UVA434 Matty‘s Blocks贪心
Posted 海岛Blog
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了UVA434 Matty‘s Blocks贪心相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Little Matty liked playing with his blocks very much. He always constructed his ‘buildings’ in the same way: he made stacks of one or more blocks, and he put those stacks on a square table that was exactly K blocks wide (K = 8 for his
largest table, so it could contain up to 8×8 block stacks). He didn’t put the stacks randomly on the table. No, he always
made a nice ‘square’ pattern. In most buildings, there was no pattern visible in the heights of the stacks. However, since
Little Matty himself was only eight blocks tall, a single stack of blocks never consisted of more than eight blocks.
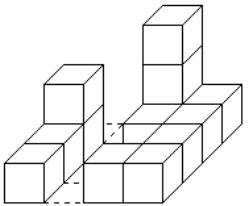
On the right, an example of one of his buildings. It was built on a table that could contain 4 × 4 block stacks.
He liked drawing too. To record his block buildings for future generations, he would draw them on paper. Since drawing a three-dimensional block building just was too hard for him, he made two drawings of a building: one straight from the front (you could only see the front of the blocks), and one from the right (you could only see the right side of the blocks). The drawings were in fact twodimensional projections of the block building, showing only its outline on the front or on the right side.
These are the drawings he made of the building shown above.
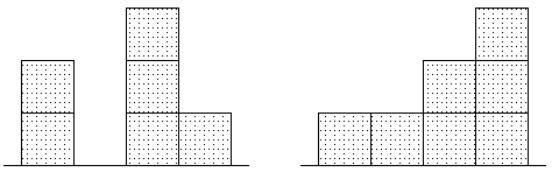
He thought that such a pair of drawings would give enough information to be able to re-build the block building later (but he never tried it).
Years later, looking again at the drawings, he realized that this was not the case: from most pairs of drawings, he was able to construct more than one building that had the same outlines (front and right side) as the original one. He found out that from every (front, side)-pair of drawings that he had made, he could construct a ‘minimal’ building, one that has the same outlines as the original building and contains a minimal number of blocks N (so it was not possible to construct a building with the same outlines with less than N blocks). Furthermore, he could add more blocks to this minimal building, so that the outlines remained the same, up to the point that he had added M (M ≥ 0) blocks and he had a ‘maximal’ building, one that still had the same outlines as his minimal one, and adding one extra block would result in a building with a different outline (so there are no buildings with the same outlines that contain more than N + M blocks).
As an example, these are minimal and maximal buildings for the drawings shown above. In this case, N = 7 and M = 10.
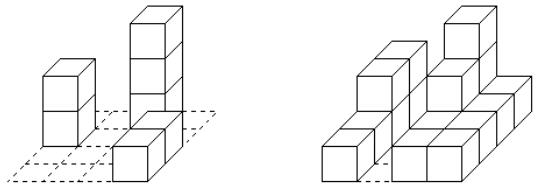
Matty started determining the N and M for every pair of drawings he had made, but soon he found this task to be tedious. Now he asks you to write a program that does the job for him!
Input
The input contains on the first line the number of test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing only the size of the table K. The next pair of lines each contain the description of one drawing. Each description consists of K non-negative integers separated by spaces. Each number indicates the height of the corresponding projection of a stack of blocks in the drawing. The description of the front drawing always precedes the description of the right side drawing. From each pair of drawings at least one block building can be constructed.
Output specification
For each test case output the following line:
Matty needs at least N blocks, and can add at most M extra blocks.
Sample Input
2
4
2 0 3 1
1 1 2 3
1
1
1
Sample Output
Matty needs at least 7 blocks, and can add at most 10 extra blocks.
Matty needs at least 1 blocks, and can add at most 0 extra blocks.
问题链接:UVA434 Matty’s Blocks
问题简述:(略)
问题分析:用贪心法来解决,尽量让大方块挡着小方块。
程序说明:(略)
参考链接:(略)
题记:(略)
AC的C++语言程序如下:
/* UVA434 Matty's Blocks */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10 + 1;
int a, cnt1[N], cnt2[N];
int main()
{
int t, n;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
memset(cnt1, 0, sizeof cnt1);
memset(cnt2, 0, sizeof cnt2);
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a);
cnt1[a]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a);
cnt2[a]++;
}
int mina = 0, maxa = 0, left = n, right = n;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
mina += max(cnt1[i], cnt2[i]) * i;
maxa += left * right;
left -= cnt1[i];
right -= cnt2[i];
}
printf("Matty needs at least %d blocks, and can add at most %d extra blocks.\\n", mina, maxa - mina - n * n);
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于UVA434 Matty‘s Blocks贪心的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章