Java集合框架 List接口实现类--ArrayList使用 & 删除小明
Posted Z && Y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合框架 List接口实现类--ArrayList使用 & 删除小明相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
List接口实现类:

1. ArrayList的使用
1.1 创建集合:
// 创建集合
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
1.2 添加元素
注意默认是添加到末尾:
list.add("zhou");
list.add("tian");
插入操作 在下标为0的元素前面插入 “jiao”:
list.add(0, "jiao");
1.3 删除元素
删除元素 这里删除的下标为0的元素:
list.remove(0);
删除元素内容为0的元素:
list.remove(new Integer(0));
删除元素内容为"tian"的元素:
list.remove("tian");
1.4 遍历集合
1.4.1 使用for遍历
System.out.println("---------------使用普通for循环遍历---------------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) {
/*
这里 get(index); 是根据元素的下标获取元素
*/
System.out.print(list.get(i) + "\\t");
}
1.4.2 使用增强for
for (Object object : list) {
System.out.print(object + "\\t");
}
1.4.3 使用Iterator迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\\t");
}
1.4.4 使用列表迭代器,listIterator可以双向遍历,添加、删除及修改元素。
从前往后:
System.out.println("从前往后遍历元素:");
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(listIterator.next() + "\\t");
}
从后往前:
System.out.println("从后往前遍历元素:");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(listIterator.previous() + "\\t");
}
1.5 判断
System.out.println("列表是否为空: " + list.isEmpty());
System.out.println("列表是否包含'jiao': " + list.contains("jiao"));
1.6 获取位置
System.out.println("第一个元素内容为jiao的下标为: (如果没有则返回-1)" + list.indexOf("jiao"));
System.out.println("最后一个元素内容为jiao的下标为: (如果没有则返回-1)" + list.lastIndexOf("jiao"));
1.7 截取集合
截取集合 截取下标为[0,1)的元素:
List myList = list.subList(0, 1);
2. 完整的测试代码:
package list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/**
* ArrayList的使用
* 存储结构:数组;
* 特点:1.查找遍历速度快 2.增删慢
* 3.有序有下标 4.可以重复
* 1.添加元素
* 2.删除元素
* 3.遍历元素
* 4.判断
* 5.获取位置
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
//1.添加元素 注意默认是添加到末尾
list.add("zhou");
list.add("tian");
list.add(0, "jiao");//插入操作 在下标为0的元素前面插入 "jiao"
System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size());
System.out.println("集合内容: " + list.toString());
System.out.println();
/*
2.删除元素 这里删除的下标为0的元素
如果要删除元素内容为0的元素 => list.remove(new Integer(0));
*/
list.remove(0);
//list.remove("tian"); 删除元素内容为"tian"的元素
System.out.println("删除下标为0的元素和元素内容为\\"tian\\"的元素之后:" + list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
System.out.println();
//3.遍历元素
//3.1 使用for遍历
System.out.println("---------------使用普通for循环遍历---------------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) {
/*
这里 get(index); 是根据元素的下标获取元素
*/
System.out.print(list.get(i) + "\\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------------使用增强for循环遍历---------------");
//3.2 使用增强for
for (Object object : list) {
System.out.print(object + "\\t");
}
System.out.println();
//3.3 使用迭代器
System.out.println("---------------使用Iterator迭代器遍历---------------");
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\\t");
}
System.out.println();
//3.4使用列表迭代器,listIterator可以双向遍历,添加、删除及修改元素。
System.out.println("---------------使用listIterator列表迭代器遍历---------------");
ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator();
//从前往后
System.out.println("\\n从前往后遍历元素:");
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(listIterator.next() + "\\t");
}
//从后往前(此时“遍历指针”已经指向末尾)
System.out.println("从后往前遍历元素:");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(listIterator.previous() + "\\t");
}
//4.判断
System.out.println();
System.out.println("列表是否为空: " + list.isEmpty());
System.out.println("列表是否包含'jiao': " + list.contains("jiao"));
//5.获取位置
System.out.println();
System.out.println("第一个元素内容为jiao的下标为: (如果没有则返回-1)" + list.indexOf("jiao"));
System.out.println("最后一个元素内容为jiao的下标为: (如果没有则返回-1)" + list.lastIndexOf("jiao"));
//截取集合 截取下标为[0,1)的元素
List myList = list.subList(0, 1);
System.out.println("\\n截取下标为[0,1)的元素" + myList);
}
}
运行结果:
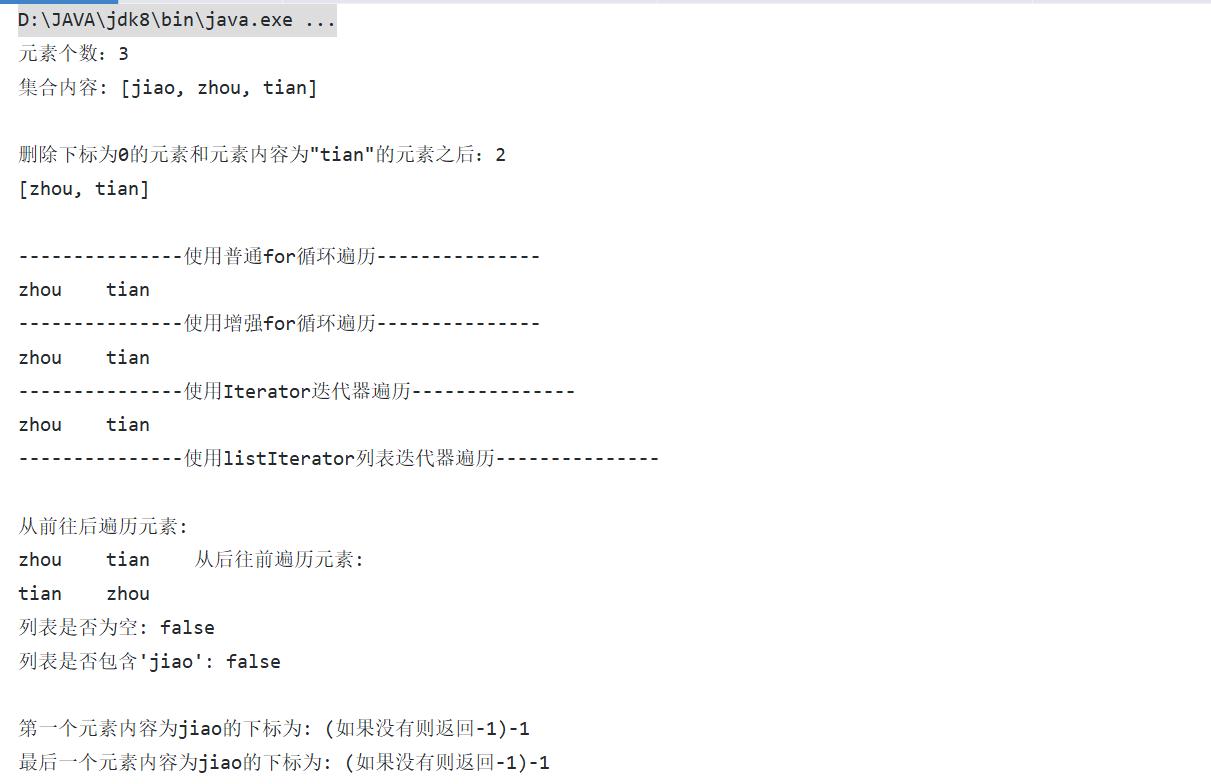

3. 思考: 删除小明
现在有一个Student类:
public class Student {
String name;
String gender;
public Student(String name, String gender) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\\'' +
'}';
}
}
我们创建一个ArrayList集合:
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1 = new Student("小明", "男");
Student s2 = new Student("小王", "男");
Student s3 = new Student("小芳", "女");
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
System.out.println("arrayList大小为: " + arrayList.size());
System.out.println("arrayList内容为: " + arrayList);
运行结果

删除小明:
// 如果我们想要删除小明我们可以这样删除
arrayList.remove(0);
// 也可以这样删
arrayList.remove(s1);
但是大家思考一下 可不可以这样删除:
arrayList.remove(new Student("小明", "男"));
/*
答案是不可以 虽然这2个对象的内容一样, 但是内存地址却不相同
所所以不可以这样删除。
*/
那么我们怎么实现这样删除呢? ⇒ 重写equals方法
-
重写equals方法,只要对象的内容相同,就判断这2个对象是同一个对象
-
现在的Student类:
class Student {
String name;
String gender;
public Student(String name, String gender) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//1.是否为同一对象
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
//2.判断是否为空
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
//3.判断是否是Student类型
if (obj instanceof Student) {
Student student = (Student) obj;
//4.比较属性
return this.name.equals(student.name) && this.gender.equals(student.gender);
}
//不满足,返回false
return false;
}
}
测试删除:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1 = new Student("小明", "男");
Student s2 = new Student("小王", "男");
Student s3 = new Student("小芳", "女");
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
System.out.println("删除前");
System.out.println("arrayList大小为: " + arrayList.size());
System.out.println("arrayList内容为: " + arrayList + "\\n");
System.out.println("删除后");
arrayList.remove(new Student("小明", "男"));
System.out.println("arrayList大小为: " + arrayList.size());
System.out.println("arrayList内容为: " + arrayList);
}

以上是关于Java集合框架 List接口实现类--ArrayList使用 & 删除小明的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java集合框架 List接口实现类--Vector的使用(了解即可)
Java知识33 集合框架 List接口 Map 和set多测师