Kotlin Coroutines 协程实现原理全解析
Posted 东海陈光剑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kotlin Coroutines 协程实现原理全解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


Hello Coroutines World
package coroutines.demo
import kotlinx.coroutines.coroutineScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
suspend fun main() = coroutineScope {
launch {
delay(1000)
println("Kotlin Coroutines World!")
}
println("Hello")
}输出:
Hello
Kotlin Coroutines World!
CoroutineScope
public interface CoroutineScope {
/**
* The context of this scope.
* Context is encapsulated by the scope and used for implementation of coroutine builders that are extensions on the scope.
* Accessing this property in general code is not recommended for any purposes except accessing the [Job] instance for advanced usages.
*
* By convention, should contain an instance of a [job][Job] to enforce structured concurrency.
*/
public val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext
}CoroutineContext : Persistent context for the coroutine
package kotlin.coroutines
/**
* Persistent context for the coroutine. It is an indexed set of [Element] instances.
* An indexed set is a mix between a set and a map.
* Every element in this set has a unique [Key].
*/
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
public interface CoroutineContext {
/**
* Returns the element with the given [key] from this context or `null`.
*/
public operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E?
/**
* Accumulates entries of this context starting with [initial] value and applying [operation]
* from left to right to current accumulator value and each element of this context.
*/
public fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R
/**
* Returns a context containing elements from this context and elements from other [context].
* The elements from this context with the same key as in the other one are dropped.
*/
public operator fun plus(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext =
if (context === EmptyCoroutineContext) this else // fast path -- avoid lambda creation
context.fold(this) { acc, element ->
val removed = acc.minusKey(element.key)
if (removed === EmptyCoroutineContext) element else {
// make sure interceptor is always last in the context (and thus is fast to get when present)
val interceptor = removed[ContinuationInterceptor]
if (interceptor == null) CombinedContext(removed, element) else {
val left = removed.minusKey(ContinuationInterceptor)
if (left === EmptyCoroutineContext) CombinedContext(element, interceptor) else
CombinedContext(CombinedContext(left, element), interceptor)
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a context containing elements from this context, but without an element with
* the specified [key].
*/
public fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext
/**
* Key for the elements of [CoroutineContext]. [E] is a type of element with this key.
*/
public interface Key<E : Element>
/**
* An element of the [CoroutineContext]. An element of the coroutine context is a singleton context by itself.
*/
public interface Element : CoroutineContext {
/**
* A key of this coroutine context element.
*/
public val key: Key<*>
public override operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E? =
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
if (this.key == key) this as E else null
public override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =
operation(initial, this)
public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext =
if (this.key == key) EmptyCoroutineContext else this
}
}Continuation
package kotlin.coroutines
import kotlin.contracts.*
import kotlin.coroutines.intrinsics.*
import kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
/**
* Interface representing a continuation after a suspension point that returns a value of type `T`.
*/
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
public interface Continuation<in T> {
/**
* The context of the coroutine that corresponds to this continuation.
*/
public val context: CoroutineContext
/**
* Resumes the execution of the corresponding coroutine passing a successful or failed [result] as the
* return value of the last suspension point.
*/
public fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>)
}CombinedContext
//--------------------- internal impl ---------------------
// this class is not exposed, but is hidden inside implementations
// this is a left-biased list, so that `plus` works naturally
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
internal class CombinedContext(
private val left: CoroutineContext,
private val element: Element
) : CoroutineContext, Serializable {
override fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E? {
var cur = this
while (true) {
cur.element[key]?.let { return it }
val next = cur.left
if (next is CombinedContext) {
cur = next
} else {
return next[key]
}
}
}
public override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =
operation(left.fold(initial, operation), element)
public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext {
element[key]?.let { return left }
val newLeft = left.minusKey(key)
return when {
newLeft === left -> this
newLeft === EmptyCoroutineContext -> element
else -> CombinedContext(newLeft, element)
}
}
private fun size(): Int {
var cur = this
var size = 2
while (true) {
cur = cur.left as? CombinedContext ?: return size
size++
}
}
private fun contains(element: Element): Boolean =
get(element.key) == element
private fun containsAll(context: CombinedContext): Boolean {
var cur = context
while (true) {
if (!contains(cur.element)) return false
val next = cur.left
if (next is CombinedContext) {
cur = next
} else {
return contains(next as Element)
}
}
}
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean =
this === other || other is CombinedContext && other.size() == size() && other.containsAll(this)
override fun hashCode(): Int = left.hashCode() + element.hashCode()
override fun toString(): String =
"[" + fold("") { acc, element ->
if (acc.isEmpty()) element.toString() else "$acc, $element"
} + "]"
private fun writeReplace(): Any {
val n = size()
val elements = arrayOfNulls<CoroutineContext>(n)
var index = 0
fold(Unit) { _, element -> elements[index++] = element }
check(index == n)
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
return Serialized(elements as Array<CoroutineContext>)
}
private class Serialized(val elements: Array<CoroutineContext>) : Serializable {
companion object {
private const val serialVersionUID: Long = 0L
}
private fun readResolve(): Any = elements.fold(EmptyCoroutineContext, CoroutineContext::plus)
}
}


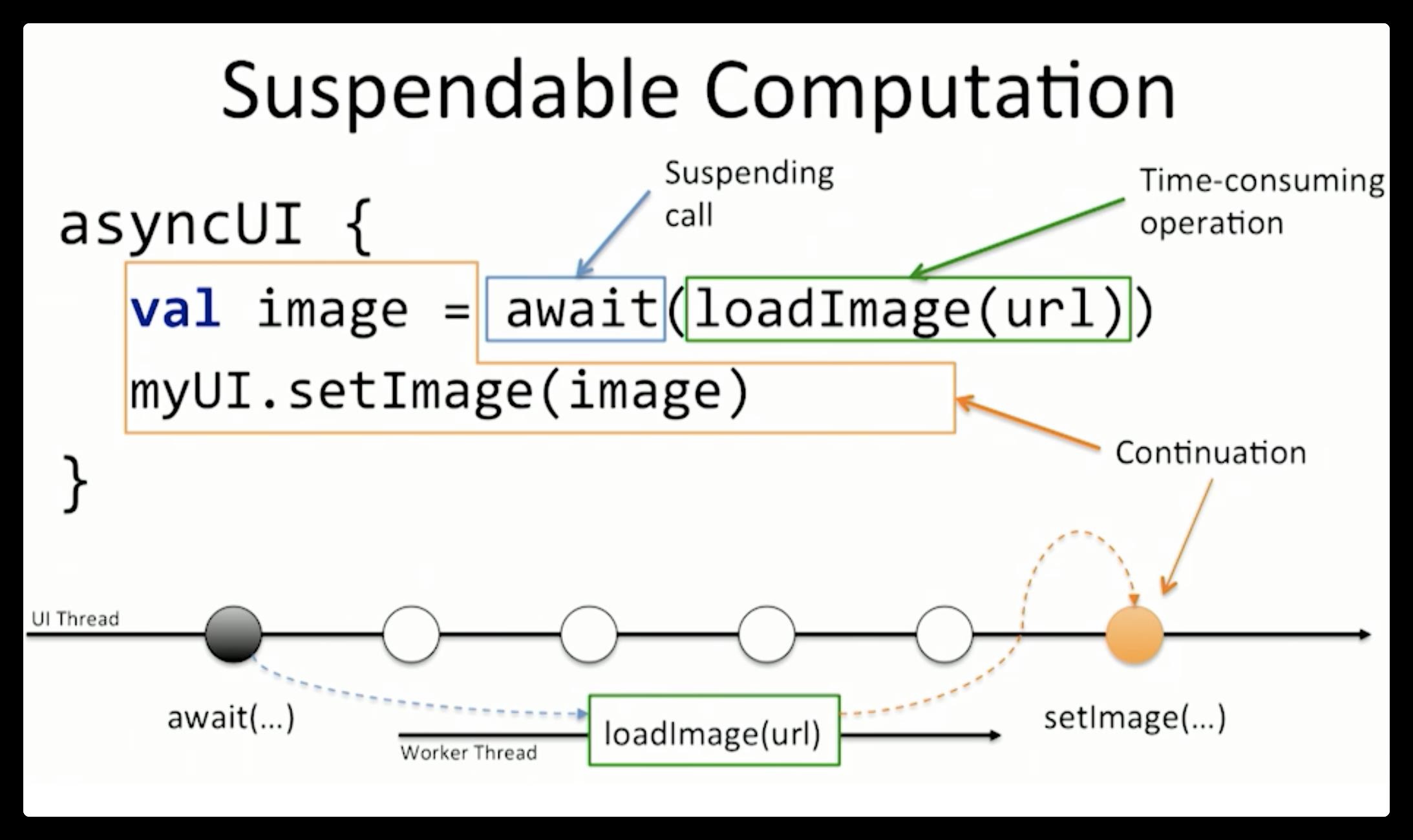


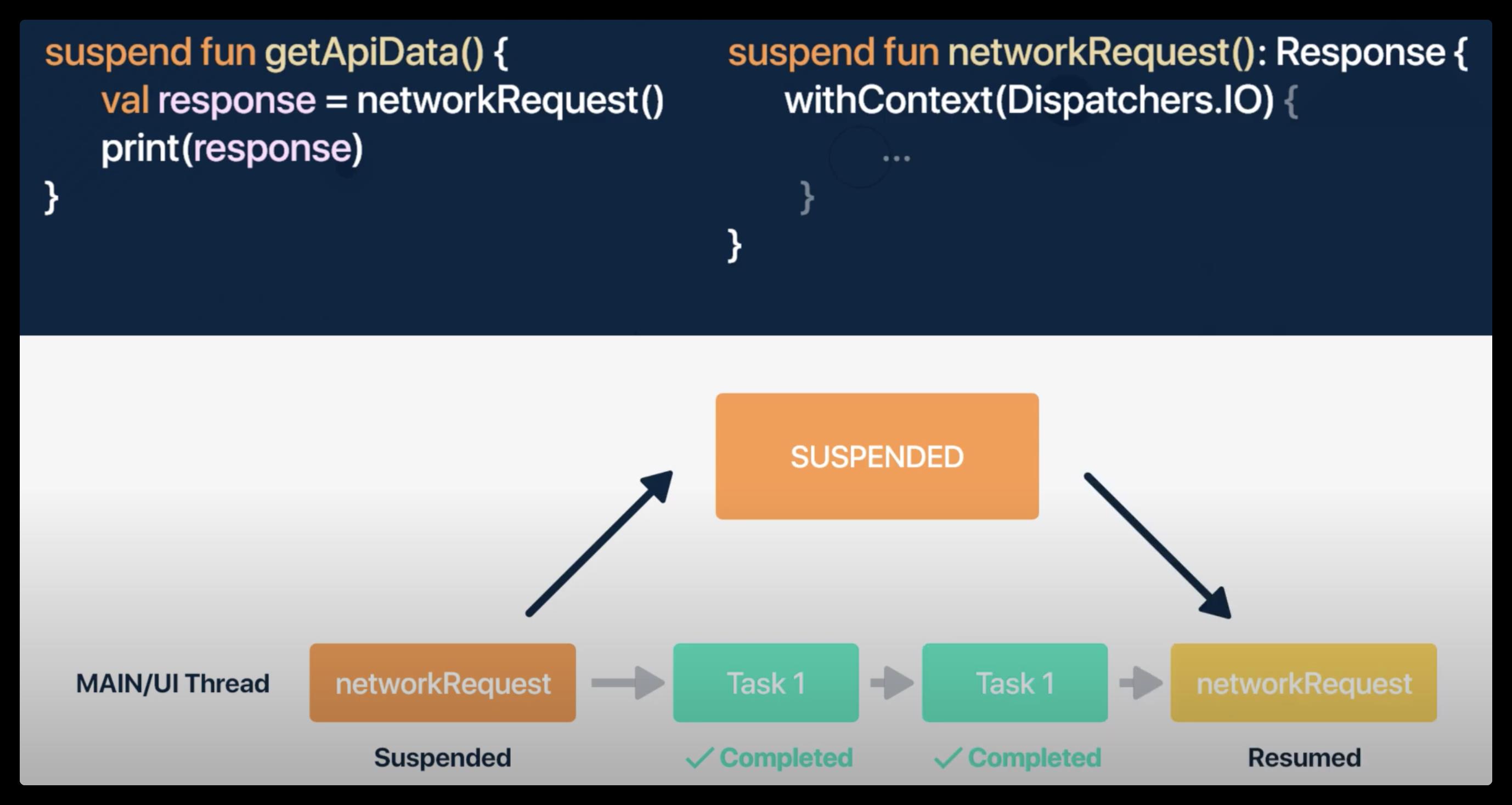



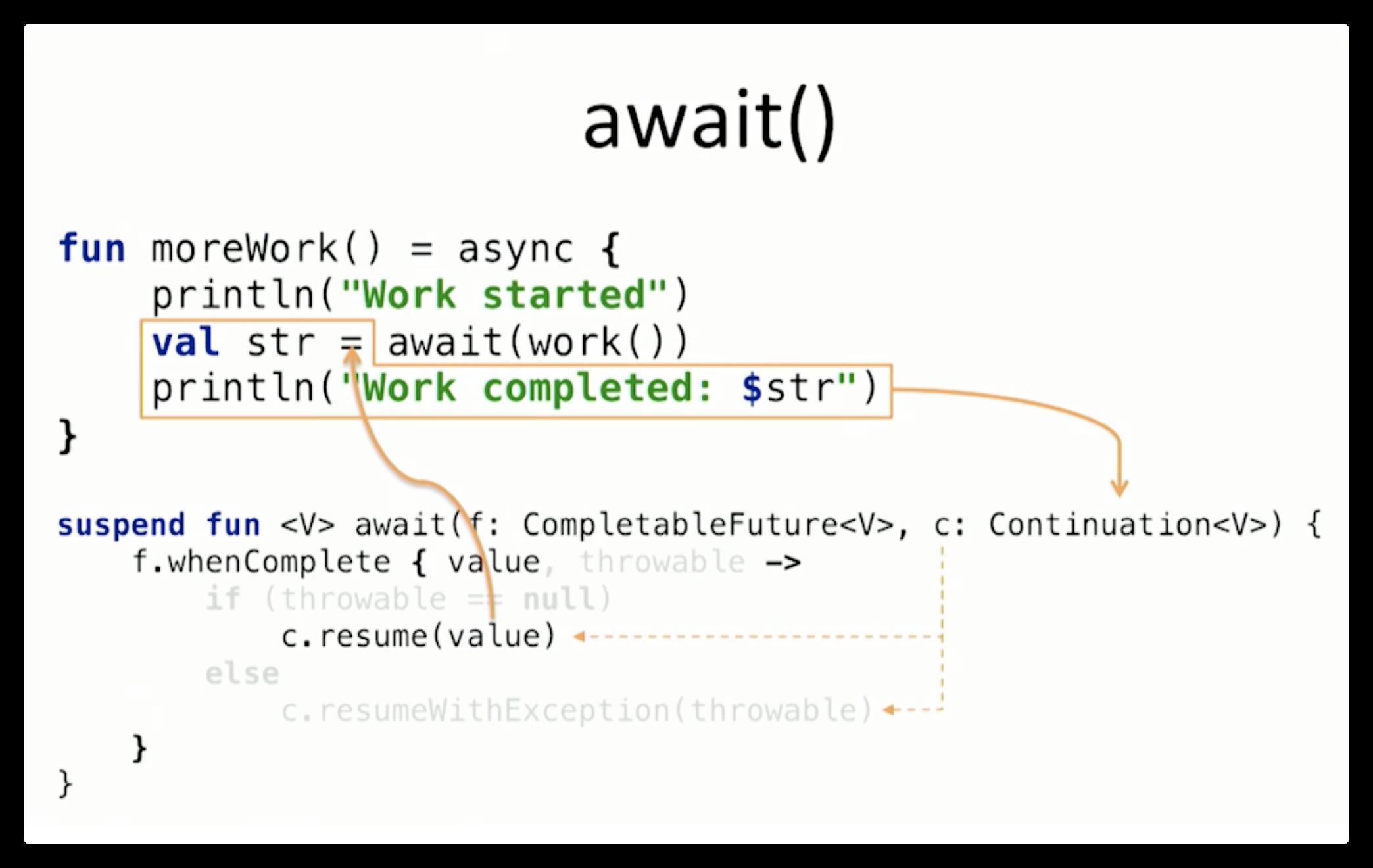
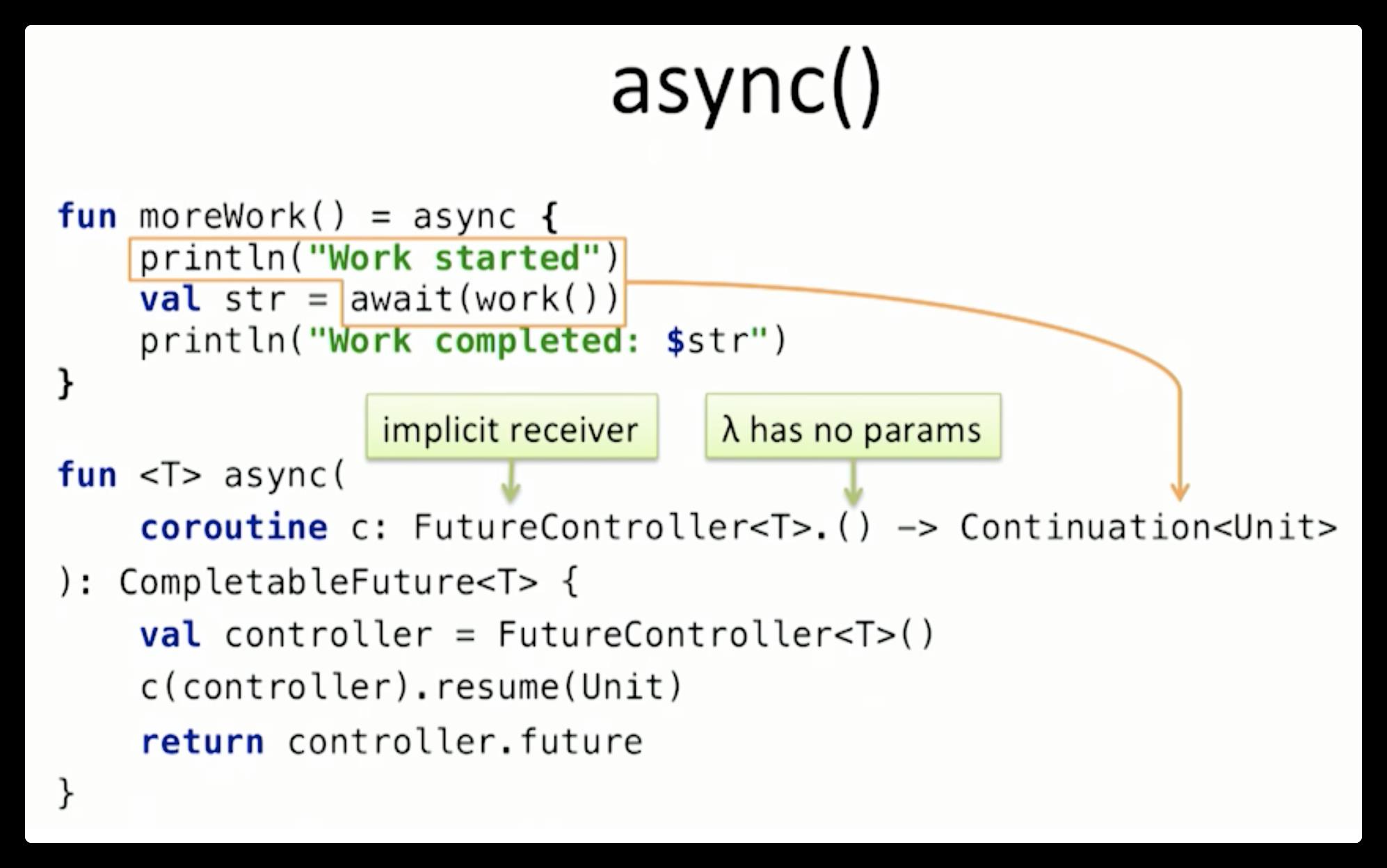









以上是关于Kotlin Coroutines 协程实现原理全解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章