P2163 [SHOI2007]园丁的烦恼(二维数点模板题)
Posted Jozky86
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了P2163 [SHOI2007]园丁的烦恼(二维数点模板题)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题意:
在一个二维平面内有一些点,给你一个左上角和右下角的点,问这个范围内有多少点
题解:
二维数点模板题
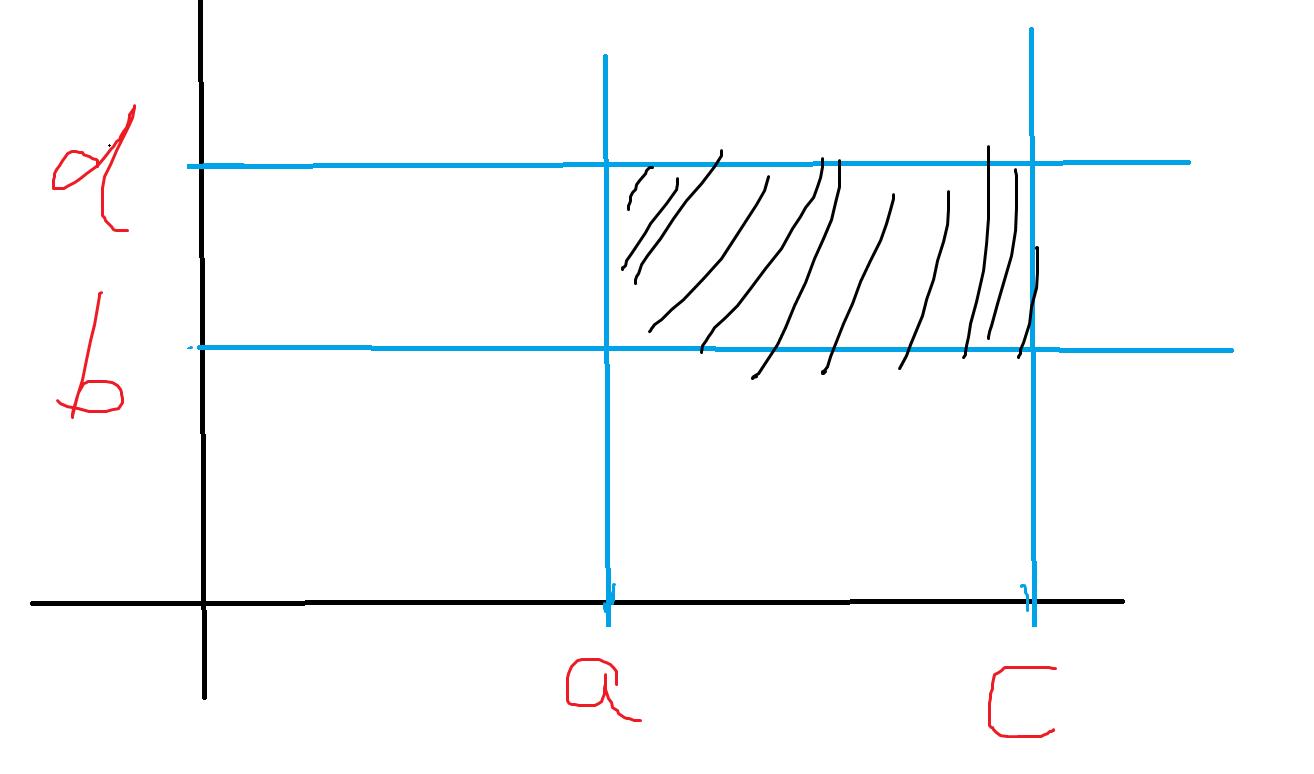
我们设F(a,b)表示以(0,0)为左下角,(a,b)为右上角的矩阵内有多少点
如图不难得到:
黑色部分为=F(c,d)+F(a-1,b-1)-F(a-1,d)-F(c,b-1)
(不就是二维前缀和)
因为数据范围过大,所以横纵坐标都离散化处理。
现在我们如何求(0,0)到(x,y)内点的数量
我们把矩阵内的点看作是插入操作,相当于在矩阵中(x,y)位置+1.
把所有插入操作和查询操作以x坐标为第一关键字,y坐标为第二关键字排序
若第i个是查询操作,仅有[1,i-1]中的插入操作能影响它,因为第i个操作后面的操作坐标都比它大
同样第i个操作是插入操作,不会影响到前面的查询
这样就利用树状数组实现二维数点问题
CDQ也可以二维数点,也是模板题
主席树也可以二维数点,这里有详细讲解
代码:
树状数组代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#define re register int
#define rl register ll
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int read() {
re x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0' || ch>'9') {
if(ch=='-') f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9') {
x=10*x+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void write(int x) {
if(x>9) write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
inline char GetChar() {
char ch=getchar();
while(ch!='A' && ch!='B' && ch!='C') ch=getchar();
return ch;
}
const int Size=500005;
int n,m,tot,maxn,ny[Size*5];
struct zyd {
int id,x,y,k,dt;
} Q[Size*5];
inline void Push(int x,int y,int k,int id) {
Q[++tot].x=x;
Q[tot].y=y;
Q[tot].k=k;
Q[tot].id=id;
Q[tot].dt=tot;
}
inline bool comp(zyd jzm,zyd xjp) {
if(jzm.x!=xjp.x) return jzm.x<xjp.x;
if(jzm.y!=xjp.y) return jzm.y<xjp.y;
return jzm.dt<xjp.dt;
}
int tree[Size];
inline void update(int x) {
for(re i=x; i<=maxn; i+=lowbit(i)) {
tree[i]++;
}
}
inline int query(int x) {
int ans=0;
for(re i=x; i; i-=lowbit(i)) {
ans+=tree[i];
}
return ans;
}
int out[Size];
void solve() {
n=read();
m=read();
for(re i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int x=read();
int y=read();
Push(x,y,0,0);
}
for(re i=1; i<=m; i++) {
int a=read();
int b=read();
int c=read();
int d=read();
Push(c,d,1,i);
Push(a-1,b-1,1,i);
Push(a-1,d,-1,i);
Push(c,b-1,-1,i);
}
sort(Q+1,Q+1+tot,comp);
for(re i=1; i<=tot; i++) {
ny[i]=Q[i].y;
}
sort(ny+1,ny+1+tot);
maxn=unique(ny+1,ny+1+tot)-(ny+1);
for(re i=1; i<=tot; i++) {
Q[i].y=lower_bound(ny+1,ny+1+maxn,Q[i].y)-ny;
}
for(re i=1; i<=tot; i++) {
if(!Q[i].k) {
update(Q[i].y);
} else if(Q[i].k==1) {
out[Q[i].id]+=query(Q[i].y);
} else {
out[Q[i].id]-=query(Q[i].y);
}
}
for(re i=1; i<=m; i++) {
printf("%d\\n",out[i]);
}
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
CDQ代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 5000005 * 5
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
char x = getchar();
int lin = 0, f = 1;
while(x < '0' || x > '9')
{
if(x == '-') f = -1;
x = getchar();
}
while(x >= '0' && x <= '9')
{
lin = lin * 10 + x - '0';
x = getchar();
}
return lin * f;
}
struct st{
int x,y,typ,add,id,ans;
}s[maxn],ce[maxn];
int n,m,x,y,tot,a,b,c,d,ans[maxn];
void add(int x,int y,int typ,int add,int id,int ans)
{
s[++tot] = (st) {x,y,typ,add,id,ans};
}
bool com(st a,st b)
{
if(a.x == b.x)
if(a.y == b.y)
return a.typ < b.typ;
else return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
}
void cdq(int l,int r)
{
if(l == r) return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
cdq(l,mid);
cdq(mid + 1,r);
int le = l,re = mid + 1,pos = 0,ans = 0;
while(le <= mid || re <= r)
{
if(re > r || (le <= mid && s[le].y <= s[re].y))
{
if(s[le].typ == 1) ++ans;
ce[++pos] = s[le++];
}
else
{
if(s[re].typ == 2) s[re].ans += ans;
ce[++pos] = s[re++];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= pos; i++)
s[l + i - 1] = ce[i];
}
int main(){
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
x = read(); y = read();
add(x,y,1,0,0,0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
a = read(); b = read();
c = read(); d = read();
add(a - 1,b - 1,2,1,i,0);
add(c,d,2,1,i,0);
add(a - 1,d,2,-1,i,0);
add(c,b - 1,2,-1,i,0);
}
sort(s + 1,s + 1 + tot,com);
cdq(1,tot);
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++)
if(s[i].typ == 2)
ans[s[i].id] += s[i].add * s[i].ans;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
printf("%d\\n",ans[i]);
}
以上是关于P2163 [SHOI2007]园丁的烦恼(二维数点模板题)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章