对象的构造顺序
Posted 阿弥陀佛.a
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了对象的构造顺序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
private:
int mi;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mi = i;
printf("Test(int i): %d\\n", mi);
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
mi = obj.mi;
printf("Test(const Test& obj): %d\\n", mi);
}
};
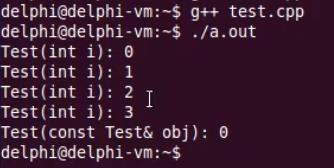
int main()
{
int i = 0;
Test a1 = i;
while( i < 3 )
{
Test a2 = ++i;
}
if( i < 4 )
{
Test a = a1;
}
else
{
Test a(100);
}
return 0;
}

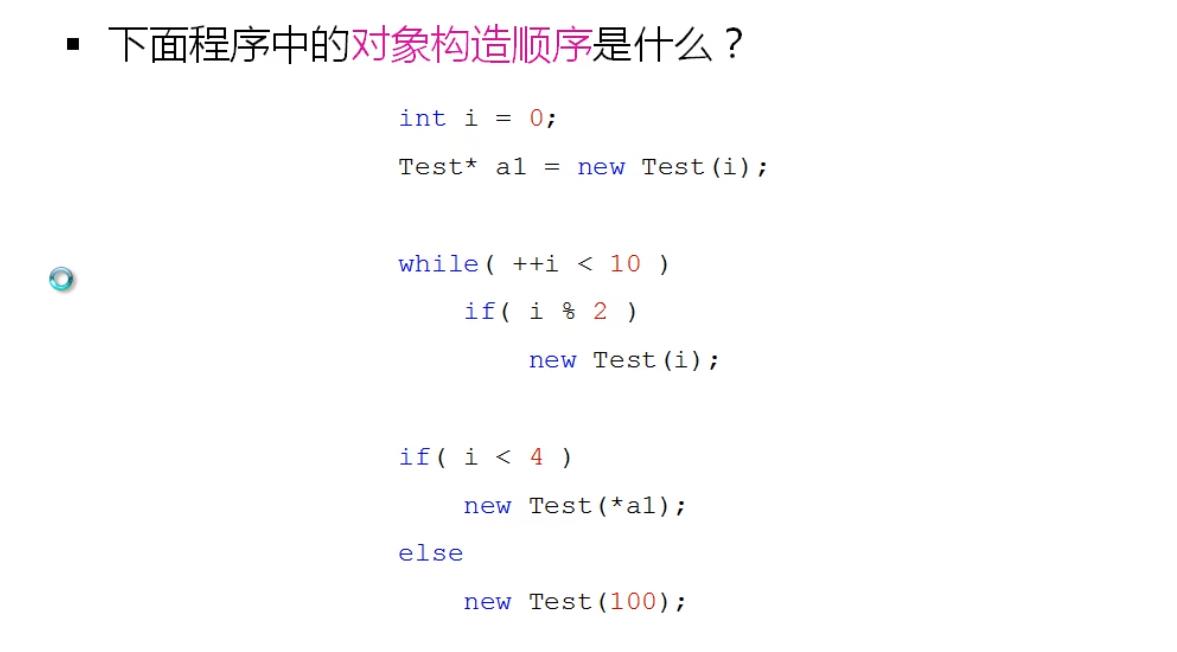
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
private:
int mi;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mi = i;
printf("Test(int i): %d\\n", mi);
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
mi = obj.mi;
printf("Test(const Test& obj): %d\\n", mi);
}
int getMi()
{
return mi;
}
};
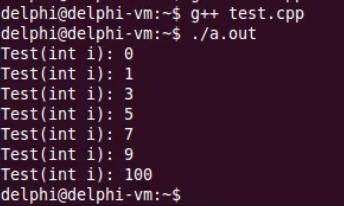
int main()
{
int i = 0;
Test* a1 = new Test(i); // Test(int i): 0
while( ++i < 10 )
if( i % 2 )
new Test(i); // Test(int i): 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
if( i < 4 )
new Test(*a1);
else
new Test(100); // Test(int i): 100
return 0;
}

//t1.cpp
#include "test.h"
Test t1("t1");
//t2.cpp
#include "test.h"
Test t2("t2");
//t3.cpp
#include "test.h"
Test t3("t2");
//test.h
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
public:
Test(const char* s)
{
printf("%s\\n", s);
}
};
#endif
//main.cpp
#include "test.h"
Test t4("t4");
int main()
{
Test t5("t5");
}
Linux输出:
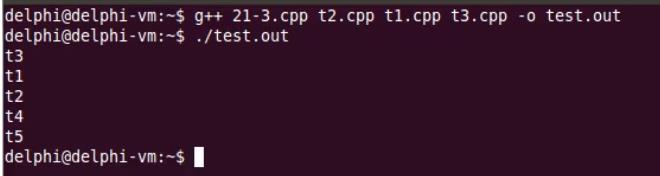
Windows输出:
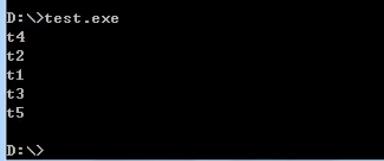
足以说明全局对象构造顺序不确定
要避开全局对象
小结

以上是关于对象的构造顺序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章