<int>& array) {
// write code here
vector<int> ans;
map<int,int> m;
for(int i=0;i<array.size();i++)
m[array[i]]++;
for(int i=0;i<array.size();i++)
if(m[array[i]]==1) ans.push_back(array[i]);
return ans;
}
};
以上是关于《剑指offer》JZ31 ~ JZ40的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章