目标检测回归损失函数 IOUGIOUDIOUCIOUEIOUFocal EIOUalpha IOU损失函数分析
Posted 中科哥哥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了目标检测回归损失函数 IOUGIOUDIOUCIOUEIOUFocal EIOUalpha IOU损失函数分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目标检测回归损失函数 IOU、GIOU、DIOU、CIOU、EIOU、Focal EIOU、alpha IOU损失函数分析
一、IOU Loss
2016文章《UnitBox: An Advanced Object Detection Network》中提出了IOU Loss将4个点构成的box看成一个整体做回归。
函数特性
IOU Loss的定义是先求出预测框和真实框之间的交集和并集之比,再求负对数,但是在实际使用中我们常常将IOU Loss写成1-IOU。如果两个框重合则交并比等于1,Loss为0说明重合度非常高。


IOU满足非负性、同一性、对称性、三角不等性,相比于L1/L2等损失函数还具有尺度不变性,不论box的尺度大小,输出的iou损失总是在0-1之间。所以能够较好的反映预测框与真实框的检测效果。
伪代码如下:
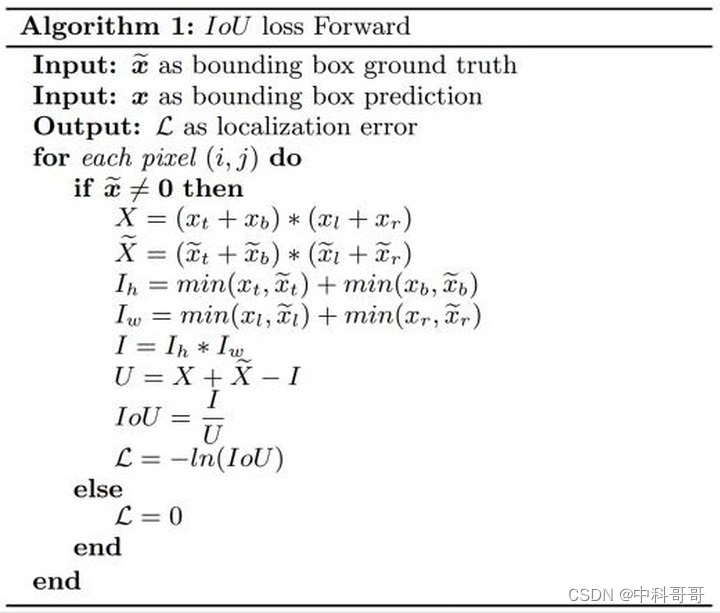
其中,

其中:


从这个公式可以看出惩罚来自两个部分,预测框四个变量和预测框和真实框相交区域:
1 .损失函数和 成正比,因此预测的面积越大,损失越多;
成正比,因此预测的面积越大,损失越多;
2 .同时损失函数和 成反比,因此我们希望交集尽可能的大;
成反比,因此我们希望交集尽可能的大;
根据求导公式为了减小IOU Loss,会尽可能增大相交面积同时预测更小的框。
Python实现如下:
def calculate_iou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate iou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of iou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# if there is an intersect area
if left >= right or top >= bottom:
return 0
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
return iou
Tensorflow实现如下:
def bbox_iou(self, boxes_1, boxes_2):
"""
calculate regression loss using iou
:param boxes_1: boxes_1 shape is [x, y, w, h]
:param boxes_2: boxes_2 shape is [x, y, w, h]
:return:
"""
# transform [x, y, w, h] to [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
boxes_1 = tf.concat([boxes_1[..., :2] - boxes_1[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes_1[..., :2] + boxes_1[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes_2 = tf.concat([boxes_2[..., :2] - boxes_2[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes_2[..., :2] + boxes_2[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes_1 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_1[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_1[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
boxes_2 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes_2[..., :2], boxes_2[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes_2[..., :2], boxes_2[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
# calculate area of boxes_1 boxes_2
boxes_1_area = (boxes_1[..., 2] - boxes_1[..., 0]) * (boxes_1[..., 3] - boxes_1[..., 1])
boxes_2_area = (boxes_2[..., 2] - boxes_2[..., 0]) * (boxes_2[..., 3] - boxes_2[..., 1])
# calculate the two corners of the intersection
left_up = tf.maximum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_2[..., :2])
right_down = tf.minimum(boxes_1[..., 2:], boxes_2[..., 2:])
# calculate area of intersection
inter_section = tf.maximum(right_down - left_up, 0.0)
inter_area = inter_section[..., 0] * inter_section[..., 1]
# calculate union area
union_area = boxes_1_area + boxes_2_area - inter_area
# calculate iou add epsilon in denominator to avoid dividing by 0
iou = inter_area / (union_area + tf.keras.backend.epsilon())
return iou
存在的问题
IOU Loss虽然解决了Smooth L1系列变量相互独立和不具有尺度不变性的两大问题,但是它也存在两个问题:
- 预测框和真实框不相交时,不能反映出两个框的距离的远近。根据IOU定义loss等于0,没有梯度的回传无法进一步学习训练。
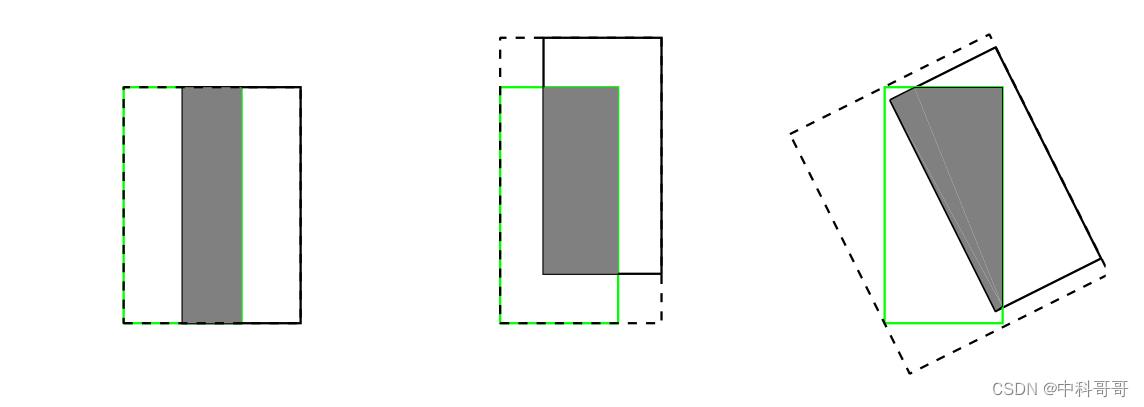
- 预测框和真实框无法反映重合度大小。借用一张图来说,三者具有相同的IOU,但是不能反映两个框是如何相交的,从直观上感觉第三种重合方式是最差的。
GIOU Loss
上面指出IOU Loss的两大缺点:无法优化两个框不相交的情况;无法反映两个框如何相交的。针对此类问题斯坦福学者在2019年的文章《Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression》中提出了GIOU Loss,在IOU的基础上引入了预测框和真实框的最小外接矩形。
函数特性
GIOU作为IOU的升级版,保持了 IOU 的主要性质并避免了 IOU 的缺点,首先计算预测框

伪代码:


Python实现如下:
def calculate_giou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate giou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of giou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# calculate minimum external frame
area_c = (max(box_1[2], box_2[2]) - min(box_1[0], box_2[0])) * (max(box_1[3], box_2[3]) - min(box_1[1], box_2[1]))
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
# calculate iou
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
# calculate giou(iou - (area_c - area_union)/area_c)
giou = iou - float((area_c - area_union)) / area_c
return giou
Tensorflow实现如下:
def bbox_giou(self, boxes_1, boxes_2):
"""
calculate regression loss using giou
:param boxes_1: boxes_1 shape is [x, y, w, h]
:param boxes_2: boxes_2 shape is [x, y, w, h]
:return:
"""
# transform [x, y, w, h] to [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
boxes_1 = tf.concat([boxes_1[..., :2] - boxes_1[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes_1[..., :2] + boxes_1[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes_2 = tf.concat([boxes_2[..., :2] - boxes_2[..., 2:] * 0.5,
boxes_2[..., :2] + boxes_2[..., 2:] * 0.5], axis=-1)
boxes_1 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_1[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_1[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
boxes_2 = tf.concat([tf.minimum(boxes_2[..., :2], boxes_2[..., 2:]),
tf.maximum(boxes_2[..., :2], boxes_2[..., 2:])], axis=-1)
# calculate area of boxes_1 boxes_2
boxes_1_area = (boxes_1[..., 2] - boxes_1[..., 0]) * (boxes_1[..., 3] - boxes_1[..., 1])
boxes_2_area = (boxes_2[..., 2] - boxes_2[..., 0]) * (boxes_2[..., 3] - boxes_2[..., 1])
# calculate the two corners of the intersection
left_up = tf.maximum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_2[..., :2])
right_down = tf.minimum(boxes_1[..., 2:], boxes_2[..., 2:])
# calculate area of intersection
inter_section = tf.maximum(right_down - left_up, 0.0)
inter_area = inter_section[..., 0] * inter_section[..., 1]
# calculate union area
union_area = boxes_1_area + boxes_2_area - inter_area
# calculate iou add epsilon in denominator to avoid dividing by 0
iou = inter_area / (union_area + tf.keras.backend.epsilon())
# calculate the upper left and lower right corners of the minimum closed convex surface
enclose_left_up = tf.minimum(boxes_1[..., :2], boxes_2[..., :2])
enclose_right_down = tf.maximum(boxes_1[..., 2:], boxes_2[..., 2:])
# calculate width and height of the minimun closed convex surface
enclose_wh = tf.maximum(enclose_right_down - enclose_left_up, 0.0)
# calculate area of the minimun closed convex surface
enclose_area = enclose_wh[..., 0] * enclose_wh[..., 1]
# calculate the giou add epsilon in denominator to avoid dividing by 0
giou = iou - 1.0 * (enclose_area - union_area) / (enclose_area + tf.keras.backend.epsilon())
return giou
存在的问题
在预测框和真实框没有很好地对齐时,会导致最小外接框C的面积增大,从而使GIOU的值变小,而两个矩形框不重合时,也可以计算GIOU。GIOU Loss虽然解决了IOU的上述两个问题,但是当两个框属于包含关系时,借用下图来说:GIOU会退化成IOU,无法区分其相对位置关系。
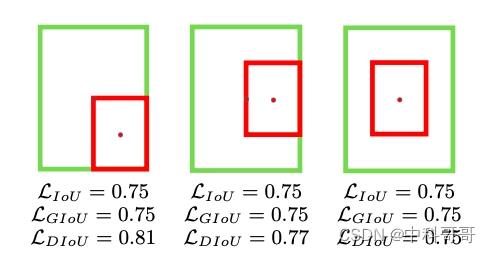
由于GIOU仍然严重依赖IOU,因此在两个垂直方向,误差很大,基本很难收敛,这就是GIoU不稳定的原因。借用下图来说:红框内部分:C为两个框的最小外接矩形,此部分表征除去两个框的其余面积,预测框和真实框在相同距离的情况下,水平垂直方向时,此部分面积最小,对loss的贡献也就越小,从而导致在垂直水平方向上回归效果较差。

DIOU Loss
针对上述GIOU的两个问题(预测框和真实框是包含关系的情况或者处于水平/垂直方向上,GIOU损失几乎已退化为IOU损失,即
 导致收敛较慢)。有学者将GIOU中引入最小外接框来最大化重叠面积的惩罚项修改成最小化两个BBox中心点的标准化距离从而加速损失的收敛过程。
导致收敛较慢)。有学者将GIOU中引入最小外接框来最大化重叠面积的惩罚项修改成最小化两个BBox中心点的标准化距离从而加速损失的收敛过程。
函数特性
DIOU损失函数公式如下:


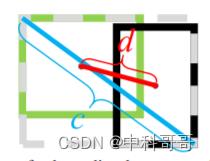
DIOU Loss的惩罚项能够直接最小化中心点间的距离,而GIOU Loss旨在减少外界包围框的面积,所以DIOU Loss具有以下特性:
-
DIOU与IOU、GIOU一样具有尺度不变性;
-
DIOU与GIOU一样在与目标框不重叠时,仍然可以为边界框提供移动方向;
-
DIOU可以直接最小化两个目标框的距离,因此比GIOU Loss收敛快得多;
-
DIOU在包含两个框水平/垂直方向上的情况回归很快,而GIOU几乎退化为IOU;
-
当预测框和真实框完全重合时

当预测框和真实框不相交时

Python实现如下:
def calculate_diou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate diou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of diou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# calculate center point of each box
center_x1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) / 2
center_y1 = (box_1[3] - box_1[1]) / 2
center_x2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) / 2
center_y2 = (box_2[3] - box_2[1]) / 2
# calculate square of center point distance
p2 = (center_x2 - center_x1) ** 2 + (center_y2 - center_y1) ** 2
# calculate square of the diagonal length
width_c = max(box_1[2], box_2[2]) - min(box_1[0], box_2[0])
height_c = max(box_1[3], box_2[3]) - min(box_1[1], box_2[1])
c2 = width_c ** 2 + height_c ** 2
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right