Arduino EEPROM读写实例
Posted perseverance52
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Arduino EEPROM读写实例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Arduino EEPROM读写实例
读写函数
EEPROM.write();//按字节写入EEPROM.read();//按字节读EEPROM.put();//按数据类型写入EEPROM.get();//按数据类型读取EEPROM.commit();//提交保存EEPROM.end();//提交保存
读写实例
#include <EEPROM.h>
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
EEPROM.begin(32); //EEPROM.begin(Size)
// 使用ESP8266 EEPROM不同于标准的Arduino EEPROM类。
// 在开始读或写之前,需要调用EEPROM.begin(size),其中size参数是要使用的存储字节数
// 大小可以是最小4字节到最大4096字节之间的任何位置.
}
void loop() {
// 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // 32-bytes of random data
// EEPROM.put(eeAddress, variable_name); // Writes a variable type e.g. float = 4-bytes, int = 4-bytes, boolean = 1 byte
// EEPROM.get(eeAddress, variable_name); // Reads a variable type e.g. float = 4-bytes, int = 4-bytes, boolean = 1 byte
// int value = EEPROM.read(eeAddress); // Read a single byte
// EEPROM.write(eeAddress, variable_name); // Write a single byte
// EEEPROM.commit() commands such as EEPROM.write or EEPROM.put do not write to flash immediately, to invoke them you must call EEPROM.commit() to save changes to flash/EEPROM.
// EEPROM.end() will also commit, but releases the RAM copy of EEPROM contents.
// Commands to determine variable sizes, needed for storing to EEPROM
Serial.println(" Floating point variables need: "+String(sizeof(float))+" Bytes"); // 确定需要多少字节(4)来保存一个浮点变量
Serial.println("Double size floating point variables need: "+String(sizeof(double))+ " Bytes"); // 确定需要多少字节(8)来保存一个浮点变量
Serial.println(" Integer variables need: "+String(sizeof(int))+" Bytes"); // 确定需要多少字节(4)来保存一个整数变量
Serial.println(" Boolean values or variables need: "+String(sizeof(bool))+" Bytes"); // 确定需要多少字节(1)来保存一个布尔变量
Serial.println(" String variables need at least: "+String(sizeof(String))+" Bytes"); // 确定需要多少字节(最少12)来保存一个字符串变量
Serial.println();
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-1 Write a value to EEPROM at address = 0
int EEaddress = 0;
EEPROM.write(EEaddress,123); // 将值123写入EEPROM
// 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // EEPROM的内容
// 7B 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of RAM copy of EEPROM 从RAM拷贝到EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
// 7B 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // EEPROM的内容
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=0 is : ");
Serial.println(EEPROM.read(EEaddress));
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-2 Write a value to EEPROM at address = 0
// 7B 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
EEPROM.write(EEaddress,257); // 将值257写入EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
// 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=0 is : ");
Serial.println(EEPROM.read(EEaddress));
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-3 Write an integer variable to EEPROM at address = 0
int integer_variable = 257;
// 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
EEPROM.put(EEaddress,integer_variable); // 将值257写入EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
// 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=0 is : ");
integer_variable = 0; // 证明它是从EEPROM读取的!
EEPROM.get(EEaddress,integer_variable);
Serial.println(integer_variable);
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-4 Write another integer variable to EEPROM
int integer_variable2 = 1234;
// 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
EEaddress = EEaddress + sizeof(int); // 将地址向前移动4
EEPROM.put(EEaddress,integer_variable2); // 将值1234写入EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
// 01 01 00 00 D2 04 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 // Contents of EEPROM
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=4 is : ");
integer_variable2 = 0; // To prove it read from EEPROM!
EEPROM.get(EEaddress,integer_variable2);
Serial.println(integer_variable2);
EEaddress = EEaddress + sizeof(int); // Moves the address along by 4
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-5 Write a floating point variable to EEPROM
float floatingpoint_variable = 3.141592654;
EEPROM.put(EEaddress,floatingpoint_variable); // Writes the value 3.141592654 to EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=8 is : ");
floatingpoint_variable = 0; // To prove it read from EEPROM!
EEPROM.get(EEaddress,floatingpoint_variable);
Serial.println(floatingpoint_variable,8);//0.00000000
EEaddress = EEaddress + sizeof(float); // 将地址向前移动4
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-6 Write a string variable to EEPROM
String string_variable = "Hello world";
EEPROM.put(EEaddress,string_variable); // Writes the value 3.141592654 to EEPROM
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.print("EEPROM contents at Address=12 is : ");
floatingpoint_variable = 0; // To prove it read from EEPROM!
EEPROM.get(EEaddress,string_variable);
Serial.println(string_variable);//Hello world
EEaddress = EEaddress + sizeof(string_variable); // Moves the address along by 4
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-7 Write a series of values to EEPROM
for (int i = 1000; i <= 1032; i = i + 4) {
EEPROM.put(i-1000,i); // Address range 0-32
}
EEPROM.commit();
for (int j = 1000; j <= 1032; j = j + 4) {
EEPROM.get((j-1000),integer_variable); // Read the 32 values
Serial.println(integer_variable);
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-8 Testing that the EEPROM extent has not been exceeded, remember not to exceed address space
if (EEaddress == 32) {
EEaddress = 0;
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example-9 Compact method of writing and reading values from EEPROM
EEaddress = 20;
// Writing写
floatingpoint_variable = 2 * PI;
EEaddress += EEPROM.put(EEaddress, floatingpoint_variable);
integer_variable = 123456789;
EEaddress += EEPROM.put(EEaddress, integer_variable);
EEPROM.end();
EEaddress = 20;
// Reading读
EEaddress += EEPROM.get(EEaddress, floatingpoint_variable);
EEaddress += EEPROM.get(EEaddress, integer_variable);
Serial.println(floatingpoint_variable,7);//打印浮点数,精度到点后7位;6.2831855
Serial.println(integer_variable);//123456789
delay(200000);
}
- 串口打印
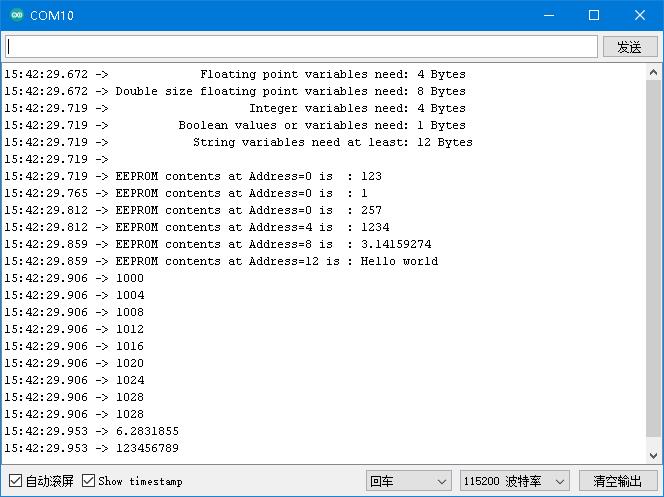
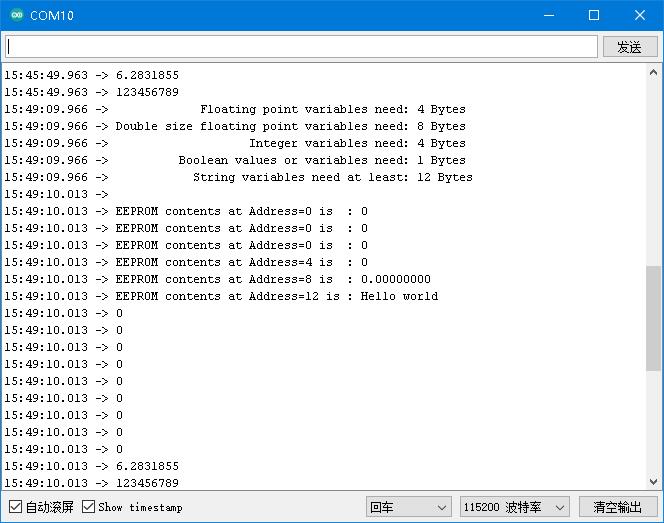
- 一个循环周期后,读取的数据
以上是关于Arduino EEPROM读写实例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章