Java版流媒体编解码和图像处理(JavaCPP+FFmpeg)
Posted 程序员欣宸
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java版流媒体编解码和图像处理(JavaCPP+FFmpeg)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
欢迎访问我的GitHub
这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
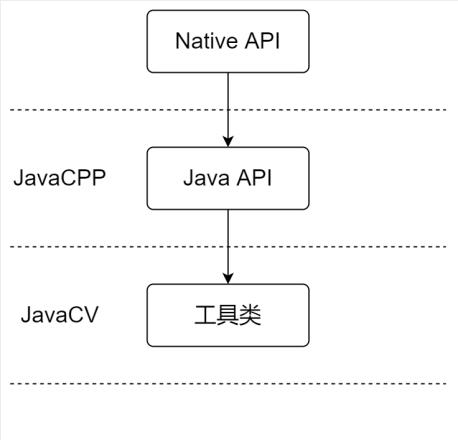
FFmpeg、JavaCPP、JavaCV的关系
- 先简单的梳理一下FFmpeg、JavaCPP、JavaCV的关系:
- FFmpeg、OpenCV可以理解成C语言版的本地库(Native library),Java应用无法直接使用
- JavaCPP将FFmpeg、OpenCV这些常用库做了包装(wrapper),使得Java应用也能使用这些Native API(JavaCPP的底层实现是JNI)
- 这些JavaCPP包装后的API,被JavaCV封装成了工具类(utility classes),这些工具类比原生API更简单易用
- 简单的说如下图所示,JavaCPP是Native API转Java API,JavaCV是Java API封装成工具类,这些工具类更加简单易用:
学习目的
- 欣宸的目标是学习和掌握JavaCV,而深入JavaCV内部去了解它用到的JavaCPP,就相当于打好基础,今后使用JavaCV的时候,也能看懂其内部的实现原理;
- 于是乎,通过JavaCPP使用FFmpeg就成了基本功,本文会开发一个java应用,调用JavaCPP的API完成以下任务:
- 打开指定的流媒体
- 取一帧解码,得到YUV420P格式的图像
- 将YUV420P格式的图像转为YUVJ420P格式
- 将图像用jpg格式保存在指定位置
- 释放所有打开的资源
- 可见上述一系列步骤已覆盖编解码和图像处理等常见操作,对咱们了解FFmpeg库有很大帮助
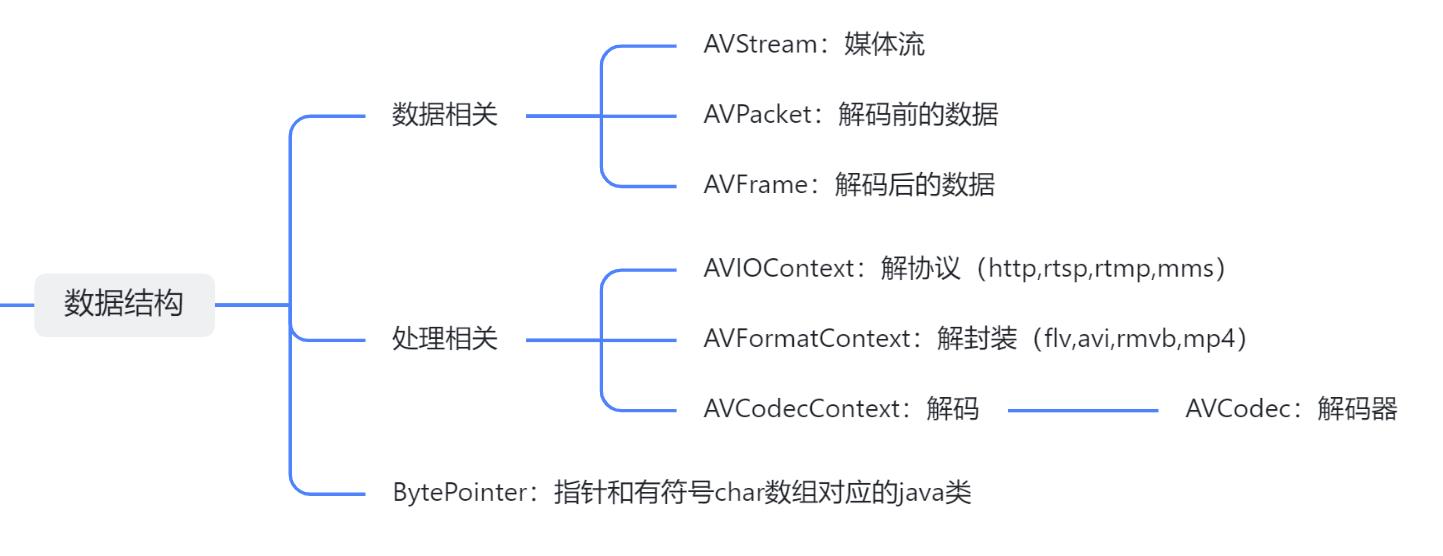
知识储备
- 在实际编码前,建议您对FFmpeg的重要数据结构和API做一些了解,这方面最经典的资料莫过于雷神的系列教程了,尤其是解协议、解封装、解码涉及到的数据结构(上下文)和API,都应该简单了解一遍
- 如果您实在太忙没有时间翻阅这些经典,我这准备了一份快餐版,对重要知识点做了简单的小结,这里要申明一下:欣宸的快餐版远不如雷神的经典系列…
- 先看数据结构,主要分为媒体数据和上下文两大类,以及底层指针对应的java类:
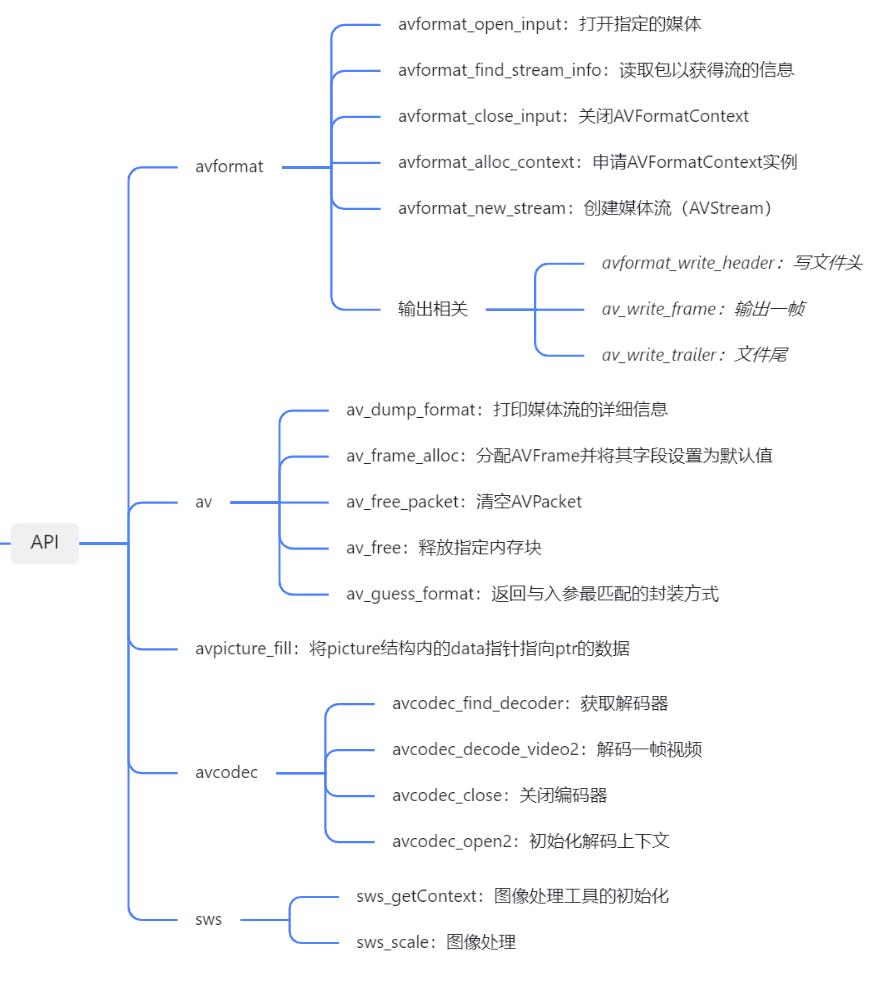
- 接着是常用API,按照雷神的解协议、解封装、解码思路(还有反过来的编码和封装处理)去分类和理解,很容易将它们梳理清楚:
版本信息
本次编码涉及的操作系统、软件、库的版本信息如下:
- 操作系统:win10 64位
- IDE:IDEA 2021.1.3 (Ultimate Edition)
- JDK:1.8.0_291
- maven:3.8.1
- javacpp:1.4.3
- ffmpeg:4.0.2(所以ffmpeg-platform库的版本是4.0.2-1.4.3)
源码下载
- 本篇实战中的完整源码可在GitHub下载到,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos):
| 名称 | 链接 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 项目主页 | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos | 该项目在GitHub上的主页 |
| git仓库地址(https) | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议 |
| git仓库地址(ssh) | git@github.com:zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议 |
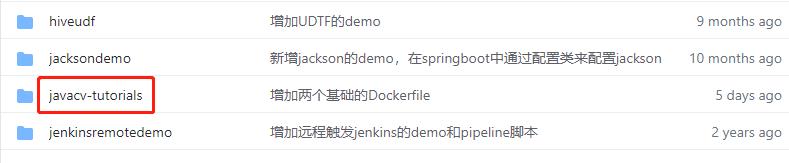
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本篇的源码在javacv-tutorials文件夹下,如下图红框所示:
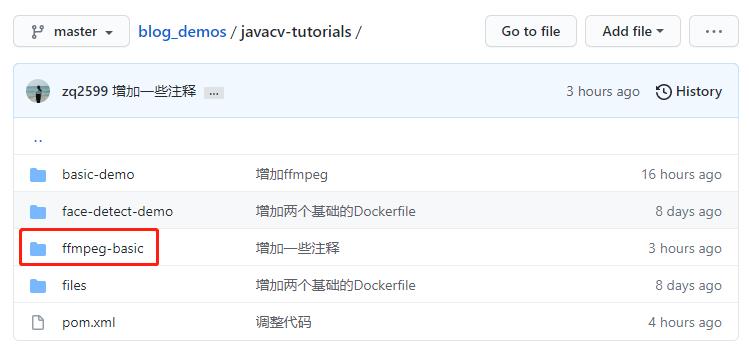
- javacv-tutorials文件夹下有多个子工程,本篇的源码在ffmpeg-basic文件夹下,如下图红框:
开始编码
- 为了统一管理源码和jar依赖,项目采用了maven父子结构,父工程名为javacv-tutorials,里面有一些jar的版本定义,就不多说了
- 在javacv-tutorials下面新建名为ffmpeg-basic的子工程,其pom.xml内容如下,可见仅用了JavaCPP,并未用到JavaCV:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>javacv-tutorials</artifactId>
<groupId>com.bolingcavalry</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>ffmpeg-basic</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bytedeco</groupId>
<artifactId>javacpp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bytedeco.javacpp-presets</groupId>
<artifactId>ffmpeg-platform</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- 接下来开始编码,先写一个最简单的内部类,将AVFrame和它对应的数据指针BytePointer都放在这个类中,在调用方法的时候便于传递:
class FrameData {
AVFrame avFrame;
BytePointer buffer;
public FrameData(AVFrame avFrame, BytePointer buffer) {
this.avFrame = avFrame;
this.buffer = buffer;
}
}
- 接下来是整个程序最重要的方法openMediaAndSaveImage,该方法是整个程序的主体,负责将打开流媒体、解码、转格式、保存、释放等五个步骤串起来,外部只要调用这个方法就能完成整个功能:
/**
* 打开流媒体,取一帧,转为YUVJ420P,再保存为jpg文件
* @param url
* @param out_file
* @throws IOException
*/
public void openMediaAndSaveImage(String url,String out_file) throws IOException {
log.info("正在打开流媒体 [{}]", url);
// 打开指定流媒体,进行解封装,得到解封装上下文
AVFormatContext pFormatCtx = getFormatContext(url);
if (null==pFormatCtx) {
log.error("获取解封装上下文失败");
return;
}
// 控制台打印流媒体信息
av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, url, 0);
// 流媒体解封装后有一个保存了所有流的数组,videoStreamIndex表示视频流在数组中的位置
int videoStreamIndex = getVideoStreamIndex(pFormatCtx);
// 找不到视频流就直接返回
if (videoStreamIndex<0) {
log.error("没有找到视频流");
return;
}
log.info("视频流在流数组中的第[{}]个流是视频流(从0开始)", videoStreamIndex);
// 得到解码上下文,已经完成了初始化
AVCodecContext pCodecCtx = getCodecContext(pFormatCtx, videoStreamIndex);
if (null==pCodecCtx) {
log.error("生成解码上下文失败");
return;
}
// 从视频流中解码一帧
AVFrame pFrame = getSingleFrame(pCodecCtx,pFormatCtx, videoStreamIndex);
if (null==pFrame) {
log.error("从视频流中取帧失败");
return;
}
// 将YUV420P图像转成YUVJ420P
// 转换后的图片的AVFrame,及其对应的数据指针,都放在frameData对象中
FrameData frameData = YUV420PToYUVJ420P(pCodecCtx, pFrame);
if (null==frameData) {
log.info("YUV420P格式转成YUVJ420P格式失败");
return;
}
// 持久化存储
saveImg(frameData.avFrame,out_file);
// 按顺序释放
release(true, null, null, pCodecCtx, pFormatCtx, frameData.buffer, frameData.avFrame, pFrame);
log.info("操作成功");
}
- 现在整体逻辑已经清楚了,再来看里面openMediaAndSaveImage里面调用的那些方法的源码,先看打开流媒体的getFormatContext:
/**
* 生成解封装上下文
* @param url
* @return
*/
private AVFormatContext getFormatContext(String url) {
// 解封装上下文
AVFormatContext pFormatCtx = new avformat.AVFormatContext(null);
// 打开流媒体
if (avformat_open_input(pFormatCtx, url, null, null) != 0) {
log.error("打开媒体失败");
return null;
}
// 读取流媒体数据,以获得流的信息
if (avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx, (PointerPointer<Pointer>) null) < 0) {
log.error("获得媒体流信息失败");
return null;
}
return pFormatCtx;
}
- 流媒体解封装后有一个保存了所有流的数组,getVideoStreamIndex方法会找到视频流在数组中的位置:
/**
* 流媒体解封装后得到多个流组成的数组,该方法找到视频流咋数组中的位置
* @param pFormatCtx
* @return
*/
private static int getVideoStreamIndex(AVFormatContext pFormatCtx) {
int videoStream = -1;
// 解封装后有多个流,找出视频流是第几个
for (int i = 0; i < pFormatCtx.nb_streams(); i++) {
if (pFormatCtx.streams(i).codec().codec_type() == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
videoStream = i;
break;
}
}
return videoStream;
}
- 解封装之后就是解码,getCodecContext方法得到解码上下文对象:
/**
* 生成解码上下文
* @param pFormatCtx
* @param videoStreamIndex
* @return
*/
private AVCodecContext getCodecContext(AVFormatContext pFormatCtx, int videoStreamIndex) {
//解码器
AVCodec pCodec;
// 得到解码上下文
AVCodecContext pCodecCtx = pFormatCtx.streams(videoStreamIndex).codec();
// 根据解码上下文得到解码器
pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx.codec_id());
if (pCodec == null) {
return null;
}
// 用解码器来初始化解码上下文
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, (AVDictionary)null) < 0) {
return null;
}
return pCodecCtx;
}
- 紧接着从视频流解码取帧解码:
/**
* 取一帧然后解码
* @param pCodecCtx
* @param pFormatCtx
* @param videoStreamIndex
* @return
*/
private AVFrame getSingleFrame(AVCodecContext pCodecCtx, AVFormatContext pFormatCtx, int videoStreamIndex) {
// 分配帧对象
AVFrame pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
// frameFinished用于检查是否有图像
int[] frameFinished = new int[1];
// 是否找到的标志
boolean exists = false;
AVPacket packet = new AVPacket();
try {
// 每一次while循环都会读取一个packet
while (av_read_frame(pFormatCtx, packet) >= 0) {
// 检查packet所属的流是不是视频流
if (packet.stream_index() == videoStreamIndex) {
// 将AVPacket解码成AVFrame
avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, frameFinished, packet);// Decode video frame
// 如果有图像就返回
if (frameFinished != null && frameFinished[0] != 0 && !pFrame.isNull()) {
exists = true;
break;
}
}
}
} finally {
// 一定要执行释放操作
av_free_packet(packet);
}
// 找不到就返回空
return exists ? pFrame : null;
}
- 解码后的图像是YUV420P格式,咱们将其转成YUVJ420P:
/**
* 将YUV420P格式的图像转为YUVJ420P格式
* @param pCodecCtx 解码上下文
* @param sourceFrame 源数据
* @return 转换后的帧极其对应的数据指针
*/
private static FrameData YUV420PToYUVJ420P(AVCodecContext pCodecCtx, AVFrame sourceFrame) {
// 分配一个帧对象,保存从YUV420P转为YUVJ420P的结果
AVFrame pFrameRGB = av_frame_alloc();
if (pFrameRGB == null) {
return null;
}
int width = pCodecCtx.width(), height = pCodecCtx.height();
// 一些参数设定
pFrameRGB.width(width);
pFrameRGB.height(height);
pFrameRGB.format(AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P);
// 计算转为YUVJ420P之后的图片字节数
int numBytes = avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P, width, height);
// 分配内存
BytePointer buffer = new BytePointer(av_malloc(numBytes));
// 图片处理工具的初始化操作
SwsContext sws_ctx = sws_getContext(width, height, pCodecCtx.pix_fmt(), width, height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P, SWS_BICUBIC, null, null, (DoublePointer) null);
// 将pFrameRGB的data指针指向刚才分配好的内存(即buffer)
avpicture_fill(new avcodec.AVPicture(pFrameRGB), buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P, width, height);
// 转换图像格式,将解压出来的YUV420P的图像转换为YUVJ420P的图像
sws_scale(sws_ctx, sourceFrame.data(), sourceFrame.linesize(), 0, height, pFrameRGB.data(), pFrameRGB.linesize());
// 及时释放
sws_freeContext(sws_ctx);
// 将AVFrame和BytePointer打包到FrameData中返回,这两个对象都要做显示的释放操作
return new FrameData(pFrameRGB, buffer);
}
- 然后就是另一个很重要方法saveImg,里面是典型的编码和输出流程,咱们前面已经了解了打开媒体流解封装解码的操作,现在要看看怎么制作媒体流,包括编码、封装和输出:
/**
* 将传入的帧以图片的形式保存在指定位置
* @param pFrame
* @param out_file
* @return 小于0表示失败
*/
private int saveImg(avutil.AVFrame pFrame, String out_file) {
av_log_set_level(AV_LOG_ERROR);//设置FFmpeg日志级别(默认是debug,设置成error可以屏蔽大多数不必要的控制台消息)
AVPacket pkt = null;
AVStream pAVStream = null;
int width = pFrame.width(), height = pFrame.height();
// 分配AVFormatContext对象
avformat.AVFormatContext pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
// 设置输出格式(涉及到封装和容器)
pFormatCtx.oformat(av_guess_format("mjpeg", null, null));
if (pFormatCtx.oformat() == null) {
log.error("输出媒体流的封装格式设置失败");
return -1;
}
try {
// 创建并初始化一个和该url相关的AVIOContext
avformat.AVIOContext pb = new avformat.AVIOContext();
// 打开输出文件
if (avio_open(pb, out_file, AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE) < 0) {
log.info("输出文件打开失败");
return -1;
}
// 封装之上是协议,这里将封装上下文和协议上下文关联
pFormatCtx.pb(pb);
// 构建一个新stream
pAVStream = avformat_new_stream(pFormatCtx, null);
if (pAVStream == null) {
log.error("将新的流放入媒体文件失败");
return -1;
}
int codec_id = pFormatCtx.oformat().video_codec();
// 设置该stream的信息
avcodec.AVCodecContext pCodecCtx = pAVStream.codec();
pCodecCtx.codec_id(codec_id);
pCodecCtx.codec_type(AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO);
pCodecCtx.pix_fmt(AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P);
pCodecCtx.width(width);
pCodecCtx.height(height);
pCodecCtx.time_base().num(1);
pCodecCtx.time_base().den(25);
// 打印媒体信息
av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, out_file, 1);
// 查找解码器
avcodec.AVCodec pCodec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);
if (pCodec == null) {
log.info("获取解码器失败");
return -1;
}
// 用解码器来初始化解码上下文
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, (PointerPointer<Pointer>) null) < 0) {
log.error("解码上下文初始化失败");
return -1;
}
// 输出的Packet
pkt = new avcodec.AVPacket();
// 分配
if (av_new_packet(pkt, width * height * 3) < 0) {
return -Mac中编译FFmpeg教程(Android版)
javacpp-FFmpeg系列之2:通用拉流解码器,支持视频拉流解码并转换为YUVBGR24或RGB24等图像像素数据