面试---算法面试
Posted 蚍蜉撼树谈何易
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了面试---算法面试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
算法
二叉树
二叉树的遍历(前序、中序、后序、层序)
递归版本
前序
//递归版本
class Solution {
public:
void traver_binarytree(TreeNode*root,vector<int >&result)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
return;
}
result.push_back(root->val);
traver_binarytree(root->left,result);
traver_binarytree(root->right,result);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> result;
traver_binarytree(root,result);
return result;
}
};
中序:
class Solution {
public:
void inorder(TreeNode*root,vector<int>&result)
{
if(root==nullptr)return;
inorder(root->left,result);
result.push_back(root->val);
inorder(root->right,result);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int >result;
inorder(root,result);
return result;
}
};
后序
class Solution {
public:
void postorder(TreeNode*root,vector<int>&result)
{
if(root==nullptr)return;
postorder(root->left,result);
postorder(root->right,result);
result.push_back(root->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int >result;
postorder(root,result);
return result;
}
};
非递归版本
前序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
stack<TreeNode*>s;
if(root!=nullptr)
{
s.push(root);
}
vector<int>result;
while(!s.empty())
{
TreeNode* pd=s.top();
s.pop();
result.push_back(pd->val);
if(pd->right) s.push(pd->right);
if(pd->left) s.push(pd->left);
}
return result;
}
};
中序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*>s;
vector<int >result;
TreeNode*cur=root;
while(cur!=nullptr||!s.empty())
{
if(cur!=nullptr)
{
s.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
else
{
cur=s.top();
s.pop();
result.push_back(cur->val);
cur=cur->right;
}
}
return result;
}
};
后序:
class Solution {
public:
//由前序遍历根左右--转化为根右左 ---然后逆置数组 得到左右根的结果。
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode* >s;
if(root) s.push(root);
vector<int > result;
while(!s.empty())
{
TreeNode*pd=s.top();
s.pop();
result.push_back(pd->val);
if(pd->left) s.push(pd->left);
if(pd->right) s.push(pd->right);
}
reverse(result.begin(),result.end());
return result;
}
};
层序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>temp;
if(root!=nullptr)
{
temp.push(root);
}
vector<vector<int>>result;
while(!temp.empty())
{
vector<int>rz;
int size=temp.size();
rz.reserve(size);
for(int i=0;i<size;++i)
{
TreeNode* e=temp.front();
temp.pop();
rz.push_back(e->val);
if(e->left){temp.push(e->left);}
if(e->right){temp.push(e->right);}
}
result.push_back(rz);
}
return result;
}
};
二叉树的常见oj
二叉树的右视图
解题思路:实际上求的是层序遍历最右侧的值
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int >result;
queue<TreeNode* >q;
if(root!=nullptr)
{
q.push(root);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i)
{
TreeNode*pd=q.front();
q.pop();
if(i==size-1)
{
result.push_back(pd->val);
}
if(pd->left) q.push(pd->left);
if(pd->right) q.push(pd->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
N叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
queue<Node*>q;
if(root)
{
q.push(root);
}
vector<vector<int> > result;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size=q.size();
vector<int> temp;
temp.reserve(size);
for(int i=0;i<size;++i)
{
Node *p=q.front();
temp.push_back(p->val);
q.pop();
int size_child=p->children.size();
for(int j=0;j<size_child;++j)
{
q.push(p->children[j]);
}
}
result.push_back(temp);
}
return result;
}
};
反转二叉树
leecode链接:
解题思路:依据前序遍历的思想,先反转中间节点的左右子树,后反转左右子树。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)return root;
swap(root->left,root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
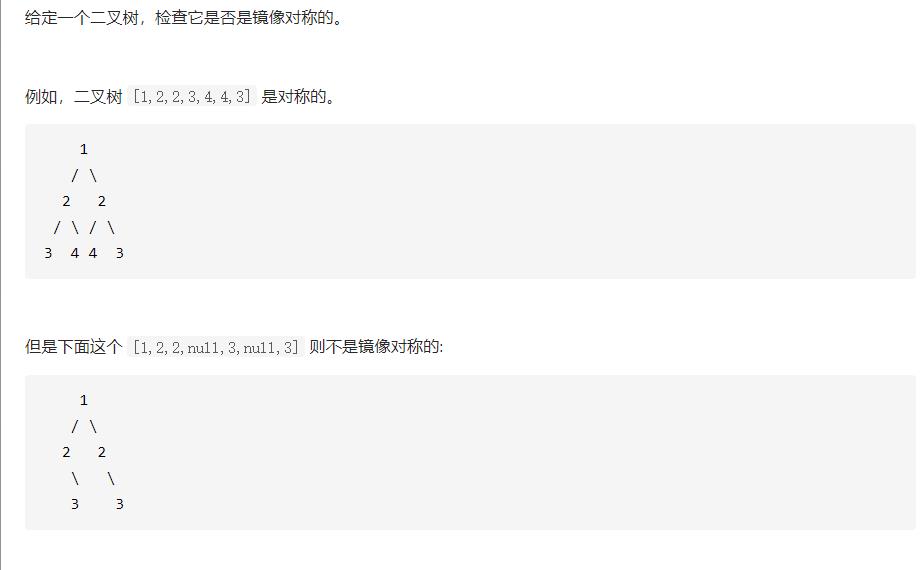
对称二叉树
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode*rleft,TreeNode * rright)
{
if(rleft==nullptr&&rright==nullptr)return true;
if(rleft==nullptr||rright==nullptr) return false;
if(rleft->val!=rright->val) return false;
return compare(rleft->left,rright->right)&&compare(rleft->right,rright->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
return true;
}
return compare(root->left,root->right);
}
};
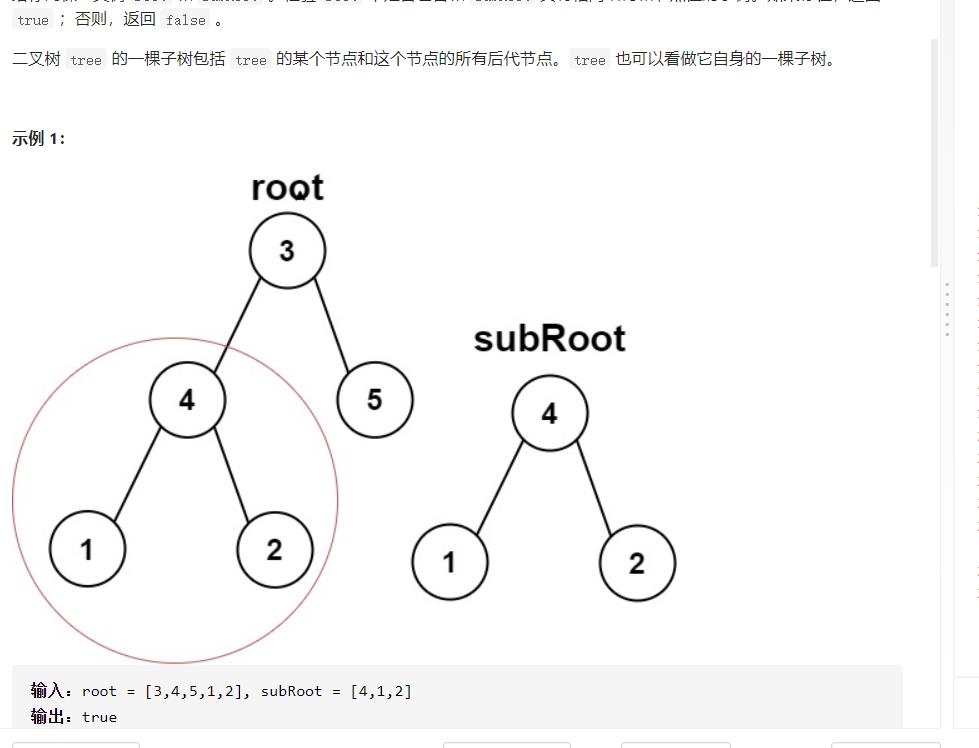
子树问题
class Solution {
public:
bool check(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*subRoot)
{
if(root==nullptr&&subRoot==nullptr) return true;
if(!root ||!subRoot) return false;
if(root->val!=subRoot->val)return false;
return check(root->left,subRoot->left)&&check(root->right,subRoot->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
if(subRoot==nullptr)return true;
if(root==nullptr)return false;
return check(root,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
};
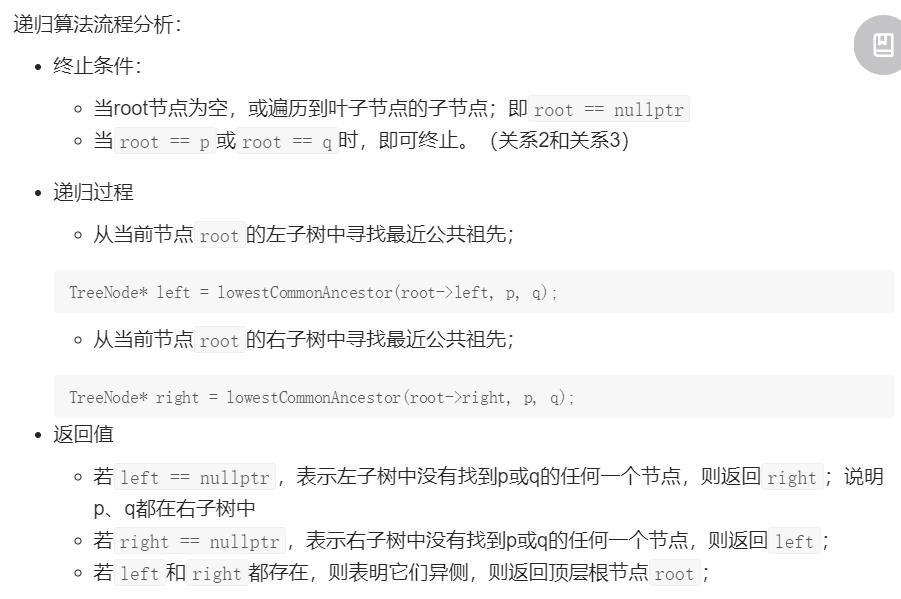
二叉树的最近祖先问题

class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == nullptr || root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left) {
if (right) {
return root;
}
return left;
}
return right;
}
};
二叉树的最大高度问题
leecode
1.确认结束条件,当递归走到为空的节点时,此时return 0
2.设置两个变量值max_left,max_right 分别记录从根节点开始左右子树的高度。
3.返回左右子树最大高度+1即为树的高度。
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int max_left=maxDepth(root->left);
int max_right=maxDepth(root->right);
return max(max_left,max_right)+1;
}
};
二叉树的最小深度
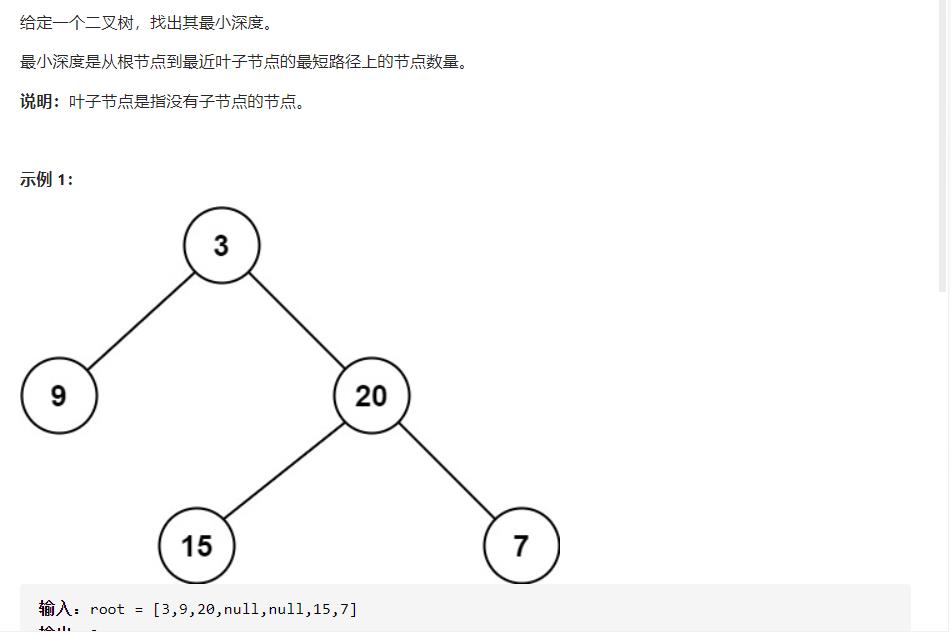
//解题思路
1.三种情况
第一种:根节点的左孩子存在,右孩子不存在。
第二种:根节点左孩子存在,右孩子不存在。
第三种:左右孩子均存在
2.对于不同情况,采取不同的递归策略。
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int min_left, min_right;
min_right=min_left=0;
if(root->left&&!root->right)
{
min_left=minDepth(root->left);
return min_left+1;
}
else if(root->right&& !root->left)
{
min_right=minDepth(root->right);
return min_right+1;
}
else
{
min_left=minDepth(root->left);
min_right=minDepth(root->right);
return min(min_left,min_right)+1;
}
}
};
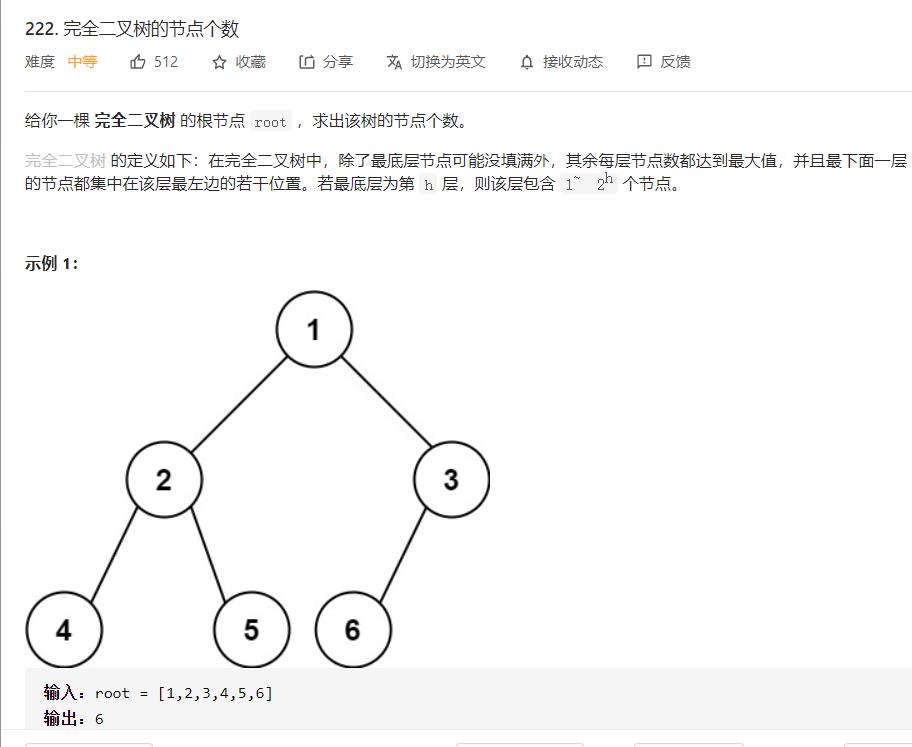
完全二叉树节点个数‘
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
//1.确定结束条件
if(root==nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
//然后依次遍历左右子树
return 1+countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right);
}
};
平衡二叉树问题

class Solution {
public:
int max_high(TreeNode*root)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int max_left=max_high(root->left);
int max_right=max_high(root->right);
return 1+max(max_left,max_right以上是关于面试---算法面试的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章