图漾深度相机开发-PCL点云实时显示
Posted Ketone Olefine
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图漾深度相机开发-PCL点云实时显示相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 相机型号:图漾科技 FS820 深度相机
【参数信息】【深度相机开发说明文档】【SDK下载】 - 编译环境:Ubuntu 18.04 / C++ / VS code
- 安装库:OpenCV + PCL
- 图漾深度相机初步使用流程见博客,在能简单应用相机示例程序的基础上,对相机进行开发,以实现三维点云处理,本文实现的功能是显示实时点云图:

1. 从示例程序 SimpleView_FetchFrame 开始
程序功能
SimpleView_FetchFrame 是深度相机获取图像数据并在数据获取线程中进行 OpenCV 渲染的示例程序,以此为例说明图像获取流程【图像获取的完整流程】
运行程序,生成 color彩色图像、depth深度图像、leftIR、rightIR 窗口

程序解读
打开 sample/SimpleView_FetchFrame/main.cpp,解读代码:
从主函数开始阅读,可以看到多个 LOGD() 函数,这些函数实现的是打印功能,相当于程序中的注释(如 LOGD("Init lib"),说明下一段代码的功能是初始化 API,初始化设备对象等数据结构)
对于开发者而言,我们需要关注的是如何获取相机的数据,以进行后续的处理,也就是下图中的 Loop 循环部分,这一循环的作用是不断获取相机的帧数据,并对数据进行处理(本例中的处理效果即为生成 color彩色图像、depth深度图像、leftIR、rightIR 窗口)
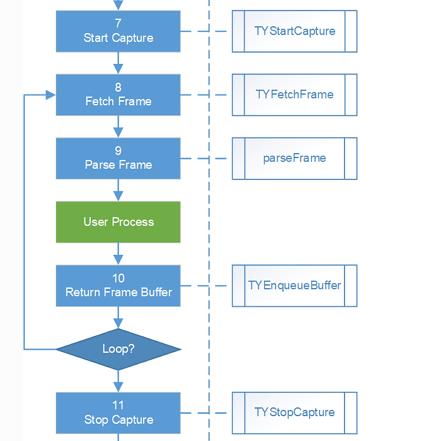
因此我们继续往下阅读代码,读到 LOGD("While loop to fetch frame") 语句,下面一段程序的功能就是获取相机帧循环,贴出代码进行解读:
LOGD("While loop to fetch frame");
bool exit_main = false;
TY_FRAME_DATA frame;
int index = 0;
while(!exit_main) {
int err = TYFetchFrame(hDevice, &frame, -1);
if( err == TY_STATUS_OK ) {
LOGD("Get frame %d", ++index);
int fps = get_fps();
if (fps > 0){
LOGI("fps: %d", fps);
}
cv::Mat depth, irl, irr, color;
parseFrame(frame, &depth, &irl, &irr, &color, hColorIspHandle);
if(!depth.empty()){
depthViewer.show(depth);
}
if(!irl.empty()){ cv::imshow("LeftIR", irl); }
if(!irr.empty()){ cv::imshow("RightIR", irr); }
if(!color.empty()){ cv::imshow("Color", color); }
int key = cv::waitKey(1);
switch(key & 0xff) {
case 0xff:
break;
case 'q':
exit_main = true;
break;
default:
LOGD("Unmapped key %d", key);
}
TYISPUpdateDevice(hColorIspHandle);
LOGD("Re-enqueue buffer(%p, %d)"
, frame.userBuffer, frame.bufferSize);
ASSERT_OK( TYEnqueueBuffer(hDevice, frame.userBuffer, frame.bufferSize) );
}
}
首先定义了 bool 型变量exit_main:作为循环的标志位,while(!exit_main) 表示当 exit_main = 1 时循环结束
- Fetch Frame
这一段代码的功能是获取相机的帧信息,即 frame:
int err = TYFetchFrame(hDevice, &frame, -1);
if( err == TY_STATUS_OK ) {
LOGD("Get frame %d", ++index);
int fps = get_fps();
if (fps > 0){
LOGI("fps: %d", fps);
}
这段代码的核心部分为:TYFetchFrame(hDevice, &frame, -1),函数功能为 Fetch one frame,即通过输入 hDevice 这一参数,获取一帧相机的信息到 frame 中,如果成功获取帧信息,则返回值为 TY_STATUS_OK
当 err == TY_STATUS_OK (成功获取帧信息)时,会打印信息:Get frame + (index 的值),表示当前获取的是第几帧,index 在每次循环中加1,如下图所示:

- Parse Frame
这一段代码的功能是解析获取的帧信息:
cv::Mat depth, irl, irr, color;
parseFrame(frame, &depth, &irl, &irr, &color, hColorIspHandle);
首先定义 cv::Mat 类型的深度图 depth,彩色图 color,左红外图像 irl,右红外图像 irr
接着通过 parseFrame() 函数解析 frame,分别生成深度图、左右红外图和彩色图
- User Process
在解析帧后,我们成功得到了相机的深度图 depth 和彩色图 color 等,用户就可以利用获取的数据进行处理和开发了,示例程序中实现的是简单的图像显示功能,即分别可视化深度图、左右红外图和彩色图:
if(!depth.empty()){
depthViewer.show(depth);
}
if(!irl.empty()){ cv::imshow("LeftIR", irl); }
if(!irr.empty()){ cv::imshow("RightIR", irr); }
if(!color.empty()){ cv::imshow("Color", color); }
int key = cv::waitKey(1);
switch(key & 0xff) {
case 0xff:
break;
case 'q':
exit_main = true;
break;
default:
LOGD("Unmapped key %d", key);
}
如果在 openCV 的图窗中,键盘按下 q 键,则exit_main = true,整个帧循环会结束
- Return Frame Buffer
TYISPUpdateDevice(hColorIspHandle);
LOGD("Re-enqueue buffer(%p, %d)" , frame.userBuffer, frame.bufferSize);
ASSERT_OK( TYEnqueueBuffer(hDevice, frame.userBuffer, frame.bufferSize) );
更新设备状态,将 frame buffer 推入帧缓冲队列
2. 创建自己的点云处理程序
文件结构
最简单的方式是直接在 sample 文件夹创建一个新的文件夹例如 point3D,并在该文件夹中创建 main.cpp ,接着在 CMakeLists.txt 中修改以下部分即可:
set(ALL_SAMPLES
point3D # 加上自己命名的文件夹
DumpAllFeatures
ListDevices
...
在 sample/build 目录下打开终端,重新编译运行即可:
cmake ..
make
cd bin
sudo ./point3D
创建点云
根据对示例程序的分析可知,通过 parseFrame(frame, &depth, &irl, &irr, &color, hColorIspHandle) 语句可以获取相机的深度图和彩色图,处理深度图得到位置信息
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
(x, y, z)
(x,y,z) ,处理彩色图得到颜色信息
(
r
,
g
,
b
)
(r, g, b)
(r,g,b) ,最终生成包含颜色信息的点云图
使用 Point CLoud Library 处理点云,首先需要安装 PCL 库:
- 安装 PCL 库
sudo apt install libpcl-dev
- 修改 CMakeLists.txt 添加 PCL 库
添加如下语句:
# ========================================
# === PCL
# ========================================
find_package(PCL 1.8 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
修改倒数第五行:
target_link_libraries(${sample} sample_common ${ABSOLUTE_TARGET_LIB} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${CLOUD_VIEWER} ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
- Map depth image to 3D points
根据深度相机的标定参数,将深度图映射为三维点云:
(1) 首先需要获取深度相机的标定参数,根据官方文档可知,利用 TYGetStruct() 函数即可:
TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO depth_calib;
TYGetStruct(hDevice, TY_COMPONENT_DEPTH_CAM
, TY_STRUCT_CAM_CALIB_DATA, &depth_calib,sizeof(depth_calib)); // 提取深度相机的标定数据
(2) 接着将深度图转换为三维数据:
std::vector<TY_VECT_3F> p3d; // p3d 用于存储三维数据
TYMapDepthImageToPoint3d(&depth_calib, depth.cols, depth.rows
, (uint16_t*)depth.data, &p3d[0]); // 输入深度数据和标定数据,输出三维数据
p3d[i].x 表示第 i 个点的 x值;p3d[i].y 表示第 i 个点的 y值;p3d[i].z 表示第 i 个点的 z值
- Map original RGB image to depth coordinate RGB image
根据彩色相机的标定参数,将彩色图与深度图对齐:
(1) 首先需要获取彩色相机的标定参数,根据官方文档可知,利用 TYGetStruct() 函数即可:
TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO color_calib;
TYGetStruct(hDevice, TY_COMPONENT_RGB_CAM, TY_STRUCT_CAM_CALIB_DATA
, &color_calib, sizeof(color_calib)); // 提取彩色相机的标定数据
(2) 彩色图与深度图对齐:
首先定义函数doRgbRegister(),实现对齐功能:
// 定义一个函数 doRgbRegister(),实现对齐功能
static void doRgbRegister(const TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO& depth_calib
, const TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO& color_calib
, const cv::Mat& depth
, const cv::Mat& color
, cv::Mat& out
)
{
// do rgb undistortion
TY_IMAGE_DATA src;
src.width = color.cols;
src.height = color.rows;
src.size = color.size().area() * 3;
src.pixelFormat = TY_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB;
src.buffer = color.data;
cv::Mat undistort_color = cv::Mat(color.size(), CV_8UC3);
TY_IMAGE_DATA dst;
dst.width = color.cols;
dst.height = color.rows;
dst.size = undistort_color.size().area() * 3;
dst.buffer = undistort_color.data;
dst.pixelFormat = TY_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB;
TYUndistortImage(&color_calib, &src, NULL, &dst);
// do register
out.create(depth.size(), CV_8UC3);
TYMapRGBImageToDepthCoordinate(
&depth_calib,
depth.cols, depth.rows, depth.ptr<uint16_t>(),
&color_calib,
undistort_color.cols, undistort_color.rows, undistort_color.ptr<uint8_t>(),
out.ptr<uint8_t>());
}
在主函数中调用函数doRgbRegister():
cv::Mat color_data_mat; // color_data_mat 为对齐后的彩色图
if (!color.empty())
{
bool hasColorCalib;
TYHasFeature(hDevice, TY_COMPONENT_RGB_CAM, TY_STRUCT_CAM_CALIB_DATA, &hasColorCalib); // 查询有无彩色相机标定参数这一属性
if (hasColorCalib)
{
doRgbRegister(depth_calib, color_calib, depth, color, color_data_mat); // 输入深度相机标定数据、彩色相机标定数据、深度图和彩色图,输出对齐后的彩色图
cv::cvtColor(color_data_mat, color_data_mat, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB); // BGR 格式转换为 RGB 格式
}
}
- 生成 PointXYZRGB 类型点云(核心代码)
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> cloud; // 生成的点云 cloud
pcl::PointXYZRGB point;
for (int m = 0; m < depth.rows; m++)
{
for (int n=0; n < depth.cols; n++)
{
point.x = p3d[(m*(depth.cols)+n)].x;
point.y = p3d[(m*(depth.cols)+n)].y;
point.z = p3d[(m*(depth.cols)+n)].z;
point.r = color_data_mat.at<cv::Vec3b>(m, n)[0];
point.g = color_data_mat.at<cv::Vec3b>(m, n)[1];
point.b =color_data_mat.at<cv::Vec3b>(m, n)[2];
cloud.points.push_back(point); // 构造xyzrgb类型点云
}
}
cloud.width = (uint32_t)cloud.points.size();
cloud.height = 1;
- 点云可视化
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer1(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr basic_cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
basic_cloud_ptr = cloud.makeShared(); // 转换为指针格式 basic_cloud_ptr
basic_cloud_ptr->is_dense = false; // 自己创建的点云,默认为dense,需要修改属性,否则removenanfrompointcloud函数无效
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
std::vector<int> mapping;
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*basic_cloud_ptr, *cloud_ptr, mapping); // 移除无效点
viewer1->removeAllPointClouds(); // 移除当前所有点云
viewer1->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> (cloud_ptr, "initial");
viewer1->updatePointCloud(cloud_ptr, "initial");
viewer1->spinOnce(100);
点云图实时显示完整代码
#include <TYApi.h>
#include "TYImageProc.h"
#include "../common.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter.h>
#include <pcl/common/impl/io.hpp>
static void doRgbRegister(const TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO& depth_calib, const TY_CAMERA_CALIB_INFO& color_calib, const cv::Mat& depth, const cv::Mat& color, cv::Mat& out)
{
// do rgb undistortion
TY_IMAGE_DATA src;
src.width = color.cols;
src.height = color.rows;
src.size = color.size().area() * 3;
src.pixelFormat = TY_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB;
src.buffer = color.data;
cv::Mat undistort_color = cv::Mat(color.size(), CV_8UC3);
TY_IMAGE_DATA dst;
dst.width = color.cols;
dst.height = color.rows;
dst.size = undistort_color.size().area() * 3;
dst.buffer = undistort_color.data;
dst.pixelFormat = TY_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB;
ASSERT_OK(TYUndistortImage(&color_calib, &src, NULL, &dst));
// do register
out.create(depth.size(), CV_8UC3);
ASSERT_OK(
TYMapRGBImageToDepthCoordinate(
&depth_calib,
depth.cols, depth.rows, depth.ptr<uint16_t>(),
&color_calib,
undistort_color.cols, undistort_color.rows, undistort_color.ptr<uint8_t>(),
out.ptr<uint8_t>()));
}
void eventCallback(TY_EVENT_INFO *event_info, void *userdata)
{
if (event_info->eventId == TY_EVENT_DEVICE_OFFLINE) {
LOGD("=== Event Callback: Device Offline!");
// Note:
// Please set TY_BOOL_KEEP_ALIVE_ONOFF feature to false if you need to debug with breakpoint!
}
else if (event_info->eventId == TY_EVENT_LICENSE_ERROR) {
LOGD("=== Event Callback: License Error!");
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string ID, IP;
TY_INTERFACE_HANDLE hIface = NULL;
TY_IS以上是关于图漾深度相机开发-PCL点云实时显示的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章