Vue 计算属性和监视属性详解细节 class类绑定和style样式绑定
Posted IT_Holmes
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue 计算属性和监视属性详解细节 class类绑定和style样式绑定 相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
1. Vue 两种实现语法(与计算属性相照应)
1.1 差值语法实现(不推荐)
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>插值语法实现</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model ="firstName"> <br>
名: <input type="text" v-model ="lastName"> <br>
姓名: <span>{{firstName + "." +lastName}}</span> <br>
<!-- slice()来截取内容 -->
姓名: <span>{{firstName.slice(0,3)}}-{{lastName}}</span>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
firstName:"张",
lastName:"三"
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
像下面这样的格式虽然不会报错,但并不推荐使用:
<span>{{firstName.slice(0,3)}}-{{lastName}}</span>
1.2 methods实现 (推荐)
使用methods来实现,相同的功能。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>methods</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
<!-- fullName不写(),相当于把函数放到了这里。 -->
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span> <br>
<!-- 加了fullName()相当于把它的返回值放到这里。 -->
姓名: <span>{{fullName()}}</span> <br>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
firstName:"张",
lastName:"三"
},methods:{
fullName(){
const temp = this.firstName.slice(0,3) + "-" +this.lastName
return temp;
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
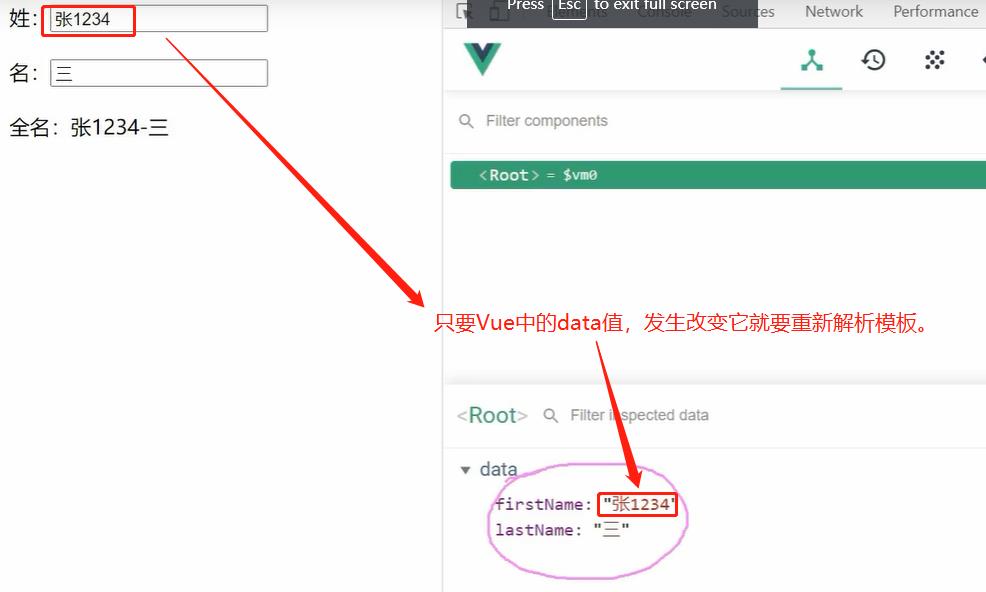
注意:
只要Vue中的data值,发生改变它就要重新解析模板。
2.Vue 计算属性 (推荐使用)
2.1 计算属性 computed get函数
在Vue中,属性就是data中的数据。
而计算属性呢,则是在computed中。compute也是在Vue实例查到,因此我们可以直接使用差值语法来嗲用fullName就行了。
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>计算属性</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
firstName:"张",
lastName:"三"
},
//compute也是在Vue实例查到,因此我们可以直接使用差值语法来嗲用fullName就行了。
computed:{
fullName:{
//get作用,当有人读取fullName时,get就会被调用,且返回值就是作为fullName的值。
get(){
console.log('get');
console.log(this); //这里的this也是指向的Vue实例对象
return this.firstName + "-" + this.lastName;
}
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
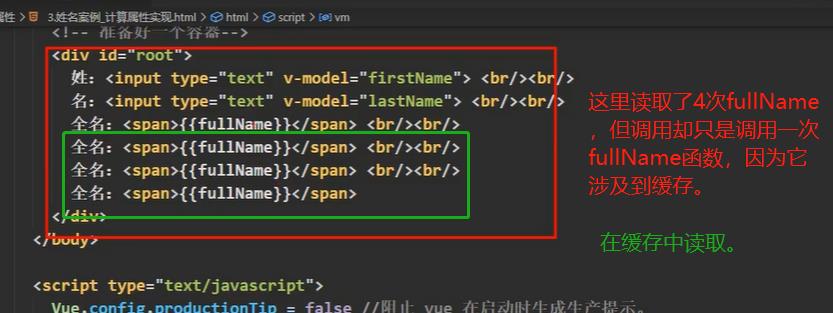
上面因为缓存内容就会考虑什么时候调用get,get什么时候调用?
1. 初次读取fullName时,get会被调用。(这里涉及了页面缓存的问题。)
2. 所依赖的数据发生变化时,也就是data的内容发生变化,自然会重新调用computed中的函数。。
这里关于fullName中的get有一个误区一定注意:

2.2 计算属性 computed set函数
有get,就会有set方法,什么时候会用到set?
当computed中的属性被修改时,就要用到set。
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>计算属性</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
名: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
姓名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
firstName:"张",
lastName:"三"
},
//compute也是在Vue实例查到,因此我们可以直接使用差值语法来嗲用fullName就行了。
computed:{
fullName:{
//get作用,当有人读取fullName时,get就会被调用,且返回值就是作为fullName的值。
get(){
console.log('get');
// console.log(this); //这里的this也是指向的Vue实例对象
return this.firstName + "-" +this.lastName;
},
set(value){
console.log("调用了set方法:",value);
const arr = value.split('-');
this.firstName = arr[0];
this.lastName = arr[1];
}
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
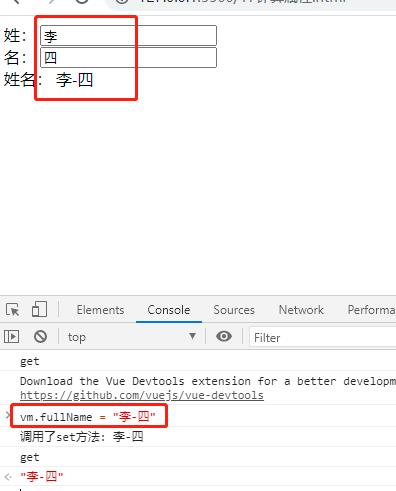
注意:被Vue管理的函数,不要用箭头函数,会改变this。
总结:

2.3 getter的简写(前提不考虑修改,配置setter时)

3. Vue 监视属性
3.1 注意事项
首先,介绍一个插件:
Vue开发者工具存在一个问题,就是如果没有牵动改变页面方面的内容,开发者工具中的root里面的data值一般不会变化,实际上是变化了。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 插值语法要写表达式,不能用if,因为if不是表达式。 因此可以用三元表达式-->
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="chengeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true
},
methods: {
chengeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot; //取反之后的isHot。
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
对于上面这种我们还可以更加简化一些,我们直接在@click中写判断式也是可以的,如下:
<button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换天气</button>
也就是说div模板里面的东西是可以直接调用Vue实例对象中的内容。如果有两个以上的语句是可以通过" ;"来分割的。不过不推荐,还是在methods对象中定义比较好。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 插值语法要写表达式,不能用if,因为if不是表达式。 因此可以用三元表达式-->
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true
},
methods: {
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽";
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
如果我们像用Vue实例对象中没有的事件,例如alert,我们可以在data中导入:

当然,像这种在事件(@xxx = “yyy”)内写的方式不推荐,只是适合比较简单的内容,内容多了就非常冗余。
3.2 监视属性
3.2.1 监视属性watch 写法一
引入新的对象,watch就是用来监视的。
hander()函数: 当被监视的对象发生改变时,它就会被调用。
hander(newValue,oldValue)函数有两个参数,分别是修改前和修改后的值。
与hander对象函数对应的有immediate对象属性,作用就是初始化时,让handler调用一下。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 插值语法要写表达式,不能用if,因为if不是表达式。 因此可以用三元表达式-->
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
},
//watch就是用来监视的。
watch:{
//指定监视isHot,并且在对象中配置监视内容。
isHot:{
//hander()函数很重要,当isHot发生改变时,它就会被调用。
//hander(newValue,oldValue)函数有两个参数,分别是修改前和修改后的值。
immediate:false, //初始化时,让handler调用一下。
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("isHot被修改了",newValue,oldValue);
}
},
//computed中的对象属性也是可以确定的。
info:{
immediate:true,
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("isHot被修改了",newValue,oldValue);
}
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.2.2 监视属性watch 写法二
这里提醒一下,曾经我们对象和值的写法是这样子的,’ key ’ : ’ value ',后来呢只不过默认可以写成了key : ’ value ’ ,这里记一下要。
我们可以使用$watch()来在Vue实例对象外面,来定义监听。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 插值语法要写表达式,不能用if,因为if不是表达式。 因此可以用三元表达式-->
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
vm.$watch('isHot',{
immediate:false,
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("监听isHot。",newValue,oldValue);
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
对于这两种写法,第二种写法比较适合在不确定监测哪一个属性时适用,第一种写法比较适合已经确定好了监听那一个属性。
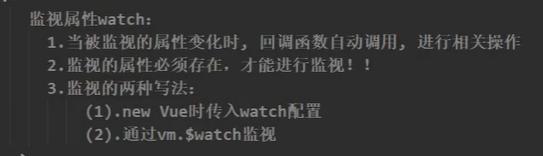
3.3 深度监视属性
因为在对象中键值的key,必须是字符串形式,所以可以写成’ key.xxx ‘:’ value '的样式。
专业术语上是:监视多级结构中某个属性的变化,用下面的样式。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 插值语法要写表达式,不能用if,因为if不是表达式。 因此可以用三元表达式-->
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<hr>
<h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a加1</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true,
numbers:{
//在这里我们只监视a,不监视b,从而达到一个深度监视的效果。
a:1,
b:1
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
},
watch:{
isHot:true,
//因为这里的键值的key,必须是字符串形式,所以可以写成下面的样式。
//专业术语上是:监视多级结构中某个属性的变化,用下面的样式。
'numbers.a'(){
console.log(this.numbers.a);
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
当然,如果有上百个需要监视的对象属性,怎么办?
首先,就是我们不能直接监视numbers本省。因为我们的目标是监视numbers里面的内容,再次就是会发生下图的情况,就算numbers中的a、b发生变化,numbers中的handler也不会执行。
如何解决,这里我们可以配置deep:true来解决。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a加1</button>
<h3>b的值是:{{numbers.b}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b加1</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true,
numbers:{
a:1,
b:1
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
},
watch:{
isHot:true,
numbers:{
//deep默认值是false,配置deep:true可以检测对象内部值发生改变。
deep:true,
handler(){
console.log("number内部发生变化了。")
}
}
}
});
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
总结:

3.5 监视的简写形式
在没有immediate,deep等其他的对象属性,只有handler时可以直接简写形式。
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>今天天气很{{info}}</h1>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a加1</button>
<h3>b的值是:{{numbers.b}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b加1</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
data:{
isHot:true,
numbers:{
a:1,
b:1
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot;
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热":"凉爽"
}
},
watch:{
// isHot:{
// immediate:true,
// deep:true,
// handler(newValue,oldValue){
// console.log('isHost被修改',newValue,oldValue)
// }
// }
//在没有immediate,deep等其他的对象属性,只有handler可以简写为下面样式:
isHot(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("isHost被修改",newValue,oldValue);
}
}
})
vm.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
同样,$watch也是可以简写的,但不能有其他配置对象属性,只能有handler()函数。
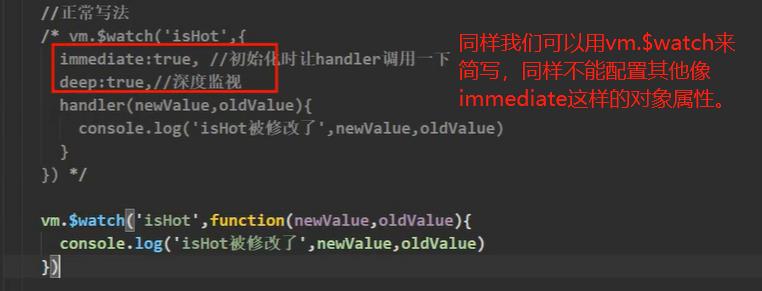
4. watch和computed比较
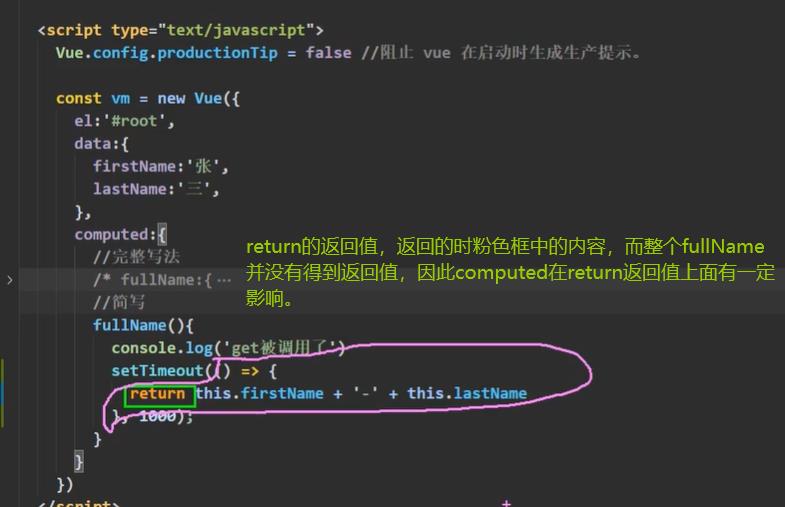
其实,watch和computed区别并不是很大,都能够实现,但computed因为必须有return返回值这一说,所以实现起来,会有一定阻碍。
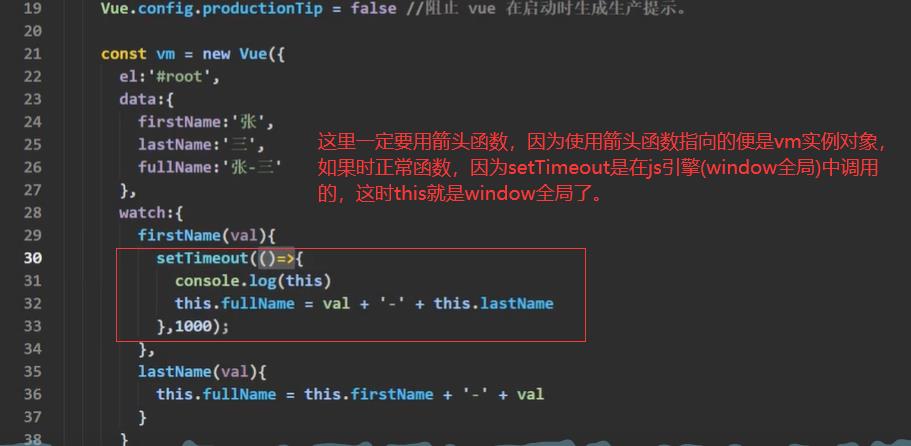
在watch中定义,像setTimeout这样的全局函数,一定要写箭头函数,多注意this的情况。看下图:
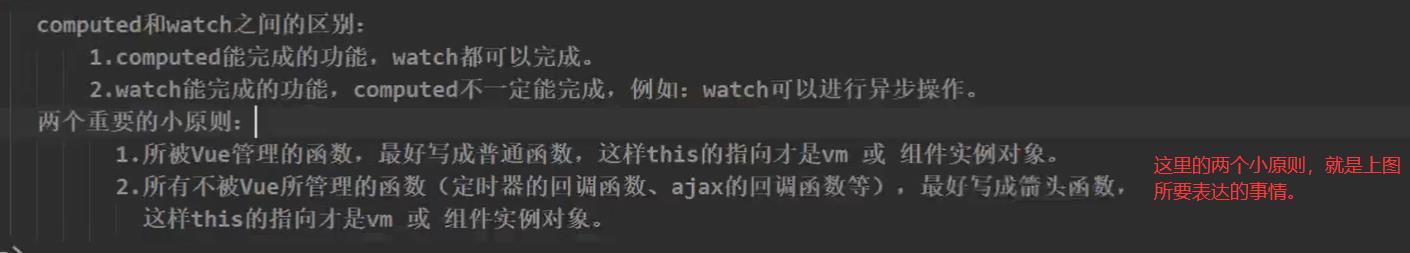
监视属性,现在在官方文档里面叫做侦听属性。

5. Vue绑定 class类
正常的样式正常写就可以,需要通过Vue来改变的样式可以用 :class=“xxx”,这样的方式来写。
5.1 字符串写法
写法一:绑定class样式,字符串写法。
适用于:样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.demo1{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
color: salmon;
}
.demo2{
border: 2px solid black;
}
.demo3{
border: 10px solid red;
}
.demo4{
border: 20px solid green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 绑定class样式,字符串写法,适用于:样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定 -->
<div class="demo1" :class="mood" @click="changeMood">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:'夏洛克',
mood:'demo2'
},
methods:{
changeMood(){
const arr = ['demo2','demo3','demo4'];
const index = Math.floor(Math.random()*3);
this.mood = arr[index];
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
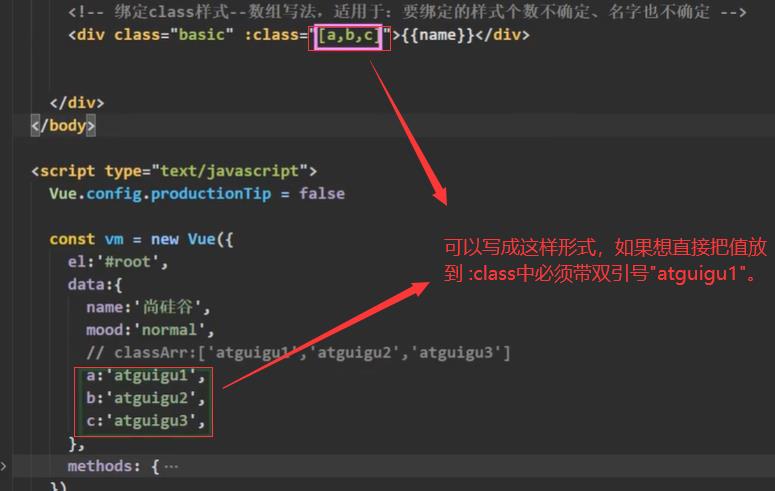
5.2 数组写法
写法二:绑定class样式,数组写法。
适用于:要绑定的样式个数不确定,名字也不确定。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.demo1{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
color: salmon;
}
.demo2{
border: 2px solid black;
}
.demo3{
border: 10px solid red;
}
.demo4{
border: 20px solid green;
}
.backg{
color: grey;
}
.border{
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 当然对于应用多个样式,可以直接在class上面操作就可以。 -->
<!-- 如果应用多个样式也可以写成一个数组形式,当然重要的是对它进行修改删除等操作。 -->
<div class="demo1" :class="arr">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:'夏洛克',
mood:'demo2',
arr:['backg','border','demo3']
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
我们可以操作一些增删改查:
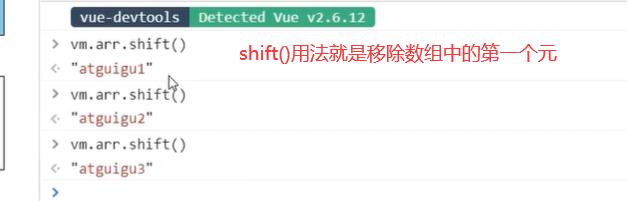
注意事项:
5.3 对象写法
绑定class样式,对象写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数确定,名字也确定,但要动态决定用不用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.demo1{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
color: salmon;
}
.demo2{
border: 2px solid black;
}
.demo3{
border: 10px solid red;
}
.demo4{
border: 20px solid green;
}
.backg{
color: grey;
}
.border{
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="demo1" :class="obj">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:'夏洛克',
mood:'demo2',
obj:{
demo2:true,
demo4:false,
border:true
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
6. Vue绑定 style样式
style样式,也是包括对象写法和数组写法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 对象写法 -->
<div :style="styleObj">{{name}}</div>
<!-- 数组写法 -->
<div :style="[styleObj,styleObj2]">{{name}}</div>
<div :style="styleArr">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script>
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:'夏洛克',
mood:'demo2',
styleObj:{
fontSize:'50px', //font-size这里设置成了fontSize。
color:'red'
},
styleObj2:{
backgroundColor:'orange'
},
styleArr: [
{ //用数组形式来表现
fontSize: '50px',
color: 'red'
},
{
backgroundColor: 'orange'
}
]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>

样式对象理解:
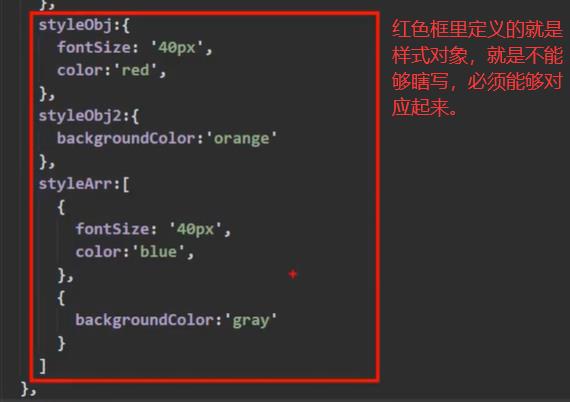
以上是关于Vue 计算属性和监视属性详解细节 class类绑定和style样式绑定 的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章