Java集合与数据结构 优先级队列堆
Posted 头发都哪去了
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合与数据结构 优先级队列堆相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java集合与数据结构 优先级队列【堆】
二叉树的顺序存储
存储方式
使用数组保存二叉树结构,方式即将二叉树用层序遍历方式放入数组中。一般只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费。这种方式的主要用法就是堆的表示。
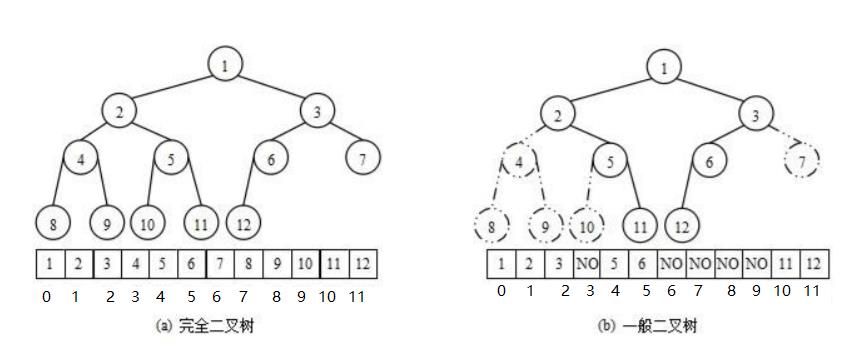
下标关系:
已知双亲(parent)的下标,则:
左孩子(left)下标 = 2 * parent + 1;
右孩子(right)下标 = 2 * parent + 2;
已知孩子(不区分左右)(child)下标,则:
双亲(parent)下标 = (child - 1) / 2;
堆(heap)
概念:
- 堆逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树。
- 堆物理上是保存在数组中。
- 满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆。
- 反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆。
- 堆的基本作用是:快速找集合中的最值。
操作-向下调整
前提:左右子树必须已经是一个堆,才能调整。
说明:
- array 代表存储堆的数组。
- size 代表数组中被视为堆数据的个数。
- index 代表要调整位置的下标。
- left 代表 index 左孩子下标。
- right 代表 index 右孩子下标。
- max 代表 index 的最大值孩子的下标。
过程(以大堆为例):
- index 如果已经是叶子结点,则整个调整过程结束。
- 判断 index 位置有没有孩子。
- 因为堆是完全二叉树,没有左孩子就一定没有右孩子,所以判断是否有左孩子
- 因为堆的存储结构是数组,所以判断是否有左孩子即判断左孩子下标是否越界,即 left >= size 越界。
- 确定 left 或 right,谁是 index 的最大孩子 max。
- 如果右孩子不存在,则 max = left。
- 否则,比较 array[left] 和 array[right] 值得大小,选择大的为 max。
- 比较 array[index] 的值 和 array[max] 的值,如果 array[index] >= array[max],则满足堆的性质,调整结束。
- 否则,交换 array[index] 和 array[max] 的值。
- 然后因为 max 位置的堆的性质可能被破坏,所以把 max 视作 index,向下重复以上过程。

逻辑代码:
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//时间复杂度分析:最坏的情况即图示的情况,从根一路比较到叶子,比较的次数为完全二叉树的高度即时间复杂度为 O(log(n))
public void adjustDown(int parent, int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < len) {
if (child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if (this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int temp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = temp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//时间复杂度分析:时间复杂度为 O(n * log(n)),实际上是 O(n)。
public void createBigHeap(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for (int i = (this.usedSize - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(i, this.usedSize);
}
}
public void show() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
测试代码:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapDemo heapDemo = new HeapDemo();
int[] array = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
heapDemo.createBigHeap(array);
heapDemo.show();
}
}
该代码的执行结果为:
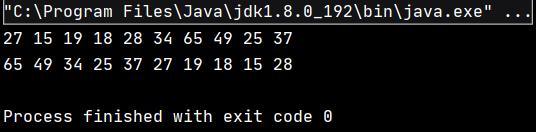
堆的应用-优先级队列
概念:
在很多应用中,我们通常需要按照优先级情况对待处理对象进行处理,比如首先处理优先级最高的对象,然后处理次高的对象。最简单的一个例子就是,在手机上玩游戏的时候,如果有来电,那么系统应该优先处理打进来的电话。
在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)。
内部原理
优先级队列的实现方式有很多,但最常见的是使用堆来构建。
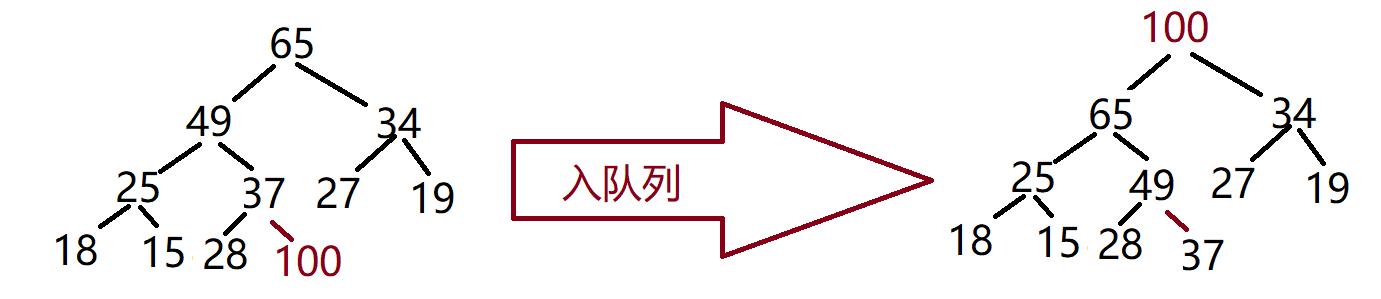
操作-入队列
过程(以大堆为例):
- 首先按尾插方式放入数组
- 比较其和其双亲的值的大小,如果双亲的值大,则满足堆的性质,插入结束
- 否则,交换其和双亲位置的值,重新进行 2、3 步骤
- 直到根结点
逻辑代码:
public void adjustUp(int child) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0) {
if (this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int temp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = temp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
public void push(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
adjustUp(this.usedSize - 1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
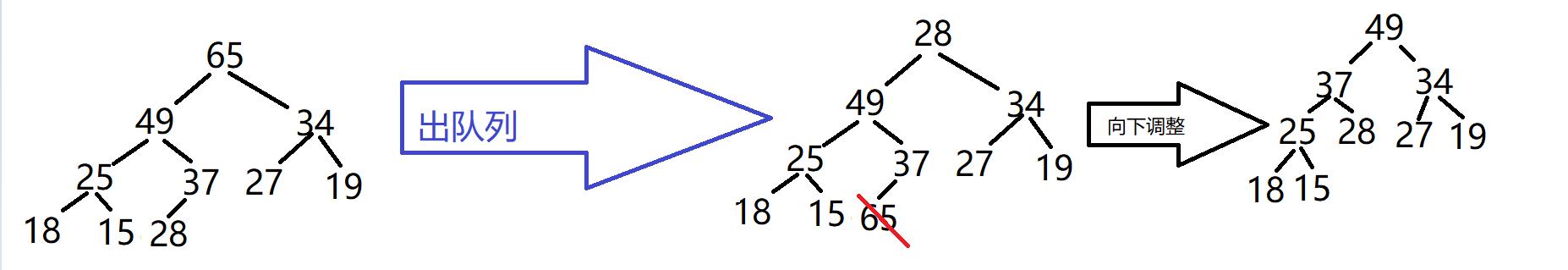
操作-出队列
过程(以大堆为例):
- 将第一个元素与最后一个元素进行交换。
- 删除最后一个下标
- 向下调整(只需要调整0号下标)
逻辑代码:
public int poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空~");
}
int ret = this.elem[0];
int temp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[usedSize-1];
this.elem[usedSize-1] = temp;
this.usedSize--;
adjustDown(0,this.usedSize);
return ret;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public void adjustDown(int parent, int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < len) {
if (child + 1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child + 1]) {
child++;
}
if (this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int temp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = temp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
java 中的优先级队列
PriorityQueue implements Queue
集合框架中的PriorityQueue底层使用堆结构,因此其内部的元素必须要能够比大小,PriorityQueue采用了:Comparble和Comparator两种方式。
- Comparble是默认的内部比较方式,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,该类对象必须要实现Comparble接口,并覆写compareTo方法。
- 用户也可以选择使用比较器对象,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,必须要提供一个比较器类,让该类实现Comparator接口并覆写compare方法。
堆的其他应用 TopK 问题
问题描述: 从array[1, n]这n个数中,找出最大的k个数,这就是经典的TopK问题。
前k个最小的元素,建大堆;
前k个最大的元素,建小堆。
例如:从int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };中找出最大的三个数。
逻辑代码:
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/*
找前k个最大的元素
创建小堆
*/
public static void topK(int[] array,int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1-o2;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (minHeap.size() < k) {
minHeap.offer(array[i]);
} else {
int top = minHeap.peek();
if (array[i] > top) {
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.println(minHeap.poll());
}
}
}
调试代码:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
HeapDemo.topK(array,3);
}
}
该代码的执行结果为:
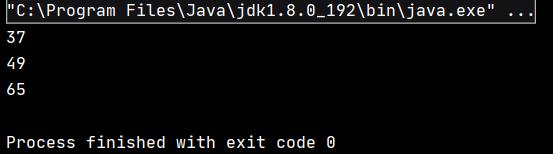
可见,该数组中最大的三个数已找到。
例如:从int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };中找出最小的三个数。
逻辑代码:
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/*
找前k个最小的元素
创建大堆
*/
public static void minTopK(int[] array,int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (maxHeap.size() < k) {
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
} else {
Integer top = maxHeap.peek();
if (top != null) {
if (array[i] < top) {
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.println(maxHeap.poll());
}
}
}
调试代码:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
HeapDemo.minTopK(array,3);
}
}
该代码的执行结果为:
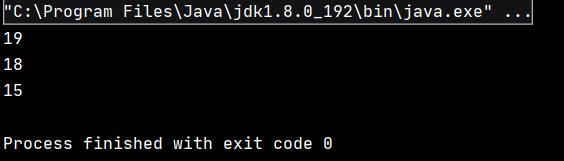
可见,该数组中最小的三个数已找到。
堆的其他应用 堆排序
基本原理是选择排序,只是不在使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数。
注意: 排升序要建大堆;排降序要建小堆。
时间复杂度:不管是最好的情况还是最坏的情况都是O(n * log(n)) 。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
以排升序为例,逻辑代码:
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public void adjustDown(int parent, int len) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < len) {
if (child + 1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child + 1]) {
child++;
}
if (this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int temp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = temp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
public void createBigHeap(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
for (int i = (this.usedSize - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(i, this.usedSize);
}
}
public void show() {
for (int i = 0