使用深度 Q 学习的 AI 驱动蛇游戏 源码分享
Posted JAVA炭烧
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用深度 Q 学习的 AI 驱动蛇游戏 源码分享相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

在构建基本的蛇游戏之后,现在我们将专注于如何将强化学习应用于它。
我们必须在这个项目中创建三个模块:
1.环境(我们刚刚构建的游戏)
2.模型(移动预测的强化模型)
3.代理(环境和模型之间的中介)

算法:
我们在棋盘上随机放置了蛇和食物。
- 使用 11 个值计算蛇的状态。如果有任何条件为真,则将该值设置为0,否则设置1。
如何定义 11 个状态
基于当前的 Head 位置代理将计算 11 个状态值,如上所述。
- 获得这些状态后,代理会将其传递给模型并执行下一步操作。
- 执行下一个状态后计算奖励。奖励定义如下:
吃食物:+10
游戏结束:-10
其他:0
更新 Q 值(稍后将讨论)并训练模型。
在分析了算法之后,现在我们必须建立思想来继续编码这个算法。
该模型:

神经网络模型
该模型是使用 Pytorch 设计的,但您也可以根据自己的舒适度使用 TensorFlow。
我们正在使用具有11 大小输入层和具有 256 个神经元和3 个神经 元 输出的 密集层的密集神经网络 。 您可以调整这些超参数以获得最佳结果。
模型如何工作?
- 游戏开始,Q值随机初始化。
- 系统获取当前状态 s。
- 它基于 s,随机或基于其神经网络执行一个动作。在训练的第一阶段,系统经常选择随机动作来最大化探索。后来,该系统越来越依赖其神经网络。
- 当 AI 选择并执行动作时,环境会给予奖励。然后,代理到达新状态并根据贝尔曼方程更新其 Q 值。

贝尔曼方程 - 此外,对于每一步,它存储原始状态、动作、执行该动作后达到的状态、获得的奖励以及游戏是否结束。这些数据随后被采样以训练神经网络。此操作称为重放记忆。
- 重复最后两个操作,直到满足某个条件(例如:游戏结束)。
该项目的核心是您将要训练的模型,因为蛇将采取的动作的正确性完全取决于您构建的模型的质量。所以我想用部分代码向你解释这一点。
第一部分

class Linear_QNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.linear2(x)
return x
def save(self, file_name='model_name.pth'):
model_folder_path = 'Path'
file_name = os.path.join(model_folder_path, file_name)
torch.save(self.state_dict(), file_name)
第二部分

class QTrainer:
def __init__(self,model,lr,gamma):
#Learning Rate for Optimizer
self.lr = lr
#Discount Rate
self.gamma = gamma
#Linear NN defined above.
self.model = model
#optimizer for weight and biases updation
self.optimer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr = self.lr)
#Mean Squared error loss function
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()
def train_step(self,state,action,reward,next_state,done):
state = torch.tensor(state,dtype=torch.float)
next_state = torch.tensor(next_state,dtype=torch.float)
action = torch.tensor(action,dtype=torch.long)
reward = torch.tensor(reward,dtype=torch.float)
#only one parameter to train, \\
Hence convert to tuple of shape(1, x)
if(len(state.shape) == 1):
#(1, x)
state = torch.unsqueeze(state,0)
next_state = torch.unsqueeze(next_state,0)
action = torch.unsqueeze(action,0)
reward = torch.unsqueeze(reward,0)
done = (done, )
# 1. Predicted Q value with current state
pred = self.model(state)
target = pred.clone()
for idx in range(len(done)):
Q_new = reward[idx]
if not done[idx]:
Q_new = reward[idx] +
self.gamma * torch.max(self.model(next_state[idx]))
target[idx][torch.argmax(action).item()] = Q_new
# 2. Q_new = reward + gamma * max(next_predicted Qvalue)
#pred.clone()
#preds[argmax(action)] = Q_new
self.optimer.zero_grad()
loss = self.criterion(target,pred)
loss.backward() # backward propogation of loss
self.optimer.step()
代理
从环境中获取蛇的当前状态。
def get_state(self, game):
head = game.snake[0]
point_l = Point(head.x - BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_r = Point(head.x + BLOCK_SIZE, head.y)
point_u = Point(head.x, head.y - BLOCK_SIZE)
point_d = Point(head.x, head.y + BLOCK_SIZE)
dir_l = game.direction == Direction.LEFT
dir_r = game.direction == Direction.RIGHT
dir_u = game.direction == Direction.UP
dir_d = game.direction == Direction.DOWN
state = [
# Danger Straight
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_r)),
# Danger right
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Danger Left
(dir_u and game.is_collision(point_r))or
(dir_d and game.is_collision(point_l))or
(dir_r and game.is_collision(point_u))or
(dir_l and game.is_collision(point_d)),
# Move Direction
dir_l,
dir_r,
dir_u,
dir_d,
# Food Location
game.food.x < game.head.x, # food is in left
game.food.x > game.head.x, # food is in right
game.food.y < game.head.y, # food is up
game.food.y > game.head.y # food is down
]
return np.array(state, dtype=int)
调用模型获取蛇的下一个状态
def get_action(self, state):
# 随机移动: tradeoff explotation / exploitation
self.epsilon = 80 - self.n_game
final_move = [0, 0, 0]
if(random.randint(0, 200) < self.epsilon):
move = random.randint(0, 2)
final_move[move] = 1
else:
state0 = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float).cuda()
prediction = self.model(state0).cuda() # prediction by model
move = torch.argmax(prediction).item()
final_move[move] = 1
return final_move

- 在环境中播放模型预测的步骤。
- 存储当前状态、执行的移动和奖励。
- 根据执行的移动和环境获得的奖励训练模型。(训练短记忆)
def train_short_memory(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.trainer.train_step(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
- 如果游戏因撞墙或身体而结束,则根据到目前为止执行的所有移动来训练模型并重置环境。(训练长记忆)。以 1000 的批量大小进行训练。
def train_long_memory(self):
if (len(self.memory) > BATCH_SIZE):
mini_sample = random.sample(self.memory, BATCH_SIZE)
else:
mini_sample = self.memory
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*mini_sample)
self.trainer.train_step(states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones)
训练模型需要大约 100 个时期才能获得更好的性能。查看我的训练进度。
输出:
- 要运行此游戏,请先在 anaconda 提示符或(任何平台)中创建一个环境。然后安装必要的模块,如 Pytorch(用于 DQ
学习模型)、Pygame(用于游戏的视觉效果)和其他基本模块。 - 然后在刚刚创建的环境中运行agent.py文件,开始训练,你会看到如下两个GUI,一个是训练进度,一个是AI驱动的snake game。
- 达到一定分数后可以退出游戏,刚刚训练好的模型会保存在models.py的save函数中定义的路径中。
将来,您只需更改 agent.py 文件中的代码即可使用此训练模型,如下所示:
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('PATH'))
注意: 注释掉所有训练函数调用。
培训进度

第一代版本
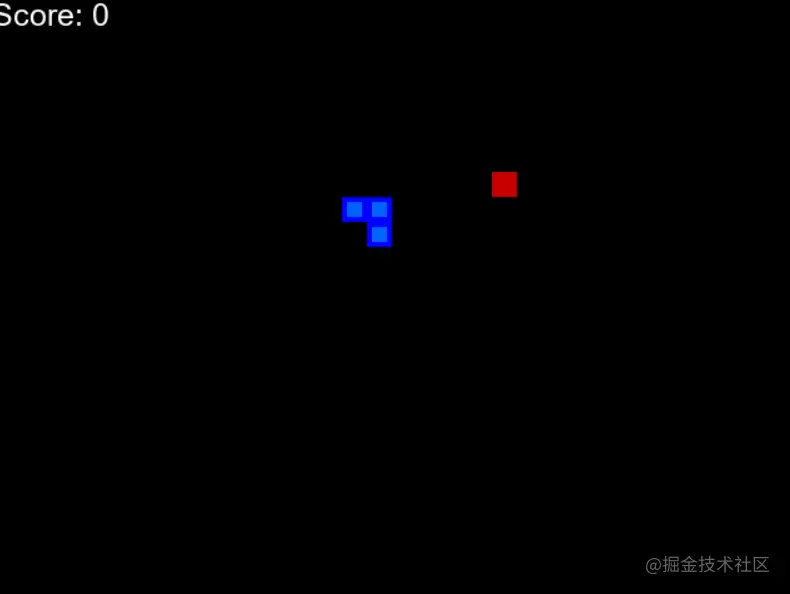
第二代版本

源代码: SnakeGameAI
应用:
该项目的目标是提出一个想法,即如何应用强化学习以及如何将其用于现实世界的应用程序,例如自动驾驶汽车(例如:AWS DeepRacer)、在装配线上训练机器人等等…
提示:
使用单独的环境并安装所有必需的模块。(可以使用anaconda环境)
为了训练模型,您可以使用 GPU 进行更快的训练。
总结
前段时间,在和群友聊天时,把今年他们见到的一些源码 书籍 学习视频整理了一番,于是有了以下合集,也一起分享给大家~ 有需要的小伙伴可以加我v:JYSH1W


有需要的小伙伴可以加我v:JYSH1W
以上是关于使用深度 Q 学习的 AI 驱动蛇游戏 源码分享的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章