链路追踪之sleuth全生命周期分析
Posted 鱼翔空
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了链路追踪之sleuth全生命周期分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
项目DDD重构后,所有依赖重新整理,试运行期间发现链路追踪的抓取信息不够丰富,就翻下原来的项目源码,再看下对应的改造下。
环境依赖
-
kafka
-
elasticsearch 7.10.0 (jdk11)
-
Kibana 7.10
-
zipkin server
sleuth
随着微服务的应用,我们运维系统时面临以下问题
-
真实情况的请求链路是什么?
-
链路请求过程中每个耗时了多少?
-
请求的参数以及每个系统的响应是什么?
分布式链路追踪解决了以上这些问题(当然需要自己手动扩展下)
分布式链路追踪(Distributed Tracing),就是将一次分布式请求,通过上下文形成调用链路,进行日志记录,性能监控,并将一次分布式请求的调用情况集中展示。比如各个服务节点上的耗时、请求具体到达哪台机器上、每个服务节点的请求状态等等。
Spring Cloud Sleuth 主要功能就是在分布式系统中提供追踪解决方案,并且兼容支持了 zipkin,它大量借鉴了Google Dapper 的设计。
我们看下整体的结构 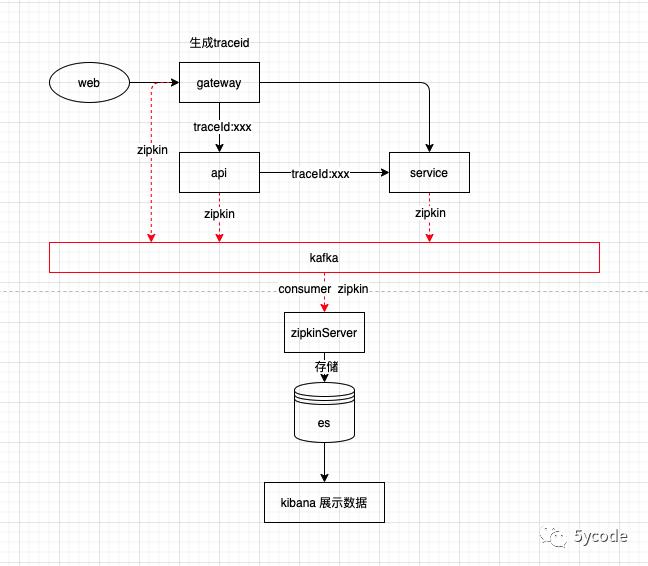
依赖引入
<spring-boot.version>2.3.10.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR11</spring-cloud.version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.10.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--接入zipkin-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--kafka start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
</dependency>
我们从spring-cloud-sleuth-core 和spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin 中查看下spring.factories文件。
Maven: org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-sleuth-core:2.2.8.RELEASE
spring.factories 文件内容
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.annotation.SleuthAnnotationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.autoconfig.TraceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.propagation.SleuthTagPropagationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.TraceHttpAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.TraceWebServletAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.client.TraceWebClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.client.TraceWebAsyncClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.async.AsyncAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.async.AsyncCustomAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.async.AsyncDefaultAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.scheduling.TraceSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.client.feign.TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.hystrix.SleuthHystrixAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.circuitbreaker.SleuthCircuitBreakerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.rxjava.RxJavaAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.reactor.TraceReactorAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.TraceWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.zuul.TraceZuulAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.rpc.TraceRpcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.grpc.TraceGrpcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.messaging.SleuthKafkaStreamsConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.messaging.TraceMessagingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.messaging.TraceSpringIntegrationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.messaging.TraceSpringMessagingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.messaging.websocket.TraceWebSocketAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.opentracing.OpentracingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.redis.TraceRedisAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.quartz.TraceQuartzAutoConfiguration
# Environment Post Processor
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.autoconfig.TraceEnvironmentPostProcessor
Maven: org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin:2.2.8.RELEASE
spring.factories 文件内容
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.zipkin2.ZipkinAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.zipkin2.ZipkinBackwardsCompatibilityAutoConfiguration
我们先看下sleuth的TraceAutoConfiguration
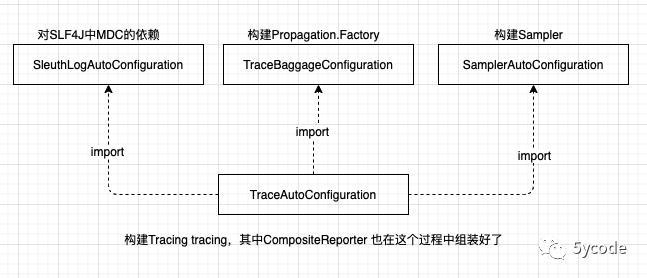
再往下看instrument下面的所有类,通过名称我们也能推测是各种场景的插桩实现。springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.* 随便点进去一个,都是有条件依赖的实现(这是根据你的环境,推断出所有的对应的插桩实现,做到链路跟踪)。
我们看一个TraceHttpAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
// 构建的HttpTracing在brave包中
HttpTracing httpTracing(......){
}
HttpTracing 中具体的servlet场景(还有一个是httpclient) 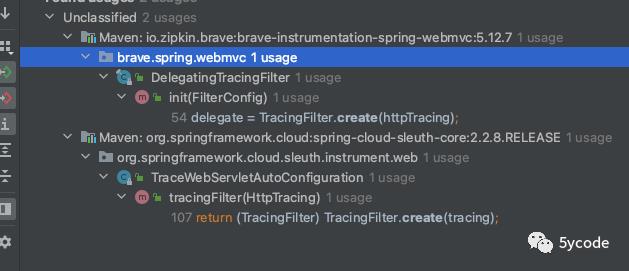
public final class HttpServerHandler<Req, Resp> extends HttpHandler {
public Span handleReceive(HttpServerRequest request) {
Span span = nextSpan(defaultExtractor.extract(request), request);
//可以继续跟下去,最后的解析在sleuth包中的SleuthHttpClientParser,里面的tag类似于SLF4J中的MDC机制
return handleStart(request, span);
}
public void handleSend(@Nullable Resp response, @Nullable Throwable error, Span span) {
if (span == null) throw new NullPointerException("span == null");
if (response == null && error == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Either the response or error parameters may be null, but not both");
}
if (response == null) {
span.error(error).finish();
return;
}
HttpServerResponse serverResponse;
if (response instanceof HttpServerResponse) {
serverResponse = (HttpServerResponse) response;
if (serverResponse.error() == null && error != null) {
span.error(error);
}
} else {
serverResponse = new FromResponseAdapter<>(adapter, response, error);
}
handleFinish(serverResponse, span);
}
void handleFinish(HttpResponse response, Span span) {
try {
parseResponse(response, span);
} catch (Throwable t) {
propagateIfFatal(t);
Platform.get().log("error parsing response {0}", response, t);
} finally {
long finishTimestamp = response.finishTimestamp();
if (finishTimestamp == 0L) {
/**
* 这里会进行资源的释放
* 追到RealSpan
* 追到pendingSpans
* spanHandler
* ZipkinSpanHandler 最后由zipkinSpanHandler进行上送
*/
span.finish();
} else {
span.finish(finishTimestamp);
}
}
}
//具体实现最后也在sleuth包中的SleuthHttpServerParser
void parseResponse(HttpResponse response, Span span) {
responseParser.parse(response, span.context(), span.customizer());
}
}
public class ZipkinSpanHandler extends SpanHandler implements Closeable {
public boolean end(TraceContext context, MutableSpan span, Cause cause) {
if (!this.alwaysReportSpans && !Boolean.TRUE.equals(context.sampled())) {
return true;
} else {
//最终是CompositeReporter,对,就是TraceAutoConfiguration里的
this.spanReporter.report(span);
return true;
}
}
}
多翻看一些sleuth的jar中的org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.中的配置类。
我们可以推断出
-
sleuth层只是按照一定的条件组装各种场景的参数构建与绑定
-
真正的实现在brave各个instrument包中
我们再看下spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin中的配置
yaml中的配置文件
# zipkin sender 选择
spring:
zipkin:
compression:
enabled: true
sender:
type: kafka
关键的几个配置
ZipkinAutoConfiguration
ZipkinSenderProperties
# sender实现的条件判断,由于我们配置的sender.type=kafka只有kafka会实例化
ZipkinSenderCondition extends SpringBootCondition
# kafka具体的配置
ZipkinKafkaSenderConfiguration
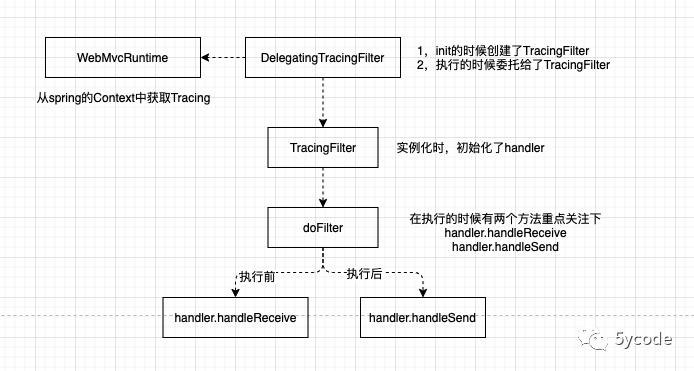
这也就和我们第一张图遥相呼应了。
-
sleuth 通过插桩不同的场景实现链路信息采集;
-
然后通过指定类型的方式,将这些信息发送到zipkinserver
-
zipkinserver 将对应的信息保存到指定的存储引擎(我用的是es)
-
kibana再链接es(用户在使用kibana的时候,能从es中查数据)
最后在根据自己的需求进行入参和出参的增强。
具体可以参考:
https://github.com/yxkong/springboot-gray.git
GatewayTracingFilter 针对gateway进行了增强
TracingFilter 针对mvc进行l 增强
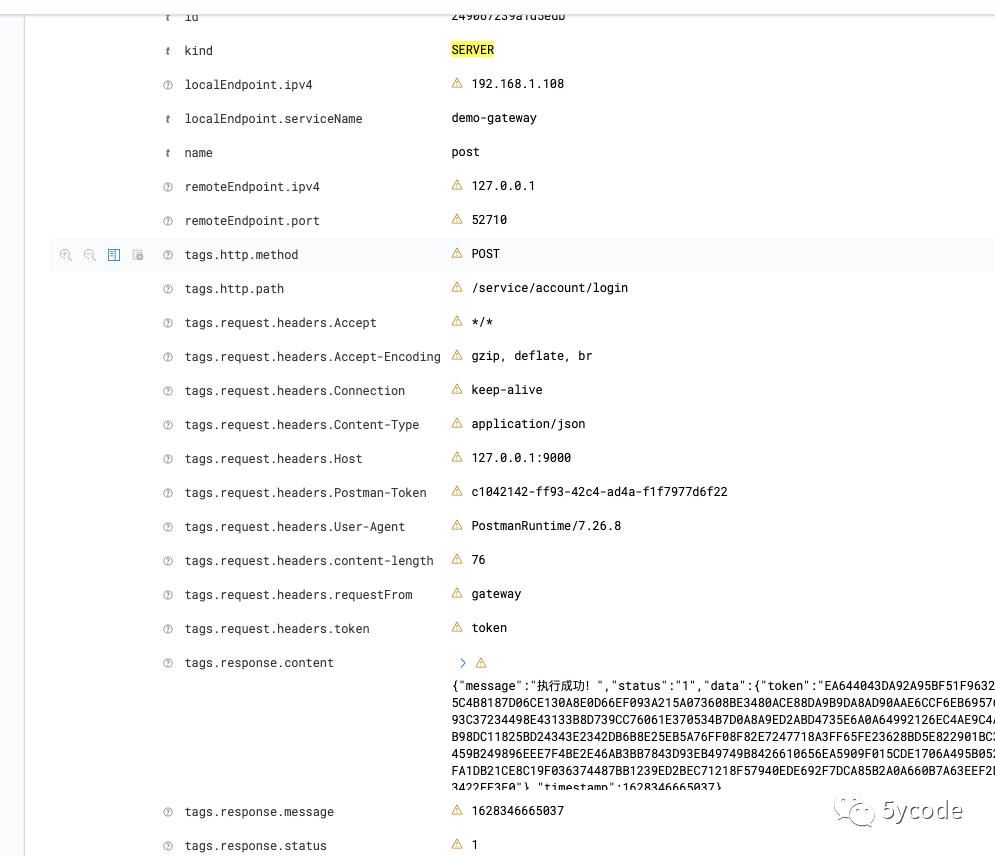
最终效果
如果觉得对你有帮助,请关注公众号:5ycode,后续会不断更新哦

以上是关于链路追踪之sleuth全生命周期分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章