YOLOV5-5.0 源码解读plots.py
Posted 满船清梦压星河HK
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了YOLOV5-5.0 源码解读plots.py相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
- 前言
- 0、导入需要的包和基本配置
- 1、Colors
- 2、plot_one_box、plot_one_box_PIL
- 3、plot_wh_methods(没用到)
- 4、output_to_target、plot_images
- 5、plot_lr_scheduler
- 6、hist2d、plot_test_txt、plot_targets_txt
- 7、plot_labels
- 8、plot_evolution
- 9、plot_results、plot_results_overlay、butter_lowpass_filtfilt
- 10、feature_visualization
- 11、plot_study_txt(没用到)、profile_idetection(没用到)
- 总结
前言
源码: YOLOv5源码.
导航: 【YOLOV5-5.0 源码讲解】整体项目文件导航.
\\qquad 这个文件都是一些画图函数,是一个工具类。代码本身逻辑并不难,主要是一些包的函数可能大家没见过。这里我总结了一些画图包的一些常见的画图函数: 【Opencv、ImageDraw、Matplotlib、Pandas、Seaborn】一些常见的画图函数。如果在下面代码中碰到不太熟的画图函数,可以查一下我的笔记或者自己百度一下。
0、导入需要的包和基本配置
import glob # 仅支持部分通配符的文件搜索模块
import math # 数学公式模块
import os # 与操作系统进行交互的模块
from copy import copy # 提供通用的浅层和深层copy操作
from pathlib import Path # Path将str转换为Path对象 使字符串路径易于操作的模块
import cv2 # opencv库
import matplotlib # matplotlib模块
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # matplotlib画图模块
import numpy as np # numpy矩阵处理函数库
import pandas as pd # pandas矩阵操作模块
import seaborn as sn # 基于matplotlib的图形可视化python包 能够做出各种有吸引力的统计图表
import torch # pytorch框架
import yaml # yaml配置文件读写模块
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont # 图片操作模块
from torchvision import transforms # 包含很多种对图像数据进行变换的函数
from utils.general import increment_path, xywh2xyxy, xyxy2xywh
from utils.metrics import fitness
# 设置一些基本的配置 Settings
matplotlib.rc('font', **{'size': 11}) # 自定义matplotlib图上字体font大小size=11
# 在PyCharm 页面中控制绘图显示与否
# 如果这句话放在import matplotlib.pyplot as plt之前就算加上plt.show()也不会再屏幕上绘图 放在之后其实没什么用
matplotlib.use('Agg') # for writing to files only
1、Colors
\\qquad 这是一个颜色类,用于选择相应的颜色,比如画框线的颜色,字体颜色等等。
Colors类代码:
class Colors:
# Ultralytics color palette https://ultralytics.com/
def __init__(self):
# hex = matplotlib.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.values()
hex = ('FF3838', 'FF9D97', 'FF701F', 'FFB21D', 'CFD231', '48F90A', '92CC17', '3DDB86', '1A9334', '00D4BB',
'2C99A8', '00C2FF', '344593', '6473FF', '0018EC', '8438FF', '520085', 'CB38FF', 'FF95C8', 'FF37C7')
# 将hex列表中所有hex格式(十六进制)的颜色转换rgb格式的颜色
self.palette = [self.hex2rgb('#' + c) for c in hex]
# 颜色个数
self.n = len(self.palette)
def __call__(self, i, bgr=False):
# 根据输入的index 选择对应的rgb颜色
c = self.palette[int(i) % self.n]
# 返回选择的颜色 默认是rgb
return (c[2], c[1], c[0]) if bgr else c
@staticmethod
def hex2rgb(h): # rgb order (PIL)
# hex -> rgb
return tuple(int(h[1 + i:1 + i + 2], 16) for i in (0, 2, 4))
colors = Colors() # 初始化Colors对象 下面调用colors的时候会调用__call__函数
使用起来也是比较简单只要直接输入颜色序号即可:
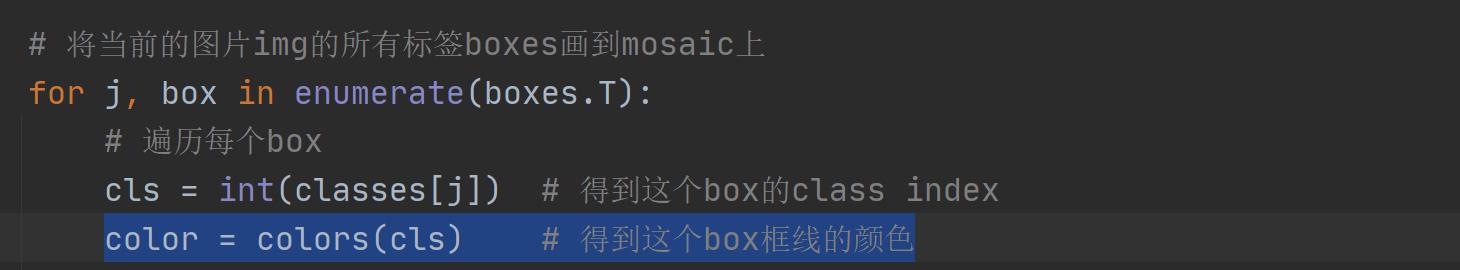
2、plot_one_box、plot_one_box_PIL
\\qquad plot_one_box 和 plot_one_box_PIL 这两个函数都是用于在原图im上画一个bounding box,区别在于前者使用的是opencv画框,后者使用PIL画框。这两个函数的功能其实是重复的,其实我们用的比较多的是plot_one_box函数,plot_one_box_PIL几乎没用,了解下即可。
2.1、plot_one_box
\\qquad 这个函数通常用在检测nms后(detect.py中)将最终的预测bounding box在原图中画出来,不过这个函数依次只能画一个框框。
plot_one_box函数代码:
def plot_one_box(x, im, color=(128, 128, 128), label=None, line_thickness=3):
"""一般会用在detect.py中在nms之后变量每一个预测框,再将每个预测框画在原图上
使用opencv在原图im上画一个bounding box
:params x: 预测得到的bounding box [x1 y1 x2 y2]
:params im: 原图 要将bounding box画在这个图上 array
:params color: bounding box线的颜色
:params labels: 标签上的框框信息 类别 + score
:params line_thickness: bounding box的线宽
"""
# check im内存是否连续
assert im.data.contiguous, 'Image not contiguous. Apply np.ascontiguousarray(im) to plot_on_box() input image.'
# tl = 框框的线宽 要么等于line_thickness要么根据原图im长宽信息自适应生成一个
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (im.shape[0] + im.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
# c1 = (x1, y1) = 矩形框的左上角 c2 = (x2, y2) = 矩形框的右下角
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
# cv2.rectangle: 在im上画出框框 c1: start_point(x1, y1) c2: end_point(x2, y2)
# 注意: 这里的c1+c2可以是左上角+右下角 也可以是左下角+右上角都可以
cv2.rectangle(im, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# 如果label不为空还要在框框上面显示标签label + score
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # label字体的线宽 font thickness
# cv2.getTextSize: 根据输入的label信息计算文本字符串的宽度和高度
# 0: 文字字体类型 fontScale: 字体缩放系数 thickness: 字体笔画线宽
# 返回retval 字体的宽高 (width, height), baseLine 相对于最底端文本的 y 坐标
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
# 同上面一样是个画框的步骤 但是线宽thickness=-1表示整个矩形都填充color颜色
cv2.rectangle(im, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
# cv2.putText: 在图片上写文本 这里是在上面这个矩形框里写label + score文本
# (c1[0], c1[1] - 2)文本左下角坐标 0: 文字样式 fontScale: 字体缩放系数
# [225, 255, 255]: 文字颜色 thickness: tf字体笔画线宽 lineType: 线样式
cv2.putText(im, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
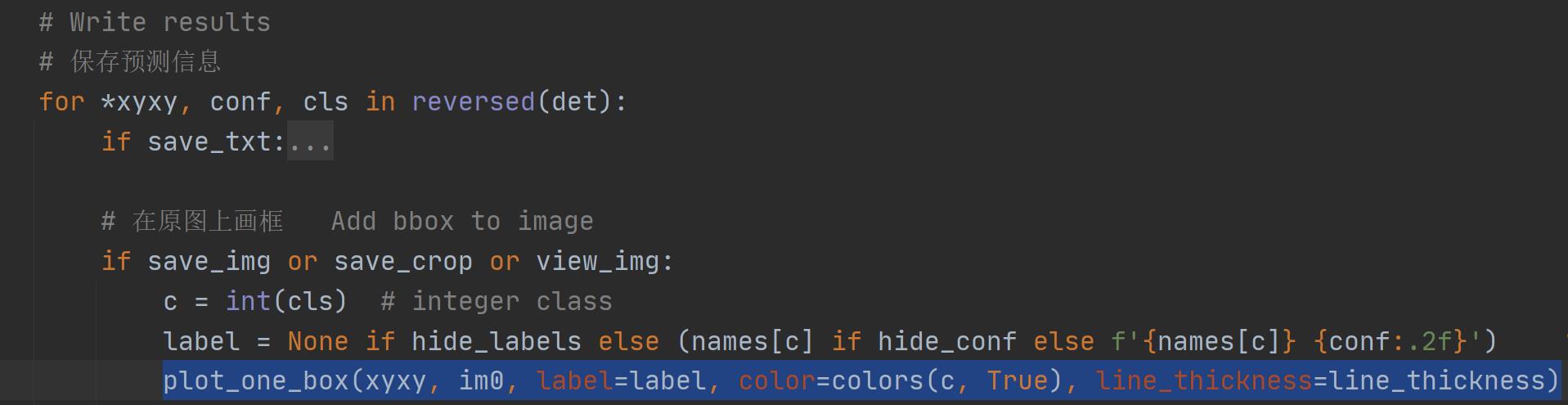
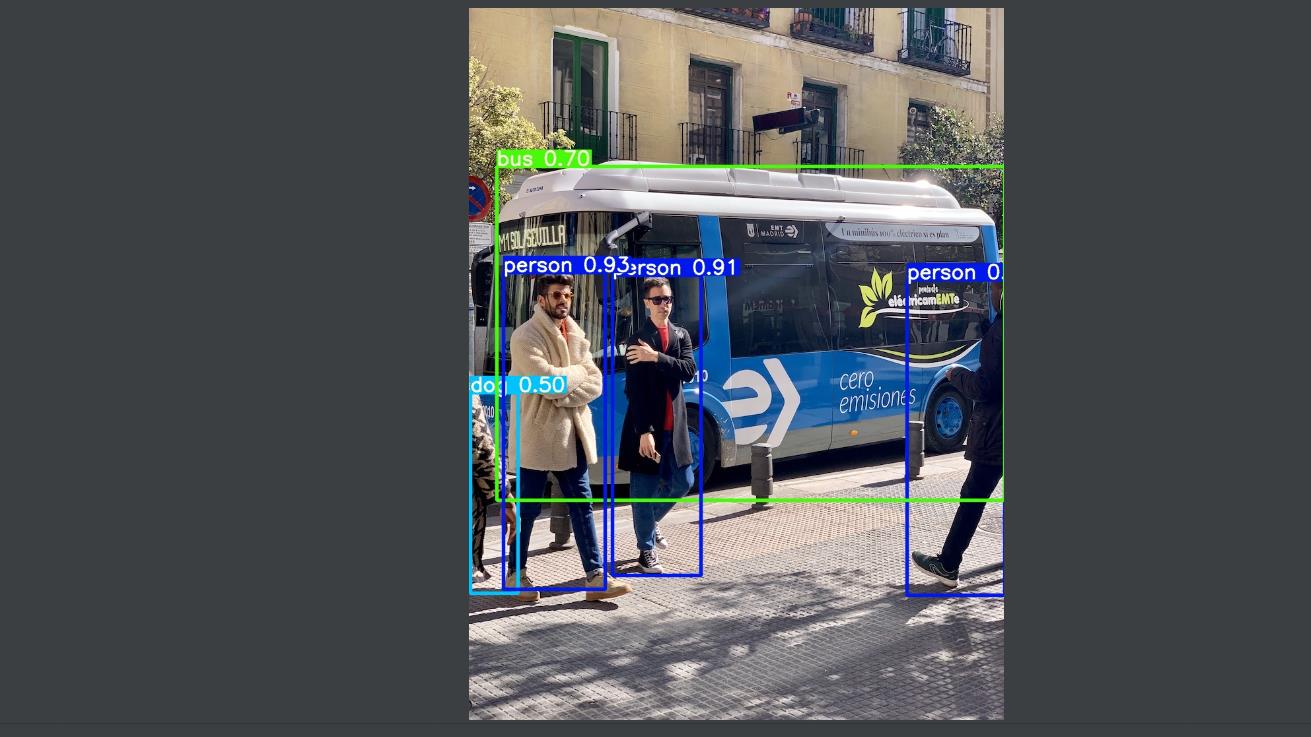
这个函数一般会用在detect.py中在nms之后变量每一个预测框,再将每个预测框画在原图上如:
效果如下所示:
2.2、plot_one_box_PIL(没用到)
\\qquad 这个函数是用PIL在原图中画一个框,作用和plot_one_box一样,而且我们一般都是用plot_one_box而不用这个函数,所以了解下即可。
plot_one_box_PIL函数代码:
def plot_one_box_PIL(box, im, color=(128, 128, 128), label=None, line_thickness=None):
"""
使用PIL在原图im上画一个bounding box
:params box: 预测得到的bounding box [x1 y1 x2 y2]
:params im: 原图 要将bounding box画在这个图上 array
:params color: bounding box线的颜色
:params label: 标签上的bounding box框框信息 类别 + score
:params line_thickness: bounding box的线宽
"""
# 将原图array格式->Image格式
im = Image.fromarray(im)
# (初始化)创建一个可以在给定图像(im)上绘图的对象, 在之后调用draw.函数的时候不需要传入im参数,它是直接针对im上进行绘画的
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
# 设置绘制bounding box的线宽
line_thickness = line_thickness or max(int(min(im.size) / 200), 2)
# 在im图像上绘制bounding box
# xy: box [x1 y1 x2 y2] 左上角 + 右下角 width: 线宽 outline: 矩形外框颜色color fill: 将整个矩形填充颜色color
# outline和fill一般根据需求二选一
draw.rectangle(box, width=line_thickness, outline=color) # plot
# 如果label不为空还要在框框上面显示标签label + score
if label:
# 加载一个TrueType或者OpenType字体文件("Arial.ttf"), 并且创建一个字体对象font, font写出的字体大小size=12
font = ImageFont.truetype("Arial.ttf", size=max(round(max(im.size) / 40), 12))
# 返回给定文本label的宽度txt_width和高度txt_height
txt_width, txt_height = font.getsize(label)
# 在im图像上绘制矩形框 整个框框填充颜色color(用来存放label信息) [x1 y1 x2 y2] 左上角 + 右下角
draw.rectangle([box[0], box[1] - txt_height + 4, box[0] + txt_width, box[1]], fill=color)
# 在上面这个矩形中写入text信息(label) x1y1 左上角
draw.text((box[0], box[1] - txt_height + 1), label, fill=(255, 255, 255), font=font)
# 再返回array类型的im(绘好bounding box和label的)
return np.asarray(im)
3、plot_wh_methods(没用到)
\\qquad 这个函数主要是用来比较 y a = e x y_a = e^x ya=ex 、 y b = ( 2 ∗ s i g m o i d ( x ) ) 2 y_b = (2 * sigmoid(x))^2 yb=(2∗sigmoid(x))2 、 y c = ( 2 ∗ s i g m o i d ( x ) ) 1.6 y_c = (2 * sigmoid(x))^{1.6} yc=(2∗sigmoid(x))1.6 这三个函数图形的。其中 y a y_a ya 是普通的yolo method, y b y_b yb 和 y c y_c yc是作者提出的powe method方法。在 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/168.中,作者由讨论过这个issue。作者在实验中发现使用原来的yolo method损失计算有时候会突然迅速走向无限None值, 而power method方式计算wh损失下降会比较平稳。最后实验证明 y b y_b yb 是最好的wh损失计算方式, yolov5-5.0的wh损失计算代码用的就是 y b y_b yb 计算方式 如:
yolo.py:
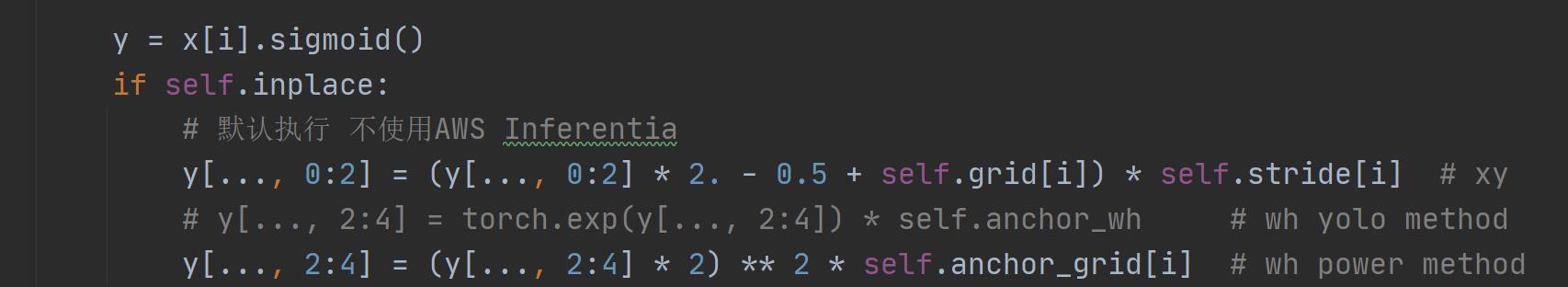
loss.py:
plot_wh_methods函数代码:
def plot_wh_methods():
"""没用到
比较ya=e^x、yb=(2 * sigmoid(x))^2 以及 yc=(2 * sigmoid(x))^1.6 三个图形
wh损失计算的方式ya、yb、yc三种 ya: yolo method yb/yc: power method
实验发现使用原来的yolo method损失计算有时候会突然迅速走向无限None值, 而power method方式计算wh损失下降会比较平稳
最后实验证明yb是最好的wh损失计算方式, yolov5-5.0的wh损失计算代码用的就是yb计算方式
Compares the two methods for width-height anchor multiplication
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/168
"""
x = np.arange(-4.0, 4.0, .1) # (-4.0, 4.0) 每隔0.1取一个值
ya = np.exp(x) # ya = e^x yolo method
yb = torch.sigmoid(torch.from_numpy(x)).numpy() * 2 # yb = 2 * sigmoid(x)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3), tight_layout=True) # 创建自定义图像 初始化画布
plt.plot(x, ya, '.-', label='YOLOv3') # 绘制折线图 可以任意加几条线
plt.plot(x, yb ** 2, '.-', label='YOLOv5 ^2')
plt.plot(x, yb ** 1.6, '.-', label='YOLOv5 ^1.6')
plt.xlim(left=-4, right=4) # 设置x轴、y轴范围
plt.ylim(bottom=0, top=6)
plt.xlabel('input') # 设置x轴、y轴标签
plt.ylabel('output')
plt.grid() # 生成网格
plt.legend() # 加上图例 如果是折线图,需要在plt.plot中加入label参数(图例名)
fig.savefig('comparison.png', dpi=200) # plt绘完图, fig.savefig()保存图片
\\qquad 其实这个函数倒不是特别重要,只是可视化一下这三个函数,看看他们的区别,在代码中也没调用过这个函数。但是了解这种新型 wh 损失计算的方式(Power Method)还是很有必要的。
4、output_to_target、plot_images
\\qquad 这两个函数其实也是对检测到的目标格式进行处理(output_to_target)然后再将其画框显示在原图上(plot_images)。不过这两个函数是用在test.py中的,针对的也不再是一张图片一个框,而是整个batch中的所有框。而且plot_images会将整个batch的图片都画在一张大图mosaic中,画不下的就删除。这些都是plot_images函数和plot_one_box的区别。
4.1、output_to_target
\\qquad 这个函数是用于将经过nms后的output [num_obj,x1y1x2y2+conf+cls] -> [num_obj,batch_id+class+xywh+conf]。并不涉及画图操作,而是转化predict的格式,通常放在画图操作plot_images之前。
output_to_target函数代码:
def output_to_target(output):
"""用在test.py中进行绘制前3个batch的预测框predictions 因为只有predictions需要修改格式 target是不需要修改格式的
将经过nms后的output [num_obj,x1y1x2y2+conf+cls] -> [num_obj, batch_id+class+x+y+w+h+conf] 转变格式
以便在plot_images中进行绘图 + 显示label
Convert model output to target format [batch_id, class_id, x, y, w, h, conf]
:params output: list{tensor(8)}分别对应着当前batch的8(batch_size)张图片做完nms后的结果
list中每个tensor[n, 6] n表示当前图片检测到的目标个数 6=x1y1x2y2+conf+cls
:return np.array(targets): [num_targets, batch_id+class+xywh+conf] 其中num_targets为当前batch中所有检测到目标框的个数
"""
targets = []
for i, o in enumerate(output): # 对每张图片分别做处理
for *box, conf, cls in o.cpu().numpy(): # 对每张图片的每个检测到的目标框进行convert格式
targets.append([i, cls, *list(*xyxy2xywh(np.array(box)[None])), conf])
return np.array(targets)
4.1、plot_images
\\qquad 这个函数是用来绘制一个batch的所有图片的框框(真实框或预测框)。使用在test.py中,且在output_to_target函数之后。而且这个函数是将一个batch的图片都放在一个大图mosaic上面,放不下删除。
plot_images函数代码:
def plot_images(images, targets, paths=None, fname='images.jpg', names=None, max_size=640, max_subplots=16):
"""用在test.py中进行绘制前3个batch的ground truth和预测框predictions(两个图) 一起保存 或者train.py中
将整个batch的labels都画在这个batch的images上
Plot image grid with labels
:params images: 当前batch的所有图片 Tensor [batch_size, 3, h, w] 且图片都是归一化后的
:params targets: 直接来自target: Tensor[num_target, img_index+class+xywh] [num_target, 6]
来自output_to_target: Tensor[num_pred, batch_id+class+xywh+conf] [num_pred, 7]
:params paths: tuple 当前batch中所有图片的地址
如: '..\\\\datasets\\\\coco128\\\\images\\\\train2017\\\\000000000315.jpg'
:params fname: 最终保存的文件路径 + 名字 runs\\train\\exp8\\train_batch2.jpg
:params names: 传入的类名 从class index可以相应的key值 但是默认是None 只显示class index不显示类名
:params max_size: 图片的最大尺寸640 如果images有图片的大小(w/h)大于640则需要resize 如果都是小于640则不需要resize
:params max_subplots: 最大子图个数 16
:params mosaic: 一张大图 最多可以显示max_subplots张图片 将总多的图片(包括各自的label框框)一起贴在一起显示
mosaic每张图片的左上方还会显示当前图片的名字 最好以fname为名保存起来
"""
if isinstance(images, torch.Tensor):
images = images.cpu().以上是关于YOLOV5-5.0 源码解读plots.py的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章