网络编程——Java
Posted yangbocsu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了网络编程——Java相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
网络编程
1、什么是计算机网络

什么是计算及网络?
计算机网络系统就是利用通信设备和线路将地理位置不同、功能独立的多个计算机系统互联起来,以功能完善的网络软件实现网络中资源共享和信息传递的系统。
网络编程的目的
数据交换----通信


2、网络通信的两个要素


小结:
1.网络编程中有两个主要的问题
- 如何准确的定位到网络.上的一台或者多台主机
- 找到主机之后如何进行通信
2.网络编程中的要素
- IP和端口号IP.
- 网络通信协议udp, tcp
3.万物皆对象
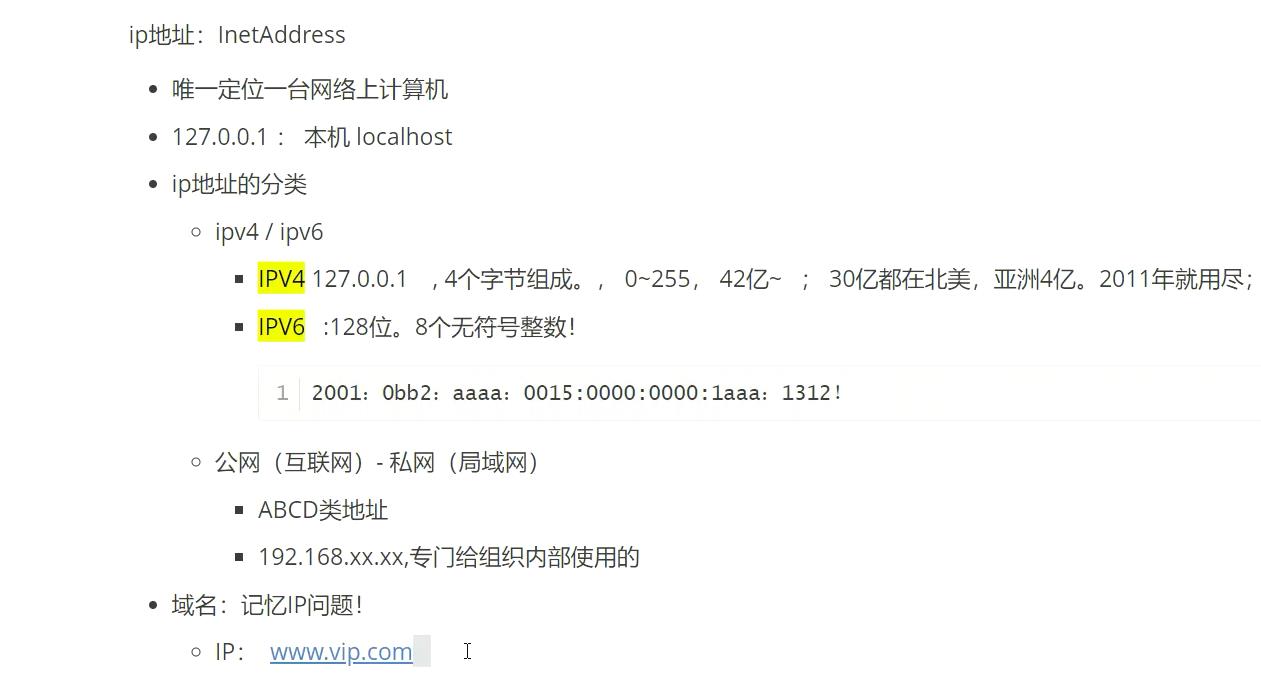
3、IP地址
java.net.InetAddress
package com.yangbocsu.lesson1;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//测试IP
public class TestInetAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//查询本机地址
InetAddress inetAddress1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println("inetAddress1:"+inetAddress1);
InetAddress inetAddress2 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println("inetAddress2:"+inetAddress2);
InetAddress inetAddress3 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("inetAddress3:"+inetAddress3);
//查询网站Ip地址
InetAddress inetAddress4 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println("inetAddress1:"+inetAddress4);
//常用方法
System.out.println(inetAddress4.getAddress());
System.out.println(inetAddress4.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(inetAddress4.getCanonicalHostName());
System.out.println(inetAddress4.getHostName());
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4、端口Port


package com.yangbocsu.lesson1;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class TestInetSocketAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8080);
System.out.println(socketAddress);
InetSocketAddress socketAddress2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8080);
System.out.println(socketAddress2);
System.out.println(socketAddress.getAddress());
System.out.println(socketAddress.getHostName());
System.out.println(socketAddress.getPort());
}
}
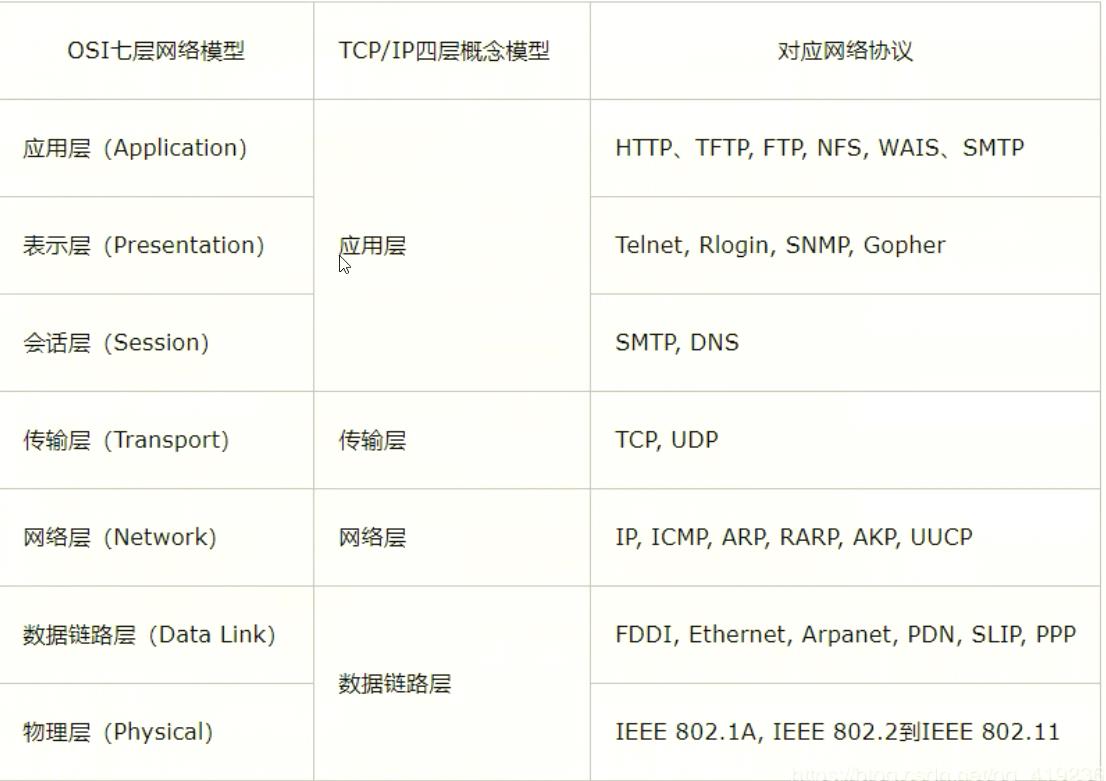
5、通信协议
协议:约定,就好比我们现在说的普通话。
网络通信协议: 速率、传输码率、代码结构、传输控制。。。。
**问题:**非常复杂?
大事化小:分层!
TCP/IP协议簇
重要:
- TCP(Transmission Control Protocol,传输控制协议)
- UDP(User Data Protocol,用户数据报协议)
出名的协议:
- TCP:
- IP : 网络互连协议


6、TCP实现聊天

服务端 - 客户端
服务端
package com.yangbocsu.lesson2;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
//服务端
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is =null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//1. 我得要有一个地址 localhost:9999
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
//2.等待客户端连接过来
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.读取客户端的消息
is = socket.getInputStream();
//管道流
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (( (len = is.read(buffer))!= -1))
{
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//关闭管道流
if (baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is!=null)
{
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null)
{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket!=null)
{
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
客户端
package com.yangbocsu.lesson2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//客户端
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os =null;
try {
//1. 要知道服务器的地址 端口号
InetAddress ServerIP= InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port= 9999;
//2.创建一个socket 连接
socket = new Socket(ServerIP, port);
//3.发送消息 IO流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("hello world!".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if (os!=null)
{
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null)
{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
服务端一直监听:
package com.yangbocsu.lesson2;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
//服务端
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is =null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//1. 我得要有一个地址 localhost:9999
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
while (true) //服务端一直监听
{
//2.等待客户端连接过来
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.读取客户端的消息
is = socket.getInputStream();
//管道流
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (( (len = is.read(buffer))!= -1))
{
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//关闭管道流
if (baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is!=null)
{
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null)
{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket!=null)
{
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
7、TCP文件上传实现
服务端
package com.yangbocsu.lesson2;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TcpServerDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1.创建服务
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
//2.监听客户端的链接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//阻塞试 监听,会一直监听到客户端连接
//3.获取输入流
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//4.文件输出
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("receive1.png"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer))!=-1)
{
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//通知客户端我接收完毕了
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("Over! Over!".getBytes());
//5.关闭资源
os.close();
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
客户端
package com.yangbocsu.lesson2;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Proxy;
import java.net.Socket;
import static java.net.InetAddress.*;
public class TcpClientDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建一个socket 连接
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9000);
//2.创建一个输出流
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.读取文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("img.png"));
//4、写出文件
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) !=-1)
{
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//通知服务器,我已经发送结束了
socket.shutdownOutput();
//确定服务器接收完毕,才能断开连接
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//String byte[]
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte以上是关于网络编程——Java的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章