「深度学习一遍过」必修18:基于pytorch的语义分割模型实现
Posted 小泽yyds
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了「深度学习一遍过」必修18:基于pytorch的语义分割模型实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本专栏用于记录关于深度学习的笔记,不光方便自己复习与查阅,同时也希望能给您解决一些关于深度学习的相关问题,并提供一些微不足道的人工神经网络模型设计思路。
专栏地址:「深度学习一遍过」必修篇
目录
1 自定义5层普通卷积
模型结构
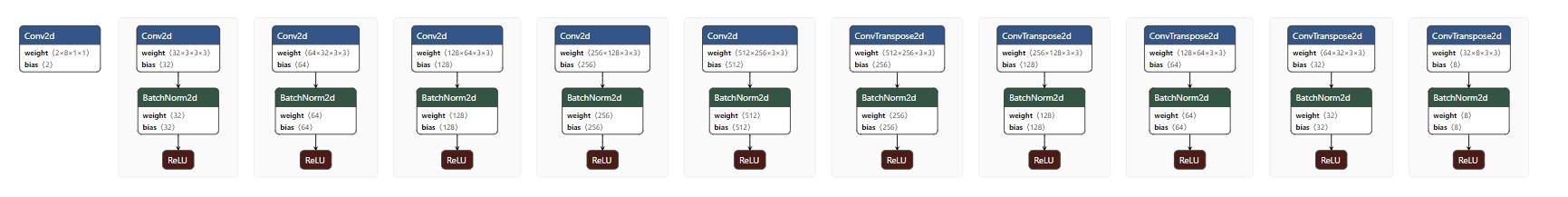
pytorch代码
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class simpleNet5(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(simpleNet5, self).__init__()
# 卷积层
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(True), )
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(True), )
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(True), )
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(True), )
self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(True), )
# 反卷积层
self.deconc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 3, 2, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.deconc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 3, 2, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.deconc3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 3, 2, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.deconc4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(64, 32, 3, 2, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.deconc5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(32, 8, 3, 2, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(8),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.classifier = nn.Conv2d(8, 2, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = self.deconc1(x)
x = self.deconc2(x)
x = self.deconc3(x)
x = self.deconc4(x)
x = self.deconc5(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
模型结构

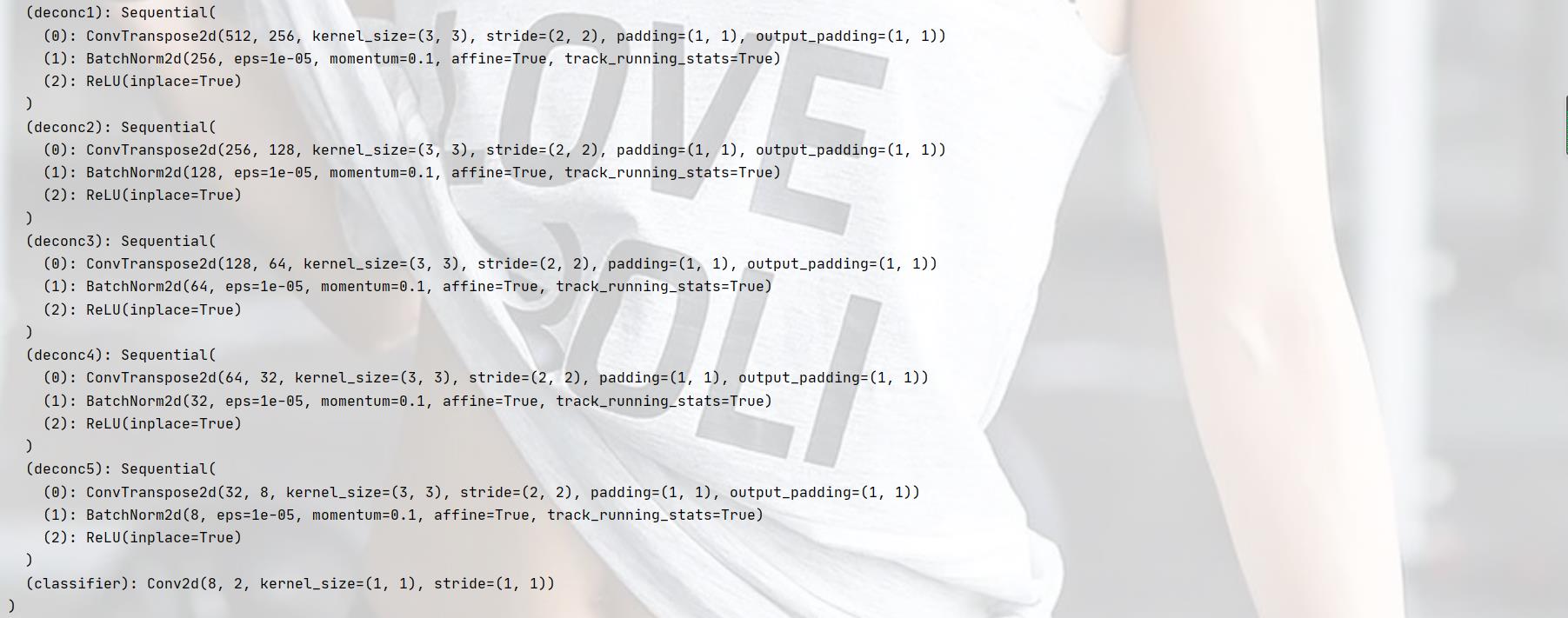
训练 acc 及 loss
模型分割测试

2 实现Unet模型结构
模型结构
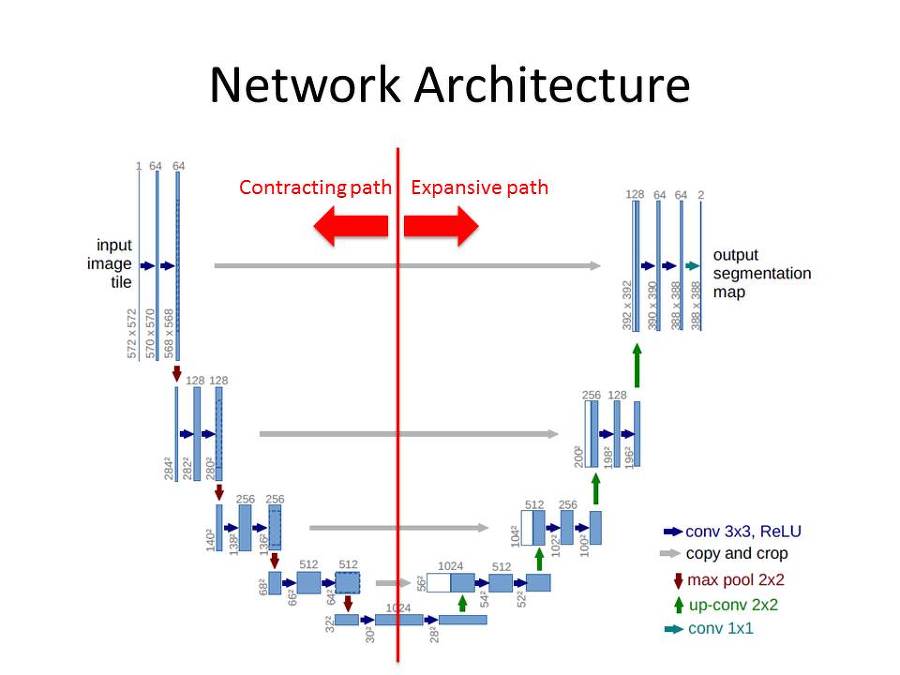
pytorch代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def double_conv(in_c, out_c):
conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_c, out_c, kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
return conv
def crop_img(img1, img2):
img1_size = img1.size()[2]
img2_size = img2.size()[2]
b = (img1_size - img2_size) // 2
img1 = img1[:, :, b:img1_size - b, b:img1_size - b]
return img1
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.max_pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.dowm_conv_1 = double_conv(3, 64)
self.dowm_conv_2 = double_conv(64, 128)
self.dowm_conv_3 = double_conv(128, 256)
self.dowm_conv_4 = double_conv(256, 512)
self.dowm_conv_5 = double_conv(512, 1024)
self.up_trans_1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1024, 512, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_1 = double_conv(1024, 512)
self.up_trans_2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_2 = double_conv(512, 256)
self.up_trans_3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_3 = double_conv(256, 128)
self.up_trans_4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_4 = double_conv(128, 64)
self.out = nn.Conv2d(64, 2, 3)
def forward(self, x):
# 下采样
x1 = self.dowm_conv_1(x)
x2 = self.max_pool_2(x1)
x3 = self.dowm_conv_2(x2)
x4 = self.max_pool_2(x3)
x5 = self.dowm_conv_3(x4)
x6 = self.max_pool_2(x5)
x7 = self.dowm_conv_4(x6)
x8 = self.max_pool_2(x7)
x9 = self.dowm_conv_5(x8)
# 上采样
x = self.up_trans_1(x9)
y = crop_img(x7, x)
x = self.up_conv_1(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_2(x)
y = crop_img(x5, x)
x = self.up_conv_2(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_3(x)
y = crop_img(x3, x)
x = self.up_conv_3(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_4(x)
y = crop_img(x1, x)
x = self.up_conv_4(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.out(x)
return x
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224))
model = UNet()
print(model(x))
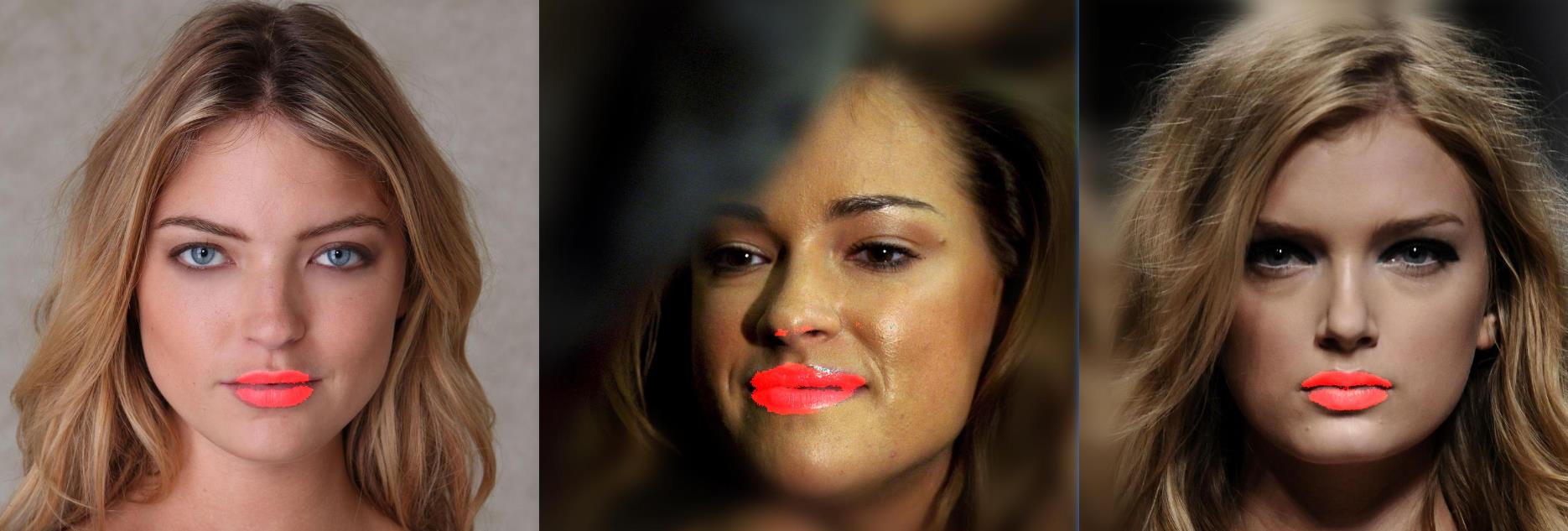
模型结构


模型分割测试

3 在Unet网络模型基础上实现膨胀卷积
模型结构
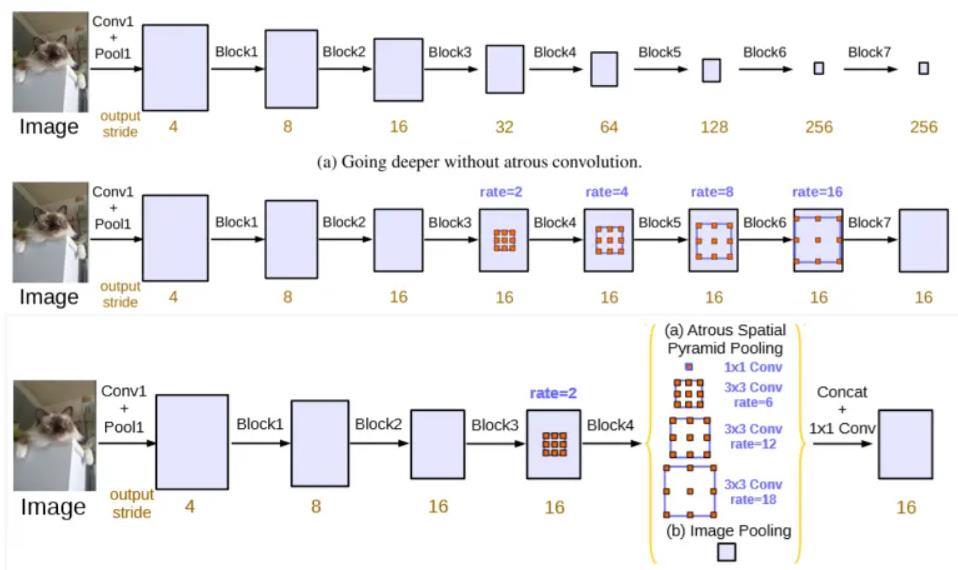
pytorch代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def double_conv(in_c, out_c):
conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_c, out_c, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
return conv
def crop_img(img1, img2):
img1_size = img1.size()[2]
img2_size = img2.size()[2]
b = (img1_size - img2_size) // 2
img1 = img1[:, :, b:img1_size - b, b:img1_size - b]
return img1
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.max_pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.dowm_conv_1 = double_conv(3, 64)
self.dowm_conv_2 = double_conv(64, 128)
self.dowm_conv_3 = double_conv(128, 256)
self.dowm_conv_4 = double_conv(256, 512)
self.dowm_conv_5 = double_conv(512, 1024)
self.up_trans_1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1024, 512, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_1 = double_conv(1024, 512)
self.up_trans_2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_2 = double_conv(512, 256)
self.up_trans_3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_3 = double_conv(256, 128)
self.up_trans_4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 2, 2)
self.up_conv_4 = double_conv(128, 64)
self.pengzhang1 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=2, dilation=2)
self.pengzhang2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=4, dilation=4)
self.out = nn.Conv2d(64, 2, 3, padding=8, dilation=8)
def forward(self, x):
# 下采样
x1 = self.dowm_conv_1(x)
x2 = self.max_pool_2(x1)
x3 = self.dowm_conv_2(x2)
x4 = self.max_pool_2(x3)
x5 = self.dowm_conv_3(x4)
x6 = self.max_pool_2(x5)
x7 = self.dowm_conv_4(x6)
x8 = self.max_pool_2(x7)
x9 = self.dowm_conv_5(x8)
# 上采样
x = self.up_trans_1(x9)
y = crop_img(x7, x)
x = self.up_conv_1(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_2(x)
y = crop_img(x5, x)
x = self.up_conv_2(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_3(x)
y = crop_img(x3, x)
x = self.up_conv_3(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.up_trans_4(x)
y = crop_img(x1, x)
x = self.up_conv_4(torch.cat([x, y], 1))
x = self.pengzhang1(x)
x = self.pengzhang2(x)
x = self.out(x)
return x
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224))
model = UNet()
print(model(x))
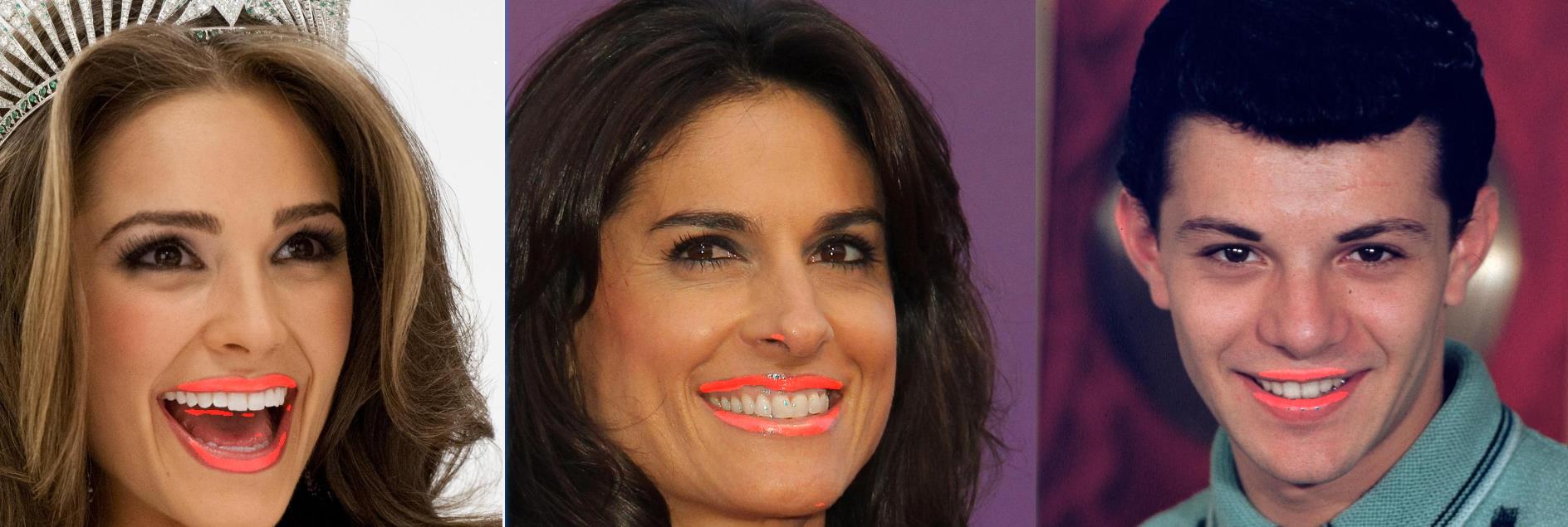
模型结构


模型分割测试

欢迎大家交流评论,一起学习
希望本文能帮助您解决您在这方面遇到的问题
感谢阅读
END
以上是关于「深度学习一遍过」必修18:基于pytorch的语义分割模型实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章