100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day4有效的括号删除有序数组中的重复项实现strStr
Posted 哪 吒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day4有效的括号删除有序数组中的重复项实现strStr相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
大家好,我是哪吒,一个热爱编码的Java工程师,本着“欲速则不达,欲达则欲速”的学习态度,在程序猿这条不归路上不断成长,所谓成长,不过是用时间慢慢擦亮你的眼睛,少时看重的,年长后却视若鸿毛,少时看轻的,年长后却视若泰山,成长之路,亦是渐渐放下执念,内心归于平静的旅程。
也许,我们永远都不会知道自己能走到何方,遇见何人,最后会变成什么样的人,但一定要记住,能让自己登高的,永远不是别人的肩膀,而是挑灯夜战的自己,人生的道路刚刚启程,当你累了倦了也不要迷茫,回头看一看,你早已不再是那个年少轻狂的少年。
1、LeetCode 20.有效的括号
题目
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
小编菜解
public static boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s.length()%2 != 0) return false;
Map<Character,Character> hashMap = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){{
put(')','(');
put('}','{');
put(']','[');
}};
//"{[]}"
Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(hashMap.containsKey(c)){
char t = queue.peek();
System.out.println(t);//这个地方弹出的是{
char tt = hashMap.get(c);//而这个对应的是],,上一处peek应该取得[
System.out.println(tt);
System.out.println(queue.peek() != hashMap.get(c));
if (queue.isEmpty() || queue.peek() != hashMap.get(c)){
return false;
}
queue.poll();
}else{
queue.offer(c);
}
}
return queue.isEmpty();
}思路及算法
判断括号的有效性可以使用「栈」这一数据结构来解决。
当我们遇到一个右括号时,我们需要将一个相同类型的左括号闭合。此时,我们可以取出栈顶的左括号并判断它们是否是相同类型的括号。如果不是相同的类型,或者栈中并没有左括号,那么字符串 ss 无效,返回 \\text{False}False。为了快速判断括号的类型,我们可以使用哈希表存储每一种括号。哈希表的键为右括号,值为相同类型的左括号。
在遍历结束后,如果栈中没有左括号,说明我们将字符串 ss 中的所有左括号闭合,返回True,否则返回False。
注意到有效字符串的长度一定为偶数,因此如果字符串的长度为奇数,我们可以直接返回False,省去后续的遍历判断过程。
大神解法
public static boolean isValid(String s){
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}思路和我的思路完全一致,就是我使用的是单向队列,结果就是失败,加油吧!
2、LeetCode 26.删除有序数组中的重复项
题目
给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
小编菜解初版
public static Integer[] removeDuplicates(Integer[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return nums;
}
List<Integer> tempList = Arrays.asList(nums);
for (int i = tempList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Integer current = tempList.get(i);
if(i-1>0){
Integer next = tempList.get(i - 1);
if(next == current){
tempList.remove(current);
}
}
}
Integer[] ret = new Integer[tempList.size()];
tempList.toArray(ret);
return ret;
}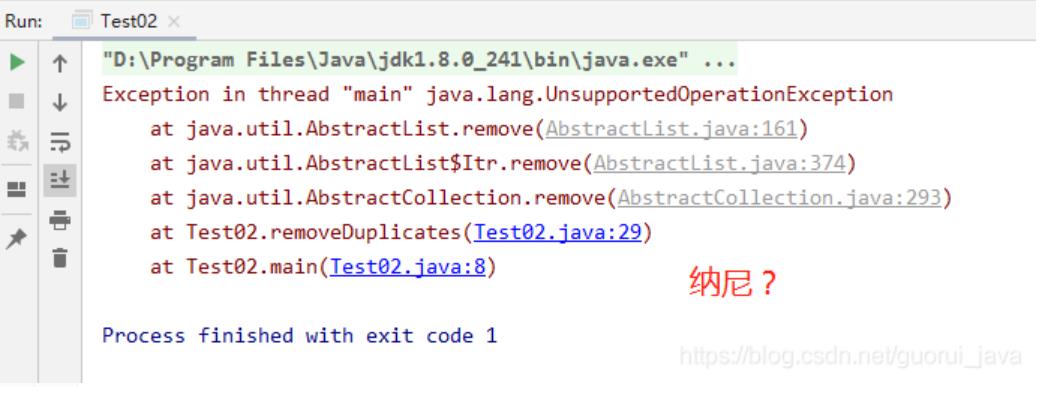
为什么为这样呢?我记得list是可以remove的啊,百思不得其解,查一下源码,猛然发现
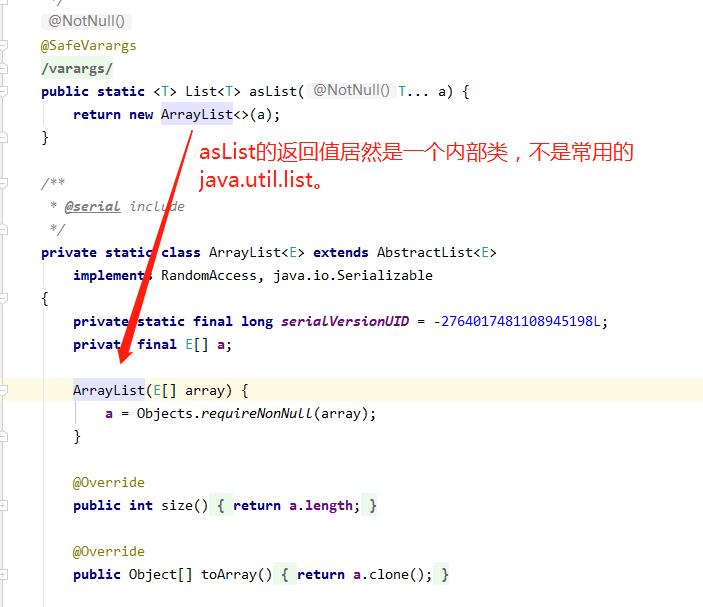
Arrays的内部类ArrayList和java.util.ArrayList都是继承AbstractList,remove、add等方法在AbstractList中是默认throw UnsupportedOperationException而且不作任何操作。java.util.ArrayList重写这些方法而Arrays的内部类ArrayList没有重写,所以会抛出异常。
小编菜解改进版
public static Integer[] removeDuplicates(Integer[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return nums;
}
List<Integer> tempList = Arrays.asList(nums);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(tempList);
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Integer current = list.get(i);
if(i-1>0){
Integer next = list.get(i - 1);
if(next == current){
list.remove(current);
}
}
}
Integer[] ret = new Integer[list.size()];
list.toArray(ret);
return ret;
}不报错了,结果也对,perfect!
思路及算法
相等的元素在数组中的下标一定是连续的。利用数组有序的特点,可以通过双指针的方法删除重复元素。
大神解法
public static int removeDuplicates2(Integer[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int fast = 1, slow = 1;
while (fast < n) {
if (nums[fast] != nums[fast - 1]) {
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
++slow;
}
++fast;
}
return slow;
}我去,无情。我的解法果然很菜,题意都没读懂,人家要的是长度,你返回一个数组,作甚??
3、LeetCode 28.实现strStr
题目
实现 strStr() 函数。
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置(下标从 0 开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1 。
说明:
当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。
对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与 C 语言的 strstr() 以及 Java 的 indexOf() 定义相符。
小编菜解
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if(haystack == null || !haystack.contains(needle)){
return -1;
}
if(needle == ""){
return 0;
}
int strLg = haystack.length();
int findLg = needle.length();
for (int i = 0; i < strLg; i++) {
char c = haystack.charAt(i);
if (c == needle.charAt(0) && i+findLg <= strLg){
String temp = haystack.substring(i,i + findLg);
if (temp.equals(needle)){
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}没看出有什么问题,可是提交总是提示解答错误,也是无奈。
大神解法
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int strLg = haystack.length();
int findLg = needle.length();
for (int i = 0; i+findLg <= strLg; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < findLg; j++) {
if (haystack.charAt(i+j)!=needle.charAt(j)){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (true == flag){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}感觉大神的解法还没我的解法简单呢?可我的为何一直提交都是出错,哎,无奈。
上一篇:【100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day3】回文数、罗马数字转数字、最大公共前缀
往期精彩内容:
以上是关于100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day4有效的括号删除有序数组中的重复项实现strStr的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day14两个数组的交集有效的完全平方数字符串中的第一个唯一字符
100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day11丢失的数字移动零单词规律
100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day12Nim游戏3的幂4的幂
100天算法入门 - 每日三题 - Day15判断子序列最长回文数Fizz Buzz