狂神说Java笔记--网络编程部分笔记
Posted 小智RE0
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了狂神说Java笔记--网络编程部分笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
传送门==>B站遇见狂神说—网络编程
笔记和练习只是跟着视频整理的;有的知识点并没有整理进来.
ml
1.什么是计算机网络
计算机网络是指将地理位置不同的具有独立功能的多台计算机及其外部设备,通过通信线路连接起来,在网络操作系统,网络管理软件及网络通信协议的管理和协调下,实现资源共享和信息传递的计算机系统。
网络编程的目的
数据交换;通信
两个主要问题:
- 如何精确定位到网络上的一台主机; — IP,端口,定位到计算机上的某个资源
- 找到这个主机,如何传输数据?— 通信协议
- javaWeb 网页编程; B/S
- TCP/IP 网络编程 C/S
2.网络通信的两个要素
(1)通信双方地址:IP ;端口号
(2)网络通信的协议:http,ftp,tcp,udp,smpt
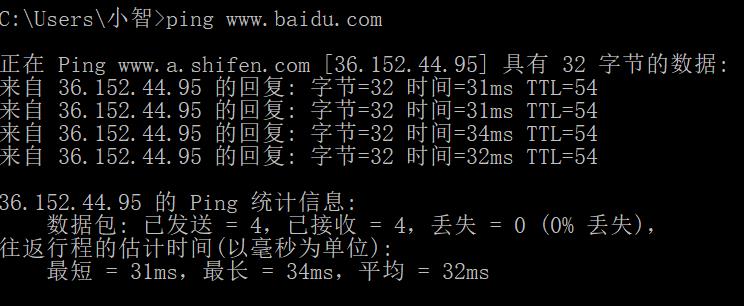
cmd打开命令窗口,输入 ping www.baidu.com
返回IP
3.IP地址
在API说明文档中找到InetAddress类,查看说明

IP地址是指互联网协议地址
IP地址可以唯一地定位到网络上的一台计算机;
127.0.0.1/localhost:本地回环地址
ip地址的分类
- ipv4/ipv6
- ipv4 :由4个字节组成 ;每个字节:0~255的数字组成;
- ipv6 :128位 ,8个无符号整数组成;
- 公网(互联网)以及私网(局域网)
- ABCD类地址
- 192.168…提供内部使用
域名 :由于IP地址记忆麻烦,所以使用域名服务器来管理全球域名.
练习:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//获取本机IP地址;方式1;
InetAddress byName0 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println("获取本机IP地址 "+byName0);
//方式2:
InetAddress byName1 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println("获取本机IP地址 "+byName1);
//方式3:
InetAddress byName3 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("获取本机IP地址 "+byName3);
System.out.println("===========================");
//获取百度ip地址
InetAddress byName4 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println("获取百度地址为 "+byName4);
//常用方法练习;
//getAddress:返回IP地址数组;
byte[] address = byName4.getAddress();
for( byte b:address){
System.out.print (b+"\\t");
}
System.out.println("\\n");
//getCanonicalHostName:返回规范的地址
String canonicalHostName = byName4.getCanonicalHostName();
System.out.println(canonicalHostName);
//getHostAddress:返回IP地址;
String hostAddress = byName4.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(hostAddress);
//getHostName:返回域名;或者电脑名;
String hostName = byName4.getHostName();
System.out.println(hostName);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
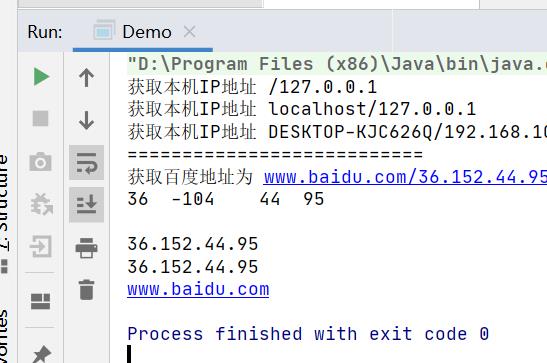
输出:
4.port:端口
端口表示计算机程序上的进程;
- 不同的进程有不同的端口号;
- 规定为0~65535
- 单个协议下,端口号不能冲突
- 端口分类
- 公用端口 0~1023 ;(例如
http: 80,https:443,ftp:21,Telent :23) - 程序端口 1024~49151 ;分配给用户或者程序(例如:
Tomcat服务器:8080😉mysql数据库:3306😉Oracle:1521😉 - 动态端口,私有端口;49152~65535
- 公用端口 0~1023 ;(例如
- 常用命令:
netstat -ano查询所有端口netstat -ano|findstr "端口号"查询指定端口tasklist|findstr "端口号"查看执行端口的进程
练习
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IP 套接字地址(IP 地址 + 端口号)
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8848);
//获取端口号:getPort()
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getPort());
}
}
5.通信协议
通信协议是指双方实体完成通信或服务所必须遵循的规则和约定。通过通信信道和设备互连起来的多个不同地理位置的数据通信系统,要使其能协同工作实现信息交换和资源共享,它们之间必须具有共同的语言。交流什么、怎样交流及何时交流,都必须遵循某种互相都能接受的规则。这个规则就是通信协议。
TCP:用户传输协议
UDP:用户数据报协议
TCP/IP:传输控制协议/网际协议;TCP/IP协议不仅仅指的是TCP 和IP两个协议,而是指一个由FTP、SMTP、TCP、UDP、IP等协议构成的协议簇
TCP:连接且稳定;传输完成才会释放连接,所以效率低;
三次握手;
客户端—>发出连接请求;
服务器—>连接吧;
客户端—>回复连接
四次挥手;
客户端:发出断开请求,可能带有数据;
服务器:发送确认信息;带有数据传递;
服务器:再次问问,确定还有数据吗?
客户端:回复断开
UDP:不连接,不稳定;直接就发过去了,也不确认是否能收到
6.TCP实现聊天
模拟客户端
//模拟客户端;
public class TCPClient01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket=null;
OutputStream out=null;
try {
//1.在客户端-获取服务器的地址;
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//2.设置端口;
int port=8848;
//3.创建socket连接;将IP和端口放入;
socket=new Socket(address,port);
//4.发送消息;使用IO流;
out=socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("服务器;你好".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源;
if(out!=null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
模拟服务端
//模拟服务端
public class TCPServer01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
Socket socket=null;
InputStream input=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream out=null;
try {
//1.创建服务器地址
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8848);
//服务器一直保持监听状态;等待客户端的消息;
while (true){
//2.等待客户端连接;
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.读取客户端消息;
input = socket.getInputStream();
//使用管道流;
out=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//设置管道大小;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
//拿到获取的客户端消息;判断是否还有;
while((len=input.read(bytes))!=-1){
out.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("输出客户端的消息=>"+out.toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源;
if(out!=null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(input!=null){
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
首先运行服务器,服务器会一直保持监听打开状态;
再运行客户端;客户端的消息发送到服务端;
7.TCP文件上传实现
模拟客户端
//模拟客户端
public class TCPClient02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream out=null;
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
InputStream in=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream outOver=null;
try {
//1.创建socket连接,注意传入ip和端口;
socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),8849);
//2.创建输出流;
out=socket.getOutputStream();
//3.创建文件流,将图片文件读取过来;
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("F:/idea使用/图片/picture01.gif"));
//4.写出文件;
//设置管道大小;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
out.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//4.通知服务器,客户端已经把文件发过去了;
socket.shutdownOutput();
//5.收到服务器的接收成功消息;然后关闭;
in = socket.getInputStream();
//6.输出收到的消息;
outOver=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes1=new byte[1024];
int len1;
while ((len1=in.read(bytes1))!=-1){
outOver.write(bytes1,0,len1);
}
System.out.println("服务器说==>"+outOver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.关闭资源;
if(outOver!=null){
try {
outOver.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(in!=null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fileInputStream!=null){
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(out!=null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
模拟服务器
//模拟服务器;
public class TCPServer02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
Socket socket=null;
InputStream in=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
OutputStream out=null;
try {
//1.创建服务器;设置端口;
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8849);
//2.监听客户端的连接;
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.获取客户端的文件;
in = socket.getInputStream();
//4.输出接收的文件;
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("F:/idea使用/图片/pc.gif"));
//设置管道大小;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//5.告诉客户端;文件已上传完成;
out = socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("文件上传完毕,你可以断开连接了".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6.关闭资源;
if(out!=null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fileOutputStream!=null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(in!=null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if(serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
先运行服务器,等待客户端连接;
运行客户端;文件上传;服务器这里接收到文件; 向客户端反馈消息已收到.
8.UDP消息发送
模拟客户端;
//模拟客户端;
public class UDPClient01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DatagramSocket socket=null;
try {
//1.创建socket;
socket = new DatagramSocket();
//2.创建数据包;
String message="客户端说:你好;服务器!";
//ip和端口设置;
InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
int port=8848;
//将要发送的消息转为数组;
byte[] bytes=message.getBytes();
Datagr以上是关于狂神说Java笔记--网络编程部分笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章