Javascript学习笔记
Posted 阿远ay
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Javascript学习笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、构造函数和原型
1、概述

2、构造函数
1、利用构造函数创建对象


<script>
// 1. 利用 new Object() 创建对象
var obj1 = new Object();
// 2. 利用 对象字面量创建对象
var obj2 = {};
// 3. 利用构造函数创建对象
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
var zxy = new Star('张学友', 19);
console.log(ldh);
ldh.sing();
zxy.sing();
</script>
2、静态成员和实例成员

<script>
// 构造函数中的属性和方法我们称为成员, 成员可以添加
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
// 1.实例成员就是构造函数内部通过this添加的成员 uname age sing 就是实例成员
// 实例成员只能通过实例化的对象来访问
console.log(ldh.uname);
ldh.sing();
// console.log(Star.uname); // 不可以通过构造函数来访问实例成员
// 2. 静态成员 在构造函数本身上添加的成员 sex 就是静态成员
Star.sex = '男';
// 静态成员只能通过构造函数来访问
console.log(Star.sex);
console.log(ldh.sex); // 不能通过对象来访问
</script>
3、构造函数的问题

4、构造函数原型prototype

<script>
// 1. 构造函数的问题.
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
// this.sing = function() {
// console.log('我会唱歌');
// }
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
var zxy = new Star('张学友', 19);
console.log(ldh.sing === zxy.sing);
// console.dir(Star);
ldh.sing();
zxy.sing();
// 2. 一般情况下,我们的公共属性定义到构造函数里面, 公共的方法我们放到原型对象身上
</script>
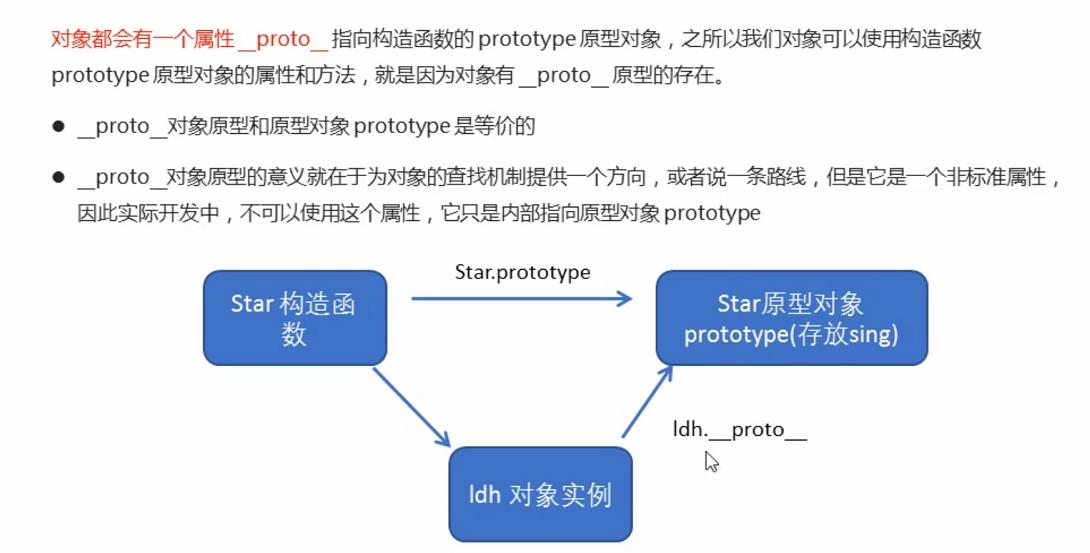
5、对象原型__proto__
<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
var zxy = new Star('张学友', 19);
ldh.sing();
console.log(ldh); // 对象身上系统自己添加一个 __proto__ 指向我们构造函数的原型对象 prototype
console.log(ldh.__proto__ === Star.prototype);
// 方法的查找规则: 首先先看ldh 对象身上是否有 sing 方法,如果有就执行这个对象上的sing
// 如果么有sing 这个方法,因为有__proto__ 的存在,就去构造函数原型对象prototype身上去查找sing这个方法
</script>
6、constructor构造函数

<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
// 很多情况下,我们需要手动的利用constructor 这个属性指回 原来的构造函数
// Star.prototype.sing = function() {
// console.log('我会唱歌');
// };
// Star.prototype.movie = function() {
// console.log('我会演电影');
// }
Star.prototype = {
// 如果我们修改了原来的原型对象,给原型对象赋值的是一个对象,则必须手动的利用constructor指回原来的构造函数
constructor: Star,
sing: function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
},
movie: function() {
console.log('我会演电影');
}
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
var zxy = new Star('张学友', 19);
console.log(Star.prototype);
console.log(ldh.__proto__);
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor);
console.log(ldh.__proto__.constructor);
</script>
7、构造函数、实例、原型对象三者之间的关系

8、原型链

<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
// 1. 只要是对象就有__proto__ 原型, 指向原型对象
console.log(Star.prototype);
console.log(Star.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype);
// 2.我们Star原型对象里面的__proto__原型指向的是 Object.prototype
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__);
// 3. 我们Object.prototype原型对象里面的__proto__原型 指向为 null
</script>
9、原型链成员查找规则

<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
}
Star.prototype.sex = '女';
// Object.prototype.sex = '男';
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
ldh.sex = '男';
console.log(ldh.sex);
console.log(Object.prototype);
console.log(ldh);
console.log(Star.prototype);
console.log(ldh.toString());
</script>
10、原型对象this指向

<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
var that;
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log('我会唱歌');
that = this;
}
var ldh = new Star('刘德华', 18);
// 1. 在构造函数中,里面this指向的是对象实例 ldh
ldh.sing();
console.log(that === ldh);
// 2.原型对象函数里面的this 指向的是 实例对象 ldh
</script>
11、扩展内置对象

<script>
// 原型对象的应用 扩展内置对象方法
Array.prototype.sum = function() {
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
sum += this[i];
}
return sum;
};
// Array.prototype = {
// sum: function() {
// var sum = 0;
// for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
// sum += this[i];
// }
// return sum;
// }
// }
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.sum());
console.log(Array.prototype);
var arr1 = new Array(11, 22, 33);
console.log(arr1.sum());
</script>
二、继承
1、call()

<script>
// call 方法
function fn(x, y) {
console.log('我想喝手磨咖啡');
console.log(this);
console.log(x + y);
}
var o = {
name: 'andy'
};
// fn();
// 1. call() 可以调用函数
// fn.call();
// 2. call() 可以改变这个函数的this指向 此时这个函数的this 就指向了o这个对象
fn.call(o, 1, 2);
</script>
2、借用构造函数继承父类型属性
<script>
// 借用父构造函数继承属性
// 1. 父构造函数
function Father(uname, age) {
// this 指向父构造函数的对象实例
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
// 2 .子构造函数
function Son(uname, age, score) {
// this 指向子构造函数的对象实例
Father.call(this, uname, age);
this.score = score;
}
var son = new Son('刘德华', 18, 100);
console.log(son);
</script>
3、借用原型对象继承父类型方法

<script>
// 借用父构造函数继承属性
// 1. 父构造函数
function Father(uname, age) {
// this 指向父构造函数的对象实例
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Father.prototype.money = function() {
console.log(100000);
};
// 2 .子构造函数
function Son(uname, age, score) {
// this 指向子构造函数的对象实例
Father.call(this, uname, age);
this.score = score;
}
// Son.prototype = Father.prototype; 这样直接赋值会有问题,如果修改了子原型对象,父原型对象也会跟着一起变化
Son.prototype = new Father();
// 如果利用对象的形式修改了原型对象,别忘了利用constructor 指回原来的构造函数
Son.prototype.constructor = Son;
// 这个是子构造函数专门的方法
Son.prototype.exam = function() {
console.log('孩子要考试');
}
var son = new Son('刘德华', 18, 100);
console.log(son);
console.log(Father.prototype);
console.log(Son.prototype.constructor);
</script>
三、ES5中的新增方法

1、数组方法

①forEach()

<script>
// forEach 迭代(遍历) 数组
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
var sum = 0;
arr.forEach(function(value, index, array) {
console.log('每个数组元素' + value);
console.log('每个数组元素的索引号' + index);
console.log('数组本身' + array);
sum += value;
})
console.log(sum);
</script>
②filter()
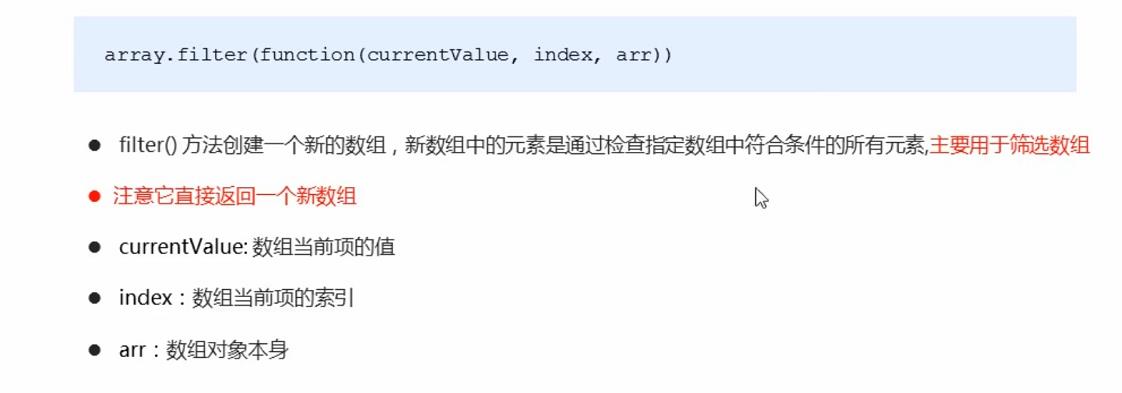
<script>
// filter 筛选数组
var arr = [12, 66, 4, 88, 3, 7];
var newArr = arr.filter(function(value, index) {
// return value >= 20;
return value % 2 === 0;
});
console.log(newArr);
</script>
③some()

<script>
// some 查找数组中是否有满足条件的元素
// var arr = [10, 30, 4];
// var flag = arr.some(function(value) {
// // return value >= 20;
// return value < 3;
// });
// console.log(flag);
var arr1 = ['red', 'pink', 'blue'];
var flag1 = arr1.some(function(value) {
return value == 'pink';
});
console.log(flag1);
// 1. filter 也是查找满足条件的元素 返回的是一个数组 而且是把所有满足条件的元素返回回来
// 2. some 也是查找满足条件的元素是否存在 返回的是一个布尔值 如果查找到第一个满足条件的元素就终止循环
</script>
4、forEach和some区别
<script>
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink'