LeetCode经典题分类(树&图 )精选 - JavaScript - ES6 - 技巧总结
Posted YK菌
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode经典题分类(树&图 )精选 - JavaScript - ES6 - 技巧总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

树类
树的遍历
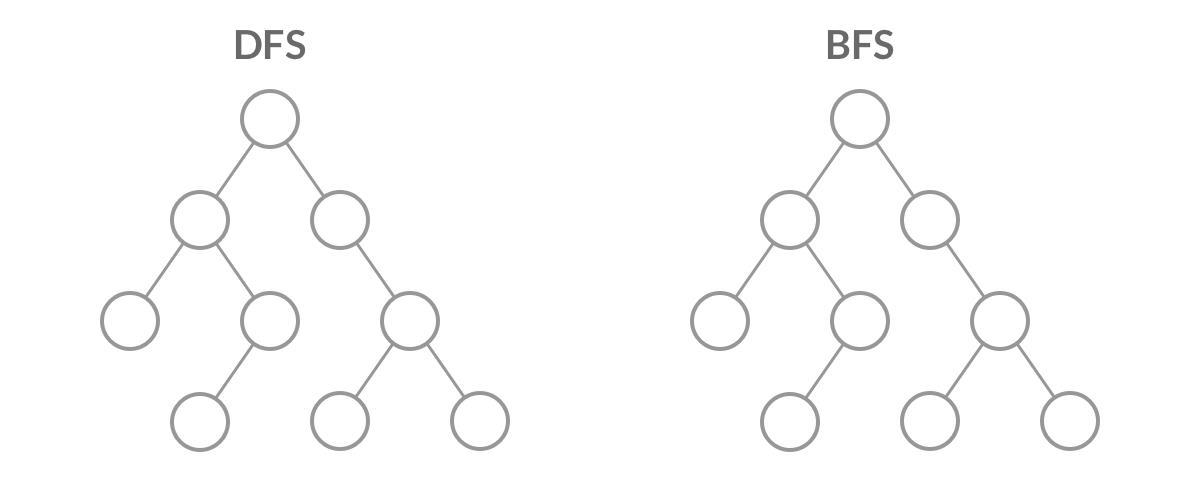
深度优先遍历DFS (递归)
function DFS(root) {
if (root === null) return;
DFS(root.left);
DFS(root.right);
}
广度优先遍历BFS (队列)
function BFS(root){
const queue = [];
queue.unshift(root);
while(queue.length > 0) {
root = queue.pop();
if(root.left) queue.unshift(root.left);
if(root.right) queue.unshift(root.right);
}
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
中序遍历是先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,然后遍历右子树。
左-中-右
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
前序:根左右;中序:左根右;后序:左右根;
中序常用来在二叉搜索数中得到递增的有序序列;
后序可用于数学中的后缀表示法,结合栈处理表达式,每遇到一个操作符,就可以从栈中弹出栈顶的两个元素,计算并将结果返回到栈中;
【解法一】递归DFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
function inorderTraversal(root) {
const result = [];
// 定义递归函数
function inorder(root) {
// 递归出口,直到节点为空,直接返回,退出递归
if (root === null) return;
// 递归调用,传入根节点的左孩子
inorder(root.left);
// 将根节点的值放入result数组中
result.push(root.val);
// 递归调用,传入根节点的右孩子
inorder(root.right);
}
// 表示当前遍历到root节点的答案
inorder(root);
return result;
}
【解法二】非递归迭代法
非递归,用一个栈
中序
function inorderTraversal(root) {
const result = []
const stack = []
while(root || stack.length > 0){
while(root){
stack.push(root)
root = root.left
}
root = stack.pop()
result.push(root.val)
root = root.right
}
return result
}
前序
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
const result = []
const stack = []
while(root || stack.length > 0){
while(root){
result.push(root.val)
stack.push(root)
root = root.left
}
root = stack.pop()
root = root.right
}
return result
};

后序
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
const result = []
const stack = []
let prev = null
while(root || stack.length > 0){
while(root){
stack.push(root)
root = root.left
}
root = stack.pop()
if(root.right === null || root.right === prev){
result.push(root.val)
prev = root
root = null
}else {
stack.push(root)
root = root.right
}
}
return result
};
【解法三】Morris 中序遍历
function inorderTraversal(root) {
const result = [];
let predecessor = null;
while (root !== null) {
if (root.left) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right && predecessor.right !== root) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (!predecessor.right) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
} else {
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
result.push(root.val);
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
} else {
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
result.push(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return result;
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
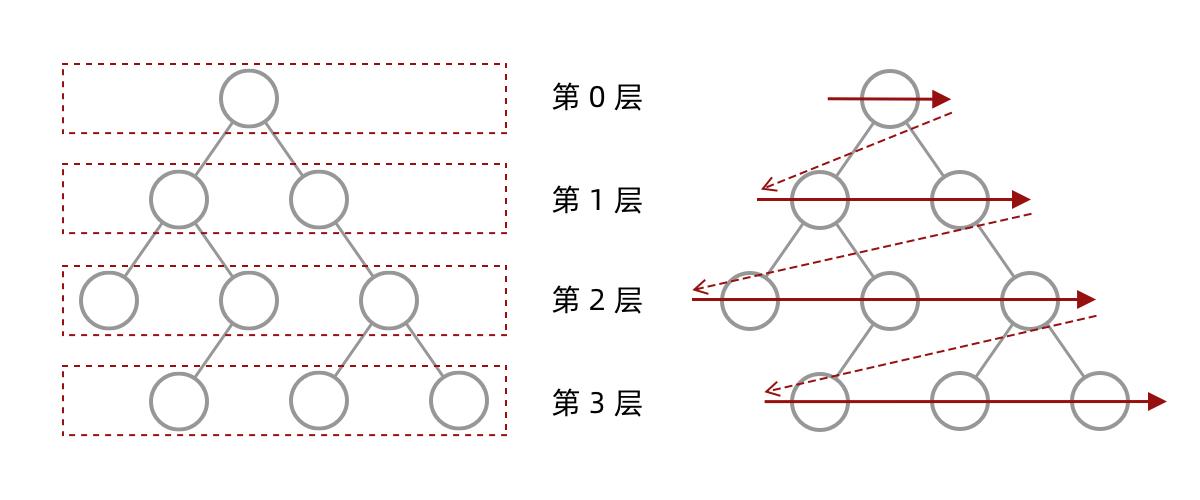
对比BFS的过程
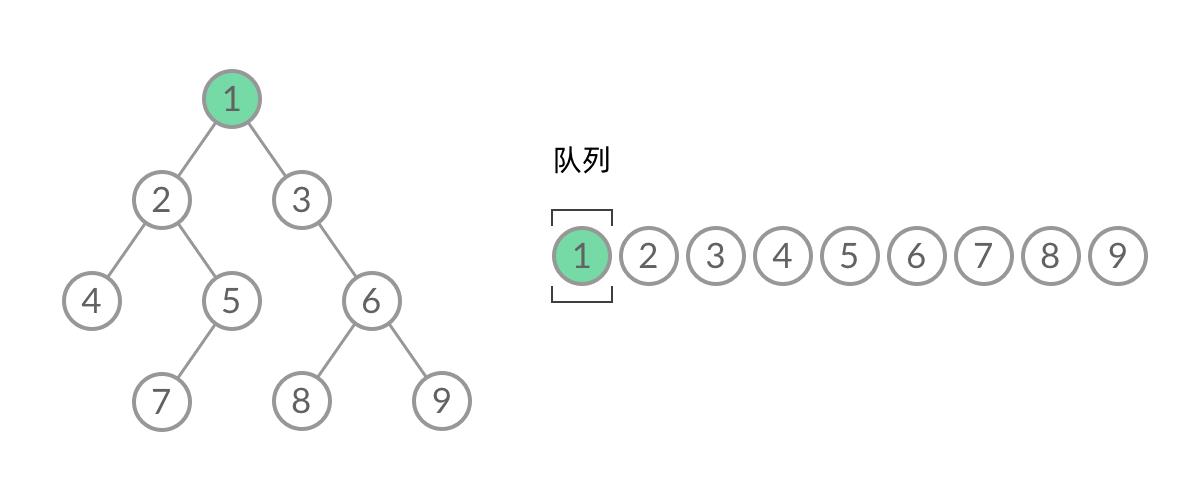
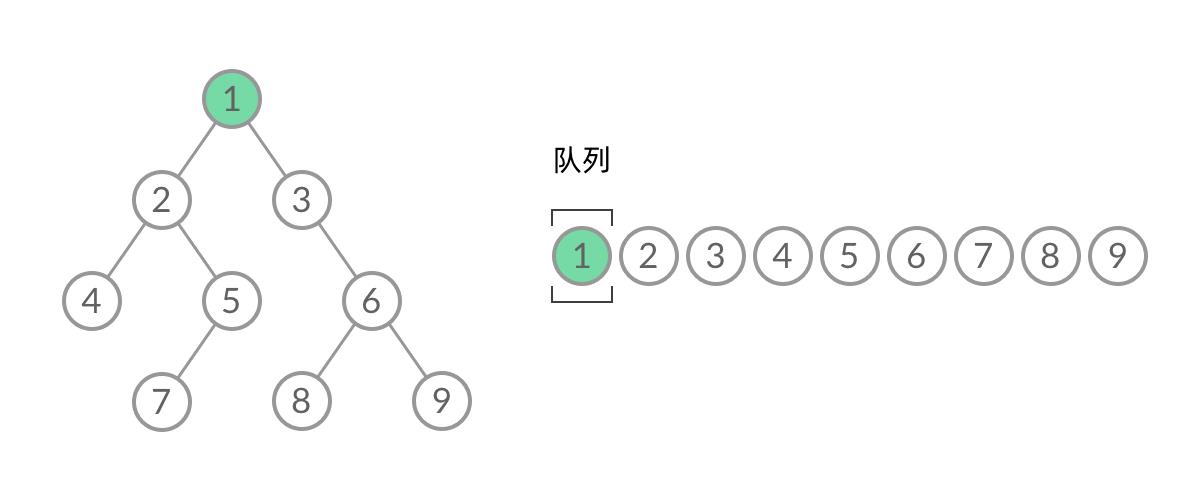
需要改进前面说的 BFS
function BFS(root) {
const queue = [];
queue.unshift(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let len = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
root = queue.pop();
if (root.left) queue.unshift(root.left);
if (root.right) queue.unshift(root.right);
}
}
}
【解法】广度优先搜索
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function levelOrder(root) {
if(!root) return [];
const result = [];
const queue = [];
queue.unshift(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let len = queue.length;
let level = [];
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
root = queue.pop();
level.push(root.val);
if (root.left) queue.unshift(root.left);
if (root.right) queue.unshift(root.right);
}
result.push(level);
}
return result;
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
递归方式有两种 一种是【自顶向下】,一种是【自底向上】
先来看看自顶向下的递归方式
【解法一】递归【自顶向下】
“自顶向下” 意味着在每个递归层级,我们将首先访问节点来计算一些值,并在递归调用函数时将这些值传递到子节点。
所以 “自顶向下” 的解决方案可以被认为是一种前序遍历。
通用代码片段是这样的
1. return specific value for null node
2. update the answer if needed // answer <-- params
3. left_ans = top_down(root.left, left_params) // left_params <-- root.val, params
4. right_ans = top_down(root.right, right_params) // right_params <-- root.val, params
5. return the answer if needed // answer <-- left_ans, right_ans
本题代码
var maxDepth = function(root) {
let result = 0
function max_depth(root, depth){
if(!root) return;
if(!root.left && !root.right){
result = Math.max(result, depth);
}
max_depth(root.left, depth + 1);
max_depth(root.right, depth + 1);
}
max_depth(root, 1);
return result;
};
【解法二】递归【自底向上】
“自底向上” 是另一种递归方法。 在每个递归层次上,我们首先对所有子节点递归地调用函数,然后根据返回值和根节点本身的值得到答案。
这个过程可以看作是后序遍历的一种。
通用代码片段
1. return specific value for null node
2. left_ans = bottom_up(root.left) // call function recursively for left child
3. right_ans = bottom_up(root.right) // call function recursively for right child
4. return answers // answer <-- left_ans, right_ans, root.val
本题代码
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0;
let lMax = maxDepth(root.left);
let rMax = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(lMax, rMax) + 1;
};
【解法三】迭代
617. 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。

来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees
【解法】递归
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root1
* @param {TreeNode} root2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {
if(!root1) return root2;
if(!root2) return root1;
root1.val = root1.val + root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
};
图类
以上是关于LeetCode经典题分类(树&图 )精选 - JavaScript - ES6 - 技巧总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章