HarmonyOS之IDL接口使用规范
Posted Forever_wj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HarmonyOS之IDL接口使用规范相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、接口描述语言简介
- 当客户端和服务器通信时,需要定义双方都认可的接口,以保障双方可以成功通信,HarmonyOS IDL(HarmonyOS Interface Definition Language)则是一种定义此类接口的工具。HarmonyOS IDL 先把需要传递的对象分解成操作系统能够理解的基本类型,并根据开发者的需要封装跨边界的对象。在 HarmonyOS 中,HarmonyOS IDL 接口包含面向应用程序的北向接口和面向硬件设备的南向接口。
- HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述语言:

- HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述语言主要用于:
-
- 声明系统服务对外提供的服务接口,根据接口声明在编译时生成跨进程调用(IPC)或跨设备调用(RPC)的代理(Proxy)和桩(Stub)的 C/C++ 代码或 Java 代码。
-
- 声明 Ability 对外提供的服务接口,根据接口声明在编译时生成跨进程调用(IPC)或跨设备调用(RPC)的代理(Proxy)和桩(Stub)的 C/C++ 代码或 Java 代码。
- IPC/RPC 通信模型如下:
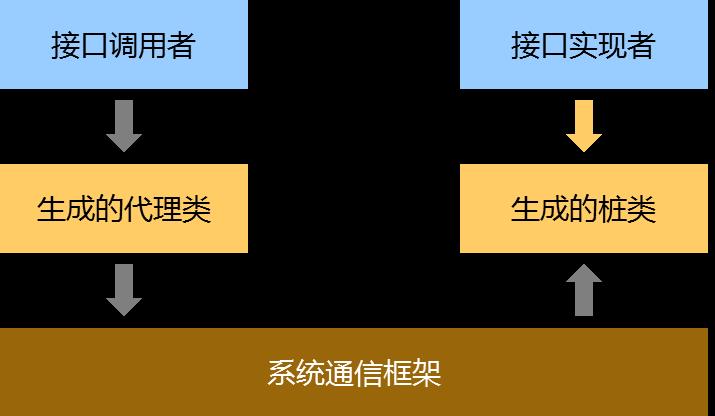
- 使用 HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述语言声明接口具有以下优点:
-
- HarmonyOS IDL 中是以接口的形式定义服务,可以专注于定义而隐藏实现细节。
-
- HarmonyOS IDL 中定义的接口可以支持跨进程调用或跨设备调用,根据HarmonyOS IDL 中的定义生成的信息或代码可以简化跨进程或跨设备调用接口的实现。
- 采用 HarmonyOS IDL 描述的接口代码示例如下:
interface ohos.app.IAbilityConnection;
interface ohos.os.IBroker;
sequenceable ohos.content.AbilityInfo;
sequenceable ohos.content.Intent;
interface ohos.app.IAbilityManager {
int StartAbility([in] Intent intent);
void SetAbilitySliceCallback([in] IBroke broker, [in] IAbilityConnection callback);
[oneway]
void ExitAbility([in] AbilityInfo abilityInfo);
}
- HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述文件是以“.idl”为扩展名的文件。
- HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述文件目录层级必须按照包名的层次进行定义,例如:IAbilityManager 类的 IDL 文件必须放在 ohos/app/ 目录下。
- HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述文件主要以接口类名命名,例如:IAbilityManager.idl。
二、接口描述语言构成
① 数据类型
- HarmonyOS IDL 支持的数据类型可分为:基本数据类型、自定义类型、声明的 Sequenceable 数据类型、声明的接口类型、数组类型以及容器类型。
- HarmonyOS IDL 基本数据类型与 Java 数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL基本数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 | 数据长度(bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| void | void | void | void | NA |
| boolean | boolean | bool | bool | 1 |
| byte | byte | int8_t | int8_t | 1 |
| short | short | int16_t | int16_t | 2 |
| int | int | int32_t | int32_t | 4 |
| long | long | int64_t | int64_t | 8 |
| float | float | float | float | 4 |
| double | double | double | double | 8 |
| String | String | std::string | cstring | NA |
| unsigned char | 不支持 | uint8_t | uint8_t | 1 |
| unsigned short | 不支持 | uint16_t | uint16_t | 2 |
| unsigned int | 不支持 | uint32_t | uint32_t | 4 |
| unsigned long | 不支持 | uint64_t | uint64_t | 8 |
- 自定义类型是指使用关键字 struct、union、enum 定义的结构体类型、联合体类型、枚举类型,以及这些类型组合嵌套定义的类型。自定义类型文件 MyTypes.idl 示例如下:
struct Example1 {
String member1;
unsigned int member2;
};
union Example2 {
String member1;
unsigned int member2;
};
enum Example3 : int {
RED,
BLUE,
GREEN,
};
struct Example1_2_3 {
struct Example1;
union Example2;
enum Example3;
};
- 在定义枚举类型时,需要指定枚举类型的基本数据类型,可以使用 byte、short、int、long、unsigned char、unsigned short、unsigned int、unsigned long。如果未指定,则默认基础类型为 int 类型。
- 一个模块在定义 HarmonyOS IDL 接口时使用的自定义类型应该定义在一个独立的文件中,不要分散到每个接口定义的文件中。自定义类型所在文件的名称可以根据实际情况进行定义,在接口定义文件中需要导入自定义类型文件,例如:MyInterface.idl 接口使用了 MyTypes.idl 中定义的自定义类型,代码示例如下:
sequenceable ohos.module.MyTypes;
interface ohos.module.MyInterface {
……
}
- HarmonyOS IDL 自定义数据类型与 Java 数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| 自定义数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| struct | 不支持 | struct | struct |
| union | 不支持 | union | union |
| enum | 不支持 | enum | enum |
- Sequenceable 数据类型是指用“Sequenceable”关键字声明的非基本数据类型,表明该数据类型可以通过 Parcel 进行跨进程(或跨设备)传递。声明放在文件的头部,形式为 “sequenceable namespace.typename;”,namespace 是该类型所属的命名空间,内部采用“.”连接不同层级的命名空间, typename 是类型名。例如:“sequenceable com.huawei.samples.ApplicationInfo;”表示 ApplicationInfo 类型可以通过 Parcel 进行跨进程传递。
- Sequenceable 数据类型并不在 HarmonyOS IDL 文件中定义,而是定义在 C++ 文件或 Java 文件中,C 语言文件不支持。因此,HarmonyOS IDL 工具将根据声明在生成的 C++ 代码文件中加入“#include “com/huawei/samples/ApplicationInfo.h””语句,在生成的 Java 代码文件中加入“import com.huawei.samples.ApplicationInfo;”语句。
- HarmonyOS IDL Sequenceable 数据类型与 Java 数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequenceable | sequenceable namespace.typename; 例如:sequenceable com.huawei.samples.ApplicationInfo; | #include namespace/typename.h" using namespace::typename 例如:#include com/huawei/samples/ApplicationInfo.h" using com::huawei::samples::ApplicationInfo | 不支持 |
- 接口类型是指 HarmonyOS IDL 文件中定义的接口。对于当前 IDL 文件中定义的接口,可以直接使用它作为方法参数类型或返回值类型。而在其它 HarmonyOS IDL 文件中定义的接口,则需要在文件的头部进行前置声明。声明的形式为“interface namespace.interfacename;”,namespace 是该接口所属的命名空间,内部采用“.”连接不同层级的命名空间,interfacename 是接口名。例如:“interface com.huawei.samples.IApplication;”声明了在其他 HarmonyOS IDL 文件定义的 IApplication 接口,该接口可以作为当前定义中方法的参数类型或返回值类型使用。
- HarmonyOS IDL 工具将根据该声明在生成的 C++ 代码文件中加入“#include “com/huawei/samples/IApplication.h””语句,在生成的 Java 代码文件中加入“import com.huawei.samples.IApplication;”语句。IBroker 也是接口类型的一种,使用它无需前置声明。
- HarmonyOS IDL 接口数据类型与Java数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interface | sequenceable namespace.interfacename; 例如:sequenceable com.huawei.samples.IApplication; | #include namespace/interfacename.h" using namespace::interfacename; 例如:#include com/huawei/samples/IApplication.h" using com::huawei::samples::IApplication; | 不支持 |
- 数组类型用“T[]”表示,T可以是基本数据类型、自定义类型、Sequenceable数据类型、接口类型和数组类型。
- 在 C++ 代码中,数组类型生成为 std::vector,在Java代码中,数组类型生成为 T[]。
- HarmonyOS IDL 数组数据类型与 Java 数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| T[] | T[] | std::vector | T*,int size |
- 容器类型当前支持两种容器:List 和 Map。List 容器用法为“List”, Map 容器用法为“Map<KT, VT>”,T、KT 和 VT 可以为基本数据类型、自定义类型、Sequenceable 类型、接口类型、数组类型或容器类型。
- 在 C++ 代码中,List 容器类型生成为 std::list,Map 容器类型生成为 std::map。在 Java 代码中,List 容器类型生成为 ArrayList,Map 容器类型生成为 HashMap。
- HarmonyOS IDL 容器数据类型与 Java 数据类型、C/C++ 数据类型的对应关系如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL数据类型 | Java数据类型 | C++数据类型 | C数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| List | List | std::list或std::vector | T*,int size |
| Map<KT, VT> | HashMap | std::map或std::unordered map | 不支持 |
② 接口定义
- 一个 HarmonyOS IDL 文件只能定义一个接口类,接口定义的形式使用 BNF 范式描述,示例如下:
<*interface_attributes_declaration*> ? interface <*interface_name_with_namespace*> { <*method_declaration*> ? }
- <interface_attributes_declaration>是接口属性声明,当前支持 oneway、callback、full、lite 属性:
-
- oneway:表示该接口中的方法都是单向方法,即调用方法后不用等待该方法执行即可返回,该属性为可选项,如果无声明,则默认为同步调用方法;
-
- callback:表示该接口为callback接口,即从下层实现中回调到上层服务中;
-
- full、lite:表示该接口在重量级部署或轻量级部署中使用。如果无声明,则默认为重量级、轻量级部署中都会使用。
- <interface_name_with_namespace>是接口名声明,接口名需包含完整的命名空间,且必须包含方法声明,不允许出现空接口。接口示例:
[oneway] interface ohos.app.IAbilityManager {
……
};
- <method_declaration>是方法声明,形式为:
<*method_attributes_declaration*> ? <*result type*> <*method declarator*>
- <method_attributes_declaration>是方法属性声明,当前支持 oneway 、full、lite 属性:
-
- oneway:表示该方法是单向方法,即调用方法后不用等待该方法执行即可返回;
-
- full、lite:表示该方法在重量级部署或轻量级部署中使用。如果无声明,则默认为重量级、轻量级部署中都会使用。
- <result type>是返回类型,<method declarator>是方法名和各个参数声明,参数声明的形式为:
\\[ <*formal_parameter_attribute*> \\] <*type*> <*identifier*>
- <formal_parameter_attribute>的值为“in”、“out”或“inout”,分别表示该参数是输入参数、输出参数或输入输出参数。oneway 方法不允许有输出参数(包含输入输出参数)和返回值。方法示例:
void SetBundles([in] Map<String, BundleInfo> bundleInfos, [in, out] int number);
[oneway] void Dump([in] ParcelableFileDescriptor fd, [in] long flags);
- 在 HarmonyOS IDL 接口描述文件中可以使用的关键字如下表所示:
| HarmonyOS IDL keywords | 详细说明 |
|---|---|
| void、boolean、byte、short、int、long、float、double | 基本数据类型,void类型、bool型、整型、浮点型等 |
| unsigned | 在定义无符号类型时使用,如unsigned char、unsigned short、unsigned int、unsigned long |
| String | 定义字符串时使用 |
| struct | 结构体类型 |
| union | 联合体类型 |
| enum | 枚举类型 |
| T[] | T可以是基本数据类型、自定义类型、Sequenceable数据类型、接口类型和数组类型 |
| List<> | 容器类型List,T为基本数据类型、自定义类型、Sequenceable类型、接口类型、数组类型或容器类型 |
| Map<> | 容器类型Map<KT, VT>: KT和VT为基本数据类型、自定义类型、Sequenceable类型、接口类型、数组类型或容器类型 |
| Sequenceable | 该类型并不在idl文件中定义,而是定义在C++文件或Java文件中 |
| extends | 接口继承 |
| interface | 接口类型 |
| [oneway] | 表示单向接口或方法 oneway方法不允许有输出参数(包含输入输出参数)和返回值 |
| [in] | 输入参数 |
| [out] | 输出参数 |
| [inout] | 输入输出参数 |
| [callback] | 标识一个接口为回调接口定义(明示工具如何生成service、client代码) |
| [full] | 仅在HarmonyOS重量级部署中使用的参数、接口、方法 |
| [lite] | 仅在HarmonyOS轻量级部署中使用的参数、接口、方法 |
③ 注释说明
- HarmonyOS IDL 文件中的注释采用与 C/C++ 相同的方式,可以采用//或者/* … */的方式进行注释说明。
三、开发步骤
① 创建 .idl 文件
- 可以使用 Java 或 C++ 编程语言构建 .idl 文件。.idl 示例如下:
sequenceable com.example
/** Example service ability interface */
interface com.example.IRemoteAbility {
int plus([in] int num1, [in] int num2);
}
- HarmonyOS SDK 工具支持生成 Java、C++ 语言的接口类、桩类和代理类。以 Java 语言开发为例,开发者只需将 .idl 文件保存至 DevEco Studio 项目的 src/ 目录内,工具则会在构建应用时,在项目的 generated/ 目录中生成 IRemoteObject 接口文件、Stub 文件、Proxy 文件。生成的接口类文件名称和.idl文件名称保持一致,区别在于其使用 .java 扩展名。例如,IRemoteAbility.idl 生成的文件名是 IRemoteAbility.java、RemoteAbilityProxy.java、RemoteAbilityStub.java。
② 服务端公开接口
- HarmonyOS IDL 工具生成的 Stub 类是接口类的抽象实现,并且会声明 .idl 文件中的所有方法:
public abstract class RemoteAbilityStub extends RemoteObject implements IRemoteAbility {
private static final String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.IRemoteAbility";
private static final int COMMAND_PLUS = IRemoteObject.MIN_TRANSACTION_ID + 0;
………
}
- 要实现 .idl 生成的接口,请扩展生成的 RemoteObject 接口,并实现继承自 .idl 文件的方法。MyRemote 定义了服务的远程过程调用接口,示例代码如下:
class MyRemote extends RemoteAbilityStub {
public MyRemote(String descriptor) {
super(descriptor);
}
@Override
public int plus(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
return num1 + num2;
}
}
- 在服务实现接口后,需要向客户端公开该接口,以便客户端进程绑定。如果开发者的服务要公开该接口,请扩展 Ability 并实现 onConnect() 从而返回 IRemoteObject,以便客户端能与服务进程交互。服务端向客户端公开 IRemoteAbility 接口的代码示例如下:
public class ServiceAbility extends Ability {
private MyRemote remote = new MyRemote("MyRemoteAbility");
class MyRemote extends RemoteAbilityStub {
public MyRemote(String descriptor) {
super(descriptor);
}
@Override
public int plus(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
return num1 + num2;
}
}
@Override
public IRemoteObject onConnect(Intent intent) {
return remote.asObject();
}
}
③ 客户端调用 IPC 方法
- 客户端调用 connectAbility() 以连接服务时,客户端的 onAbilityConnectDone() 回调会接收服务的 onConnect() 方法返回的 IRemoteObject 实例。由于客户端和服务在不同应用内,所以客户端应用的 src/ 目录内必须包含 .idl 文件(SDK 工具会自动生成 Proxy 代理类)的副本。当客户端 onAbilityConnectDone() 回调中收到 IRemoteObject,调用 RemoteAbilityStub.asInterface(IRemoteObject),以将返回的参数转换为 IRemoteAbility 类型,例如:
IRemoteAbility proxy;
private IAbilityConnection conn = new IAbilityConnection() {
@Override
public void onAbilityConnectDone(ElementName element, IRemoteObject remote, int resultCode) {
proxy = IRemoteAbilityStub.asInterface(remote);
}
@Override
public void onAbilityDisconnectDone(ElementName element, int resultCode) {
proxy = null;
}
};
- 如果要断开连接,请调用 Ability.disconnectAbility()。
④ IPC 传递 Sequenceable 对象
- 开发者可以通过 IPC 接口,将某个类从一个进程发送至另一个进程。但是,必须确保 IPC 通道的另一端可使用该类的代码,并且该类必须支持 Sequenceable 接口。HarmonyOS 需要通过该 Sequenceable 接口将对象反序列化成各进程能识别的对象。
- 如需创建支持 Sequenceable 接口的类,开发者必须执行以下操作:
-
- 自定义对象实现 Sequenceable 接口;
-
- 实现 marshalling 方法,它会获取对象的当前状态并将其序列化后写入 Parcel;
-
- 实现 unmarshalling 方法,它会从 Parcel 中反序列化出对象;
- ElementName.java 类实现 Sequenceable 接口的代码示例如下:
public class ElementName implements Sequenceable {
private String deviceId = "";
private String bundleName = "";
private String abilityName = "";
public ElementName() {
}
public ElementName(String deviceId, String bundleName, String abilityName) {
this.deviceId = deviceId;
this.bundleName = bundleName;
this.abilityName = abilityName;
}
@Override
public boolean marshalling(Parcel out) {
if (!out.writeString(bundleName)) {
return false;
}
if (!out.writeString(abilityName)) {
return false;
}
if (!out.writeString(deviceId)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean unmarshalling(Parcel in) {
this.bundleName = in.readString();
this.abilityName = in.readString();
this.deviceId = in.readString();
return true;
}
四、IDL 语法规则
| HarmonyOS IDL语法规则(BNF范式描述) | HarmonyOS IDL语法规则(文字描述) | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| ### Programs | 一个HarmonyOS IDL接口定义文件由三部分组成:包名、类型声明、接口定义。 IDL接口文件扩展名为*.idl。 一个文件只能定义一个接口,多个接口需要定义在多个不同的文件中。 文件名必须和接口名一致。 自定义类型单独成一个文件,该文件名可以按需定义。 | - |
| <*package_declaration*> :: = package <*package_name_with_namespace*> ; | 包名 | package ohos.app; |
| <*package_name_with_namespace*> ::= <*namespace*> . <*package_name*> | <*package_name*> | - | - |
| <*type_declarations*> ::= <*java_like_type_declarations*> | <*c_like_type_declarations*> | 类型声明 | - |
| <*java_like_type_declarations*> ::= <*sequenceable_class_declaration*>? <*package_type_declaration*>? <*interface_declaration*>? | 类Java语言的类型声明,包括:sequenceable类型声明、包类型声明、接口类型声明 | - |
| <*sequenceable_class_declaration*> ::= sequenceable <*sequenceable_class_name_with_namespace*> ; | sequenceable类型声明 | sequenceable ohos.content.AbilityInfo; |
| <*sequenceable_class_name_with_namespace*> ::= <*namespace*> . <*sequenceable_class_name*> | <*sequenceable_class_name*> | - | - |
| <*c_like_type_declarations*> ::= <*package_type_declaration*>? <*custom_type_declaration*>? <*interface_declaration*>? | 类C语言的类型声明,包括包类型声明、自定义类型声明、接口类型声明 | - |
| <*custom_type_file_name_with_namespace*> ::= <*namespace*> . <*custom_type_file_name*> | <*custom_type_file_name*> | - | - |
| <*interface_declaration*> ::= interface <*interface_name_with_namespace*> ; | 接口类型声明 | interface ohos.app.IAbilitySliceConnection; |
| <*interface_name_with_namespace*> ::= <*namespace*> . <*interface_name*> | <*interface_name*> | - | - |
| <*interface_definition*> ::= <*interface_attributes_declaration*>? interface <*interface_name_with_namespace*> <*interface_inheritance_declaration*>? { <*method_declaration*>+ }; | 接口定义,包括:接口属性、接口名称、接口继承声明、接口函数 | interface ohos.app.IAbilityManager { int StartAbility([in] Intent intent); …… }; |
| <*interface_attributes_declaration*> ::= \\ [ <*interface_attributes*> \\ ] | 接口属性 | - |
| <*interface_attributes*> ::= <*interface_attribute*> | <*interface_attributes*> , <*interface_attribute*> | - | - |
| <*interface_attribute*> ::= <*java_like_interface_attribute*> | <*c_like_interface_attribute*> | - | - |
| <*java_like_interface_attribute*> ::= oneway | 类Java语言的属性支持:oneway | - |
| <*c_like_interface_attribute*> ::= <*java_like_interface_attribute*> | callback | full | lite | 类C语言的属性,支持:oneway、callback、full、lite | - |
| <*interface_inheritance_declaration*> ::= extends <*parent_interface_name_with_namespace*> | 接口继承声明 | interface ohos.app.IAbilityManager extends ohos.app.IManager { …… }; |
| <*parent_interface_name_with_namespace*> ::= <*interface_name_with_namespace*> | 父接口 | - |
| <*method_declaration*> ::= <*method_attributes_declaration*>? <*result_type*> <*method_declarator*> ; | 接口函数声明,包括:函数属性、返回值、函数名称、参数列表 | - |
| <*method_attributes_declaration*> ::= \\ [ <*method_attributes*> \\ ] | 函数属性 | - |
| <*method_attributes*> ::= <*method_attribute*> | <*method_attributes*> , <*method_attribute*> | - | - |
| <*method_attribute*> ::= <*java_like_method_attribute*> | <*c_like_method_attribute*> | - | - |
| <*java_like_method_attribute*> ::= oneway | 类Java语言的函数属性支持:oneway | - |
| <*c_like_method_attribute*> ::= <*java_like_method_attribute*> | full | lite | 类C语言的函数属性,支持:oneway、full、lite | - |
| <*result_type*> ::= <*type*> | void | 返回值:可以没有返回值(void),返回一个指定类型的值 | - |
| <*method_declarator*> ::= <*method_name*> ( <*formal_parameters*>? ) | 接口函数:可以没有参数 | - |
| <*formal_parameters*> ::= <*formal_parameter*> | <*formal_parameters*> , <*formal_parameter*> | - | - |
| <*formal_parameter*> ::= \\ [ <*formal_parameter_attribute*> \\ ] <*type*> <*formal_parameter_name*> | 每个函数参数由三个部分组成:参数属性、参数类型、参数名称 | - |
| <*formal_parameter_attribute*> ::= in | out | inout | <参数属性,支持:in、out、inout/th> | - |
| ### Types | - | - |
| <*type*> ::= <*java_like_type*> | <*c_like_type*> | - | - |
| <*java_like_type*> ::= <*primitive_type*> | <*string_type*> | <*sequenceable_type*> | <*interface_type*> | <*list_type*> | <*map_type*> | <*array_type*> | 类Java语言的数据类型,包括:基本类型、String类型、sequenceable类型、接口类型、List容器类型、Map容器类型、数组类型 | - |
| <*c_like_type*> ::= <*primitive_type*> | <*string_type*> | <*interface_type*> | <*list_type*> | <*array_type*> | <*custom_type*> | 类C语言的数据类型,包括:基本类型、String类型、接口类型、List容器类型、数组类型、自定义类型 | - |
| <*primitive_type*> ::= <*java_like_primitive_type*> | <*c_like_primitive_type*> | - | - |
| <*java_like_primitive_type*> ::= boolean | byte | short | int | long | float | double | 类Java语言的基本类型 | - |
| <*c_like_primitive_type*> ::= <*java_like_primitive_type*> | unsigned char | unsigned short | unsigned int | unsigned long | 类C语言的基本类型:除类Java语言的基本类型外,还可以使用无符号类型 | - |
| <*string_type*> ::= String | String类型 | - |
| <*sequenceable_type*> ::= <*sequenceable_class_name*> | sequenceable类型 | - |
| <*interface_type*> ::= <*interface_name*> | interface接口类型 | - |
| <*list_type*> ::= List < <*type*> > | <*list_type*> ::= List < <*type*> > | - |
| <*map_type*> ::= Map < <*type*> , <*type*> > | Map容器类型 | - |
| <*array_type*> ::= <*type*> \\ [ \\ ] | 数组类型 | - |
| <*custom_type*> ::= <*enum_type*> | <*struct_type*> | <*union_type*> | 自定义类型,包括:枚举类型、结构体类型、联合体类型、三种类型的嵌套使用 | - |
| <*enum_type*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? enum <*custom_type_name*> { <*enum_members_declaration*>+ }; | 枚举类型:自定义类型属性、类型名、枚举成员 | - |
| <*struct_type*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? struct <*custom_type_name*> { <*custom_type_members_declaration*>+ }; | 结构体类型:自定义类型属性、类型名、结构体成员 | - |
| <*union_type*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? union <*custom_type_name*> { <*custom_type_members_declaration*>+ }; | 联合体类型:自定义类型属性、类型名、联合体成员 | - |
| <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*> ::= \\ [ <*custom_type_attributes*> \\ ] | - | - |
| <*custom_type_attributes*> ::= <*custom_type_attribute*> | <*custom_type_attributes*> , <*custom_type_attribute*> | - | - |
| <*custom_type_attribute*> ::= full | lite | 自定义类型的属性,支持:full、lite | - |
| <*enum_members_declaration*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? <*enum_member_name*> <*enum_member_value*>? , | 枚举类型成员:自定义类型属性、枚举成员名、枚举成员值(可选) | - |
| <*enum_member_value*> ::= = <*number_value*> | 枚举成员值 | - |
| <*custom_type_members_declaration*> ::= <*primitive_type_member*> | <*list_type_member*> | <*array_type_member*> | <*custom_type_member*> | 自定义类型成员,支持:基本类型、List容器类型、数组类型、自定义类型 | - |
| <*primitive_type_member*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? <*c_like_primitive_type*> <*custom_type_member_name*> ; | 基本类型成员:自定义类型属性、数据类型、自定义成员变量名 | - |
| <*list_type_member*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? <*custom_list_type*> <*custom_type_member_name*> ; | List容器类型成员:自定义类型属性、数据类型、自定义成员变量名 | - |
| <*array_type_member*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? <*custom_array_type*> <*custom_type_member_name*> ; | 数组类型成员:自定义类型属性、数据类型、自定义成员变量名 | - |
| <*custom_type_member*> ::= <*custom_type_attributes_declaration*>? <*custom_type*> <*custom_type_member_name*> ; | 自定义类型成员:自定义类型属性、数据类型、自定义成员变量名 | - |
| <*custom_list_type*> ::= List < <*custom_member_type*> > | 自定义类型中使用的List容器类型 | - |
| <*custom_array_type*> ::= <*custom_member_type*> \\ [ \\ ] | 自定义类型中使用的数组类型 | - |
| <*custom_member_type*> ::= <*c_like_primitive_type*> | <*string_type*> | <*custom_type*> | 自定义成员类型:类C语言的基本类型、字符串类型、自定义类型、不支持接口类型、Map容器类型等 | - |
| ### Tokens | - | - |
| <*package_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 包名 | - |
| <*custom_type_file_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 自定义类型所在的文件名 | - |
| <*namespace*> ::= <*identifier*> | <*namespace*> . <*identifier*> | 命名空间 | - |
| <*sequenceable_class_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | sequenceable类名 | - |
| <*interface_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 接口名 | - |
| <*method_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 接函数口名 | - |
| <*formal_parameter_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 参数名 | - |
| <*custom_type_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 自定义类型名 | - |
| <*enum_member_name*> ::= <*enum_letter*>+ | 枚举成员名 | - |
| <*custom_type_member_name*> ::= <*identifier*> | 自定义类型成员名 | - |
| ### identifier | - | - |
| <*identifier*> ::= <*letter*>+ | <*letter_number*> | 标识符由字母和数字组成,第一个字符不能使用数字 | - |
| <*letter*> ::= _ | <*upper_case*> | <*lower_case*> | 字符,包括:下滑线、大写字母、小写字母 | - |
| <*letter_number*> ::= <*letter*>+ | <*letter_number*> <*letter*> | <*letter_number*> <*number*> | - | - |
| <*upper_case*> ::= A|B|C|D|E|F|G|H|I|J …… | - | - |
| <*lower_case*> ::= a|b|c|d|e|f|g|h|i|j …… | - | - |
| <*number*> ::= <*dec_number*> | - | - |
| <*dec_number*> ::= <*oct_number*> | 8 | 9 | 十进制数字 | - |
| <*oct_number*> ::= 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 八进制数字 | - |
| <*number_value*> ::= <*hex_prefix*> <*hex_value*> | <*dec_value*> | 0 <*oct_value*> | 数值:枚举类型成员的值 | - |
| <*hex_prefix*> ::= 0x | 0X | - | - |
| <*hex_value*> ::= <*hex_number*>+ | - | - |
| <*dec_value*> ::= <*dec_number*>+ | - | - |
| <*oct_value*> ::= <*oct_number*>+ | - | - |
| <*hex_number*> ::= <*dec_number*> | A | B | C | D | E | F | a | b | c | d | e | f | 十六进制数字 | - |
| <*enum_letter*> ::= _ | <*upper_case*> | 枚举类型成名的命名,可以使用:下滑线、大写字母 | - |
- 语法文档使用的规则如下:
-
- 尖括号 < > 内包含的为必选项;
-
- 竖线 | 表示在其左右两边任选一项,相当于"OR"的含义;
-
- ::= 是“被定义为”的含义;
-
- ? 操作符左边的符号是可选项(可以出现 0 到多次);
-
- “+ 1”次或多次;
-
- \\ [或\\ ]是左右中括号字符本身。
以上是关于HarmonyOS之IDL接口使用规范的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章