JAVA---多线程篇
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA---多线程篇相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
进程与线程
进程
- 当一个程序被运行,就开启了一个进程, 比如启动了qq,word
- 程序由指令和数据组成,指令要运行,数据要加载,指令被cpu加载运行,数据被加载到内存,指令运行时可由cpu调度硬盘、网络等设备
线程
- 一个进程内可分为多个线程
- 一个线程就是一个指令流,cpu调度的最小单位,由cpu一条一条执行指令
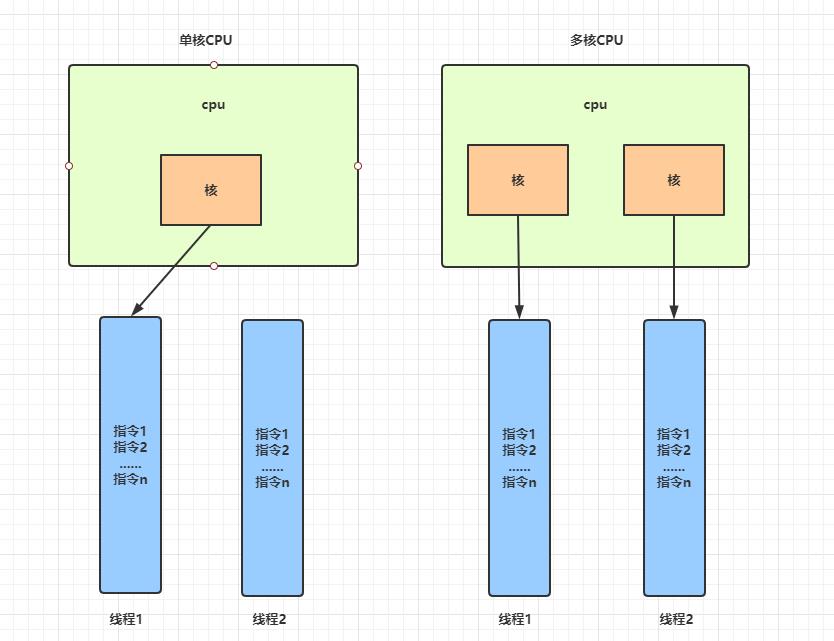
并行与并发
并发:单核cpu运行多线程时,时间片进行很快的切换。线程轮流执行cpu
并行:多核cpu运行 多线程时,真正的在同一时刻运行
多线程的创建和启动

run() :存放多线程中运行的代码逻辑
start(): 调用该线程,运行run()方法里面存放的代码
Thread类

创建线程的两种方式
方式一:继承Thread类
public class MyThread extends Thread
{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("one");
System.out.println("two");
System.out.println("three");
}
}
测试:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println("2");
System.out.println("3");
}
}
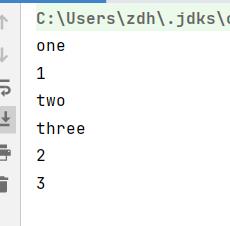
当我们调用start()方法开启线程调用后,会执行run里面的代码,此时run方法中运行的代码和主程序中strat后面运行的代码是并行执行的,没先后顺序,是异步执行
但是对于单个线程来将,他的代码执行顺序是固定的
方式二 :实现Runnable接口

Runnable 接口是一个函数式接口,因此我们可以使用lambda表达式
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
代码实现:
Thread thread1=new MyThread();
//开启线程1
thread1.start();
//开启线程2
Thread thread2=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("run1");
System.out.println("run2");
System.out.println("run3");
});
thread2.start();
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println("2");
System.out.println("3");
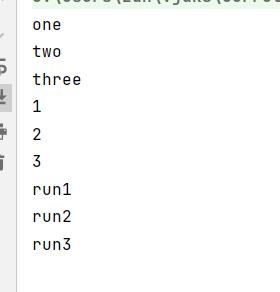
此时是在一个进程中,有两个分支线程和主进程并行执行,三者互不干扰,执行顺序也不固定
指定线程的名称,并获取
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread thread1=new MyThread();
//开启线程1
thread1.start();
//开启线程2
Thread thread2=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("当前线程: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run1");
System.out.println("当前线程: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run2");
System.out.println("当前线程: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run3");
},"run线程");
thread2.start();
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println("2");
System.out.println("3");
}
}
继承方式和实现方式的联系和区别

资源共享的案例:
public class MyThread implements Runnable
{
int count=1;
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(++count);
}
}
测试:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//开启线程2
Runnable run1=new MyThread();
Thread thread2=new Thread(run1);
thread2.start();
Thread thread3=new Thread(run1);
thread3.start();
}
}
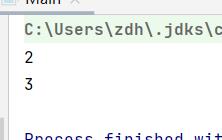
共享了run1实现类中的count变量的值
Thread类相关的方法1

演示如果没有设置线程名称的情况下,系统给出的默认线程名称:
//开启线程2
Runnable run1=new MyThread();
Thread thread2=new Thread(run1);
thread2.start();
Thread thread3=new Thread(run1);
thread3.start();
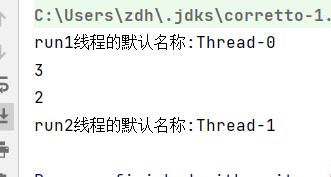
System.out.println("run1线程的默认名称:"+thread2.getName());
System.out.println("run2线程的默认名称:"+thread3.getName());
线程的优先级

线程的优先级,就是哪个线程有较大的概率被执行
优先级使用1-10的数组表示,数字越大优先级越高,线程的默认优先级都是5
设置优先级只是增大优先执行当前线程的概率
线程可以划分优先级,优先级高的线程得到的CPU资源比较多,也就是CPU优先执行优先级高的线程对象中的任务。
设置线程优先级有助于帮助线程规划器确定下一次选中哪一个线程优先执行。
演示:
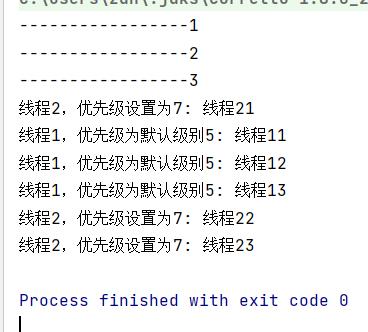
Thread t1=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程11");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程12");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程13");
},"线程1,优先级为默认级别5");
Thread t2=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程21");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程22");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程23");
},"线程2,优先级设置为7");
t2.setPriority(7);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("-----------------1");
System.out.println("-----------------2");
System.out.println("-----------------3");
Thread相关方法2

yield方法演示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程11");
Thread.yield();//让当前线程执行到此时,暂停当前线程,将机会让给优先级更高的线程执行
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程12");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程13");
},"线程1,优先级为默认级别5");
Thread t2=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程21");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程22");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程23");
},"线程2,优先级设置为7");
t2.setPriority(1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("-----------------1");
System.out.println("-----------------2");
System.out.println("-----------------3");
}

join方法演示:
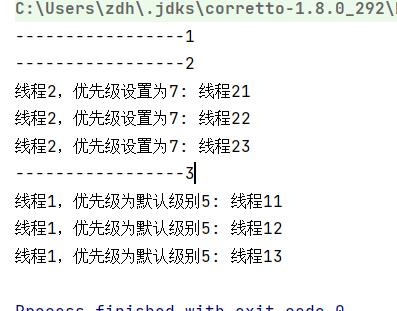
Thread t1=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程11");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程12");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程13");
},"线程1,优先级为默认级别5");
Thread t2=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程21");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程22");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程23");
},"线程2,优先级设置为7");
t2.setPriority(1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("-----------------1");
System.out.println("-----------------2");
//阻塞当前的main方法,先执行join进行的线程的代码,执行完毕后,继续执行main方法被阻塞的代码
t2.join();//相当于把t2的run方法中的代码插入到这里执行,相当于是同步执行
System.out.println("-----------------3");
sleep方法演示:
Thread t1=new Thread(()->
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程11");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程12");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程13");
},"线程1,优先级为默认级别5");
Thread t2=new Thread(()->{
try {
//当前线程睡5秒后,再执行
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程21");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程22");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": 线程23");
},"线程2,优先级设置为7");
t2.setPriority(1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("-----------------1");
System.out.println("-----------------2");
System.out.println("-----------------3");


stop方法和isAlive方法演示
Thread t1=new Thread(()->
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread(<以上是关于JAVA---多线程篇的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章