并查集的学习和模拟实现
Posted zhaocx111222333
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了并查集的学习和模拟实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
并查集
将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合,然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于那个集合的运算。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集。
采用了类似于森林的数据形式。
特点:
1.初始化为-1;
2.在一组的数据选出一个代表当根节点,根节点用负数存储该集合的元素个数
3.集合的其他节点存根节点的索引。
4.将两个数据加入到一个结合,要先判断它们的顶级跟集合是否在一起,在一起则结束,若不在一起需要将两个根节点再次构造为一个集合(被选为子节点的根节点的子节点不变)
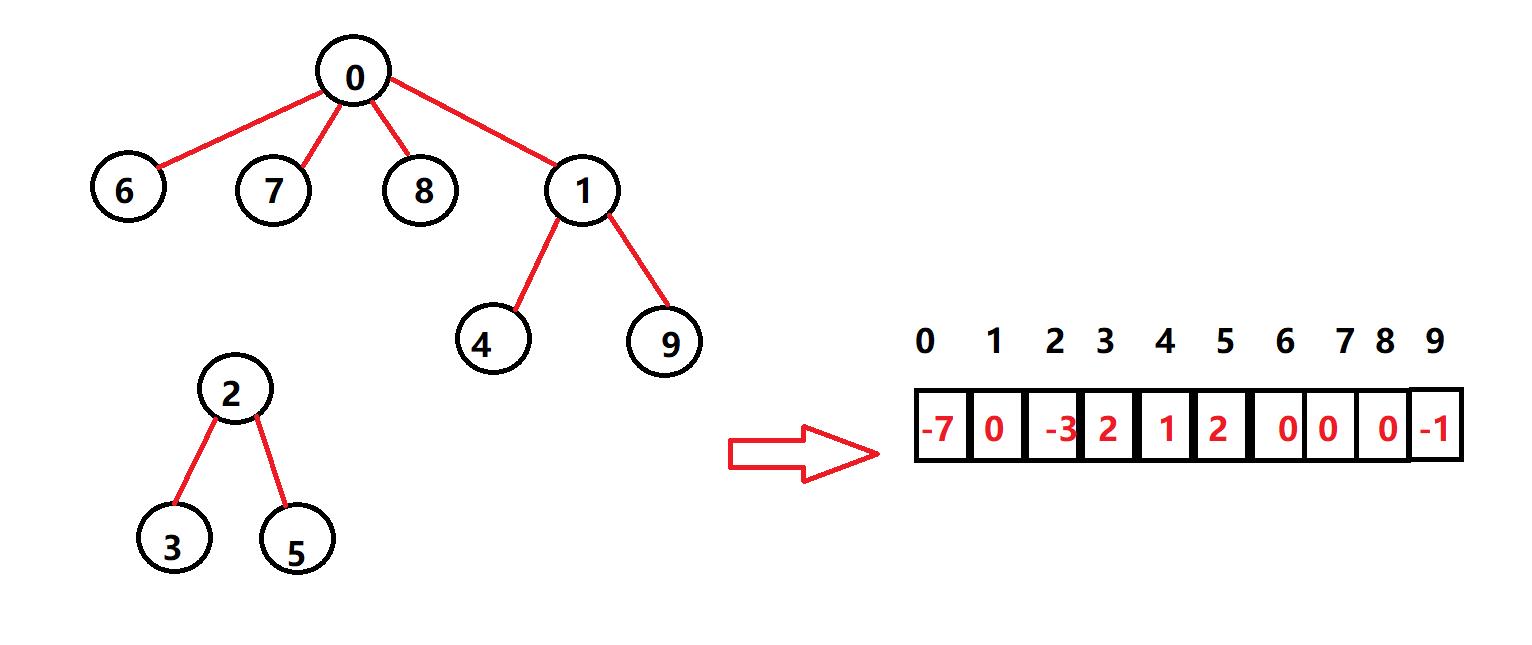
图示:
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class UnionFindSet
{
public: // 初始时,将数组中元素全部设置为-1
UnionFindSet(size_t size)
: _ufs(size, -1)
{}
int FindRoot(int index){ // 给一个元素的编号,找到该元素所在集合的名称
while (_ufs[index] >= 0){ // 根据下标拿到内容
index = _ufs[index];
}
return index; //得到根集合的索引
}
bool Union(int x1, int x2){ //将两个内容插入一个集合
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (root1 == root2) // x1已经与x2在同一个集合
return false; // 将两个集合中元素合并(两个负数相加)
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2]; //只有根节点变了,这个变化的根节点的字节的跟还是他
_ufs[root2] = root1; // 将其中一个集合名称改变成另外一个(随便指定一个根集合
return true;
}
// 数组中负数的个数,即为集合的个数
size_t Count()const{
size_t count = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs){
if (e < 0)
++count;
}
return count;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs;
};
class BCJ{
public:
BCJ(int size):v(size,-1){}
int getroot(int point){
while(v[point]>=0){
point=v[point];
}
return point;
}
bool Union(int a,int b){
int roota=getroot(a);
int rootb=getroot(b);
if(roota==rootb){return false;}
v[roota]+=v[rootb];
v[rootb]=roota;
return true;
}
private:vector<int> v;
};
class Solution {
public:
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations) {
if(equations.size()==0){return false;}
BCJ b(26);
for(auto &i:equations){
if(i[1]=='='){
b.Union(i[0]-'a',i[3]-'a');
}
}
for(auto &i:equations){
if(i[1]=='!'){
int roota=b.getroot(i[0]-'a');
int rootb=b.getroot(i[3]-'a');
if(roota==rootb){return false;}
}
}
return true;
}
};
以上是关于并查集的学习和模拟实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章