算法:二叉树倒序逐层返回列表 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Posted 架构师易筋
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了算法:二叉树倒序逐层返回列表 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Given the root of a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
Example 1:
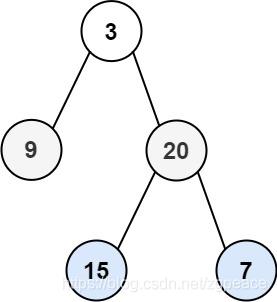
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000].
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
递归解法
数的遍历,优先用递归,记住每一层的深度即可获取到子数组。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, 0, list);
return list;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, int depth, List<List<Integer>> list) {
if (root == null) return;
if (depth == list.size()) list.add(0, new ArrayList<>());
list.get(list.size() - depth - 1).add(root.val);
helper(root.left, depth + 1, list);
helper(root.right, depth + 1, list);
}
}
以上是关于算法:二叉树倒序逐层返回列表 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章