小白学习PyTorch教程十三迁移学习:微调Alexnet实现ant和bee图像分类
Posted 刘润森!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了小白学习PyTorch教程十三迁移学习:微调Alexnet实现ant和bee图像分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
@Author:Runsen
上次微调了VGG19,这次微调Alexnet实现ant和bee图像分类。
多年来,CNN许多变体已经发展起来,从而产生了几种 CNN 架构。其中最常见的是:
-
LeNet-5 (1998)
-
AlexNet (2012)
-
ZFNet (2013)
-
GoogleNet / Inception(2014)
-
VGGNet (2014)
-
ResNet (2015)
这篇博客是 关于AlexNet 教程,AlexNet 也是之前受欢迎的 CNN 架构之一。
AlexNet
AlexNet主要由 Alex Krizhevsky 设计。它由 Ilya Sutskever 和 Krizhevsky 的博士生导师 Geoffrey Hinton 共同发表,是卷积神经网络或 CNN。
在参加 ImageNet 大规模视觉识别挑战赛后,AlexNet 一举成名。Alexnet在分类任务中实现了 84.6% 的前 5 名准确率,而排名第二的团队的前 5 名准确率为 73.8%。 由于 2012 年的计算能力非常有限,Alex 在 2 个 GPU 上对其进行了训练。

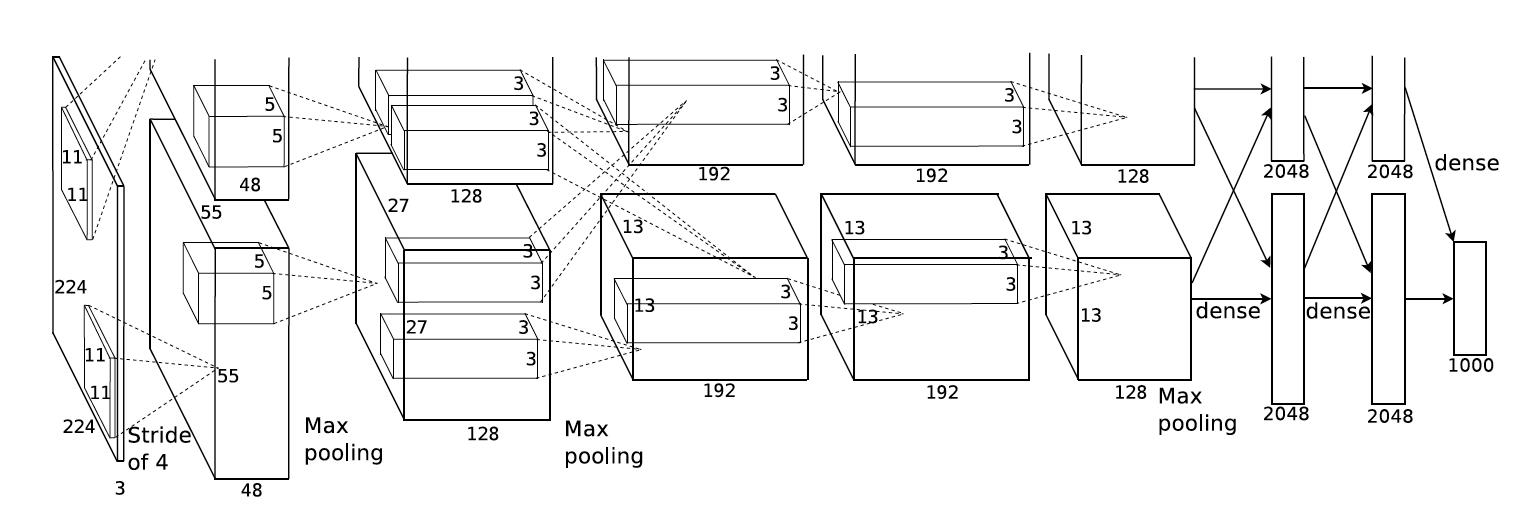
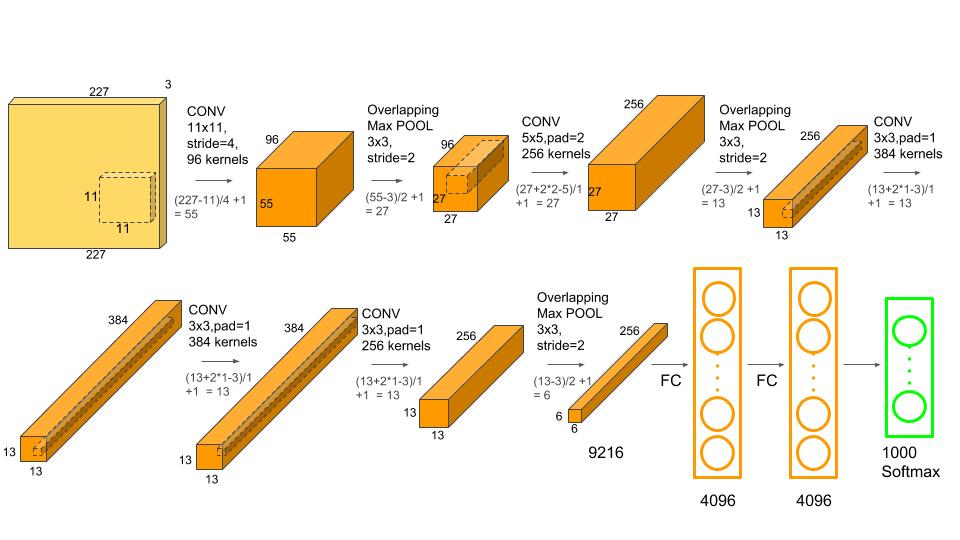
上图是2012 Imagenet 挑战赛的 Alexnet 架构
-
AlexNet 架构由 5 个卷积层、3 个最大池化层、2 个归一化层、2 个全连接层和 1 个 softmax 层组成。
-
每个卷积层由卷积滤波器和非线性激活函数ReLU组成。
-
池化层用于执行最大池化。
-
由于全连接层的存在,输入大小是固定的。
-
输入大小之前在大多数被提及为 224x224x3,但由于一些填充,变成了 227x227x3
-
AlexNet 总共有 6000 万个参数。
下面是Alexnet中的 227x227x3 模型参数
| Size / Operation | Filter | Depth | Stride | Padding | Number of Parameters | Forward Computation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3* 227 * 227 | ||||||
| Conv1 + Relu | 11 * 11 | 96 | 4 | (11 * 11 *3 + 1) * 96=34944 | (11113 + 1) * 96 * 55 * 55=105705600 | |
| 96 * 55 * 55 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 96 * 27 * 27 | ||||||
| Norm | ||||||
| Conv2 + Relu | 5 * 5 | 256 | 1 | 2 | (5 * 5 * 96 + 1) * 256=614656 | (5 * 5 * 96 + 1) * 256 * 27 * 27=448084224 |
| 256 * 27 * 27 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 256 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Norm | ||||||
| Conv3 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 384 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 256 + 1) * 384=885120 | (3 * 3 * 256 + 1) * 384 * 13 * 13=149585280 |
| 384 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Conv4 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 384 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 384=1327488 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 384 * 13 * 13=224345472 |
| 384 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Conv5 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 256 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 256=884992 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 256 * 13 * 13=149563648 |
| 256 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 256 * 6 * 6 | ||||||
| Dropout (rate 0.5) | ||||||
| FC6 + Relu | 256 * 6 * 6 * 4096=37748736 | 256 * 6 * 6 * 4096=37748736 | ||||
| 4096 | ||||||
| Dropout (rate 0.5) | ||||||
| FC7 + Relu | 4096 * 4096=16777216 | 4096 * 4096=16777216 | ||||
| 4096 | ||||||
| FC8 + Relu | 4096 * 1000=4096000 | 4096 * 1000=4096000 | ||||
| 1000 classes | ||||||
| Overall | 62369152=62.3 million | 1135906176=1.1 billion | ||||
| Conv VS FC | Conv:3.7million (6%) , FC: 58.6 million (94% ) | Conv: 1.08 billion (95%) , FC: 58.6 million (5%) |
数据集介绍
本数据集中存在PyTorch相关入门的数据集ant和bee案例,每一个ant和bee

数据来源:PyTorch深度学习快速入门教程(绝对通俗易懂!)【小土堆】
关于数据集和代码见文末
- 读取数据
这里选择将数据reshape成224*224。
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import nn
from torchvision import datasets, transforms, models
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#transforms
transform_train = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.RandomAffine(0, shear=10, scale=(0.8, 1.2)),
transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=1, contrast=1, saturation=1),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
root_train = 'ants_and_bees/train'
root_val = 'ants_and_bees/val'
training_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=root_train, transform=transform)
validation_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=root_val, transform=transform)
training_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(training_dataset, batch_size=20, shuffle=True)
validation_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validation_dataset, batch_size = 20, shuffle=False)
- 展示数据
dataiter = iter(training_loader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(25,6))
def im_convert(tensor):
image = tensor.cpu().clone().detach().numpy()
image = image.transpose(1, 2, 0) #shape 32 x 32 x 1
#de-normalisation - multiply by std and add mean
image = image * np.array((0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) + np.array((0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
image = image.clip(0, 1)
return image
for idx in np.arange(20):
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 10, idx+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
plt.imshow(im_convert(images[idx]))
#print(labels[idx].item())
ax.set_title(classes[labels[idx].item()])
plt.show()

- 微调Alexnet
model = models.alexnet(pretrained=True)
print(model)
AlexNet(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(11, 11), stride=(4, 4), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(7): ReLU(inplace=True)
(8): Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(9): ReLU(inplace=True)
(10): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(6, 6))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(1): Linear(in_features=9216, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(4): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)
)
通过转移学习,我们将使用从卷积层中提取的特征
需要把最后一层的out_features=1000,改为out_features=2
因为我们的模型只对蚂蚁和蜜蜂进行分类,所以输出应该是2,而不是AlexNet的输出层中指定的1000。因此,我们改变了AlexNet中的classifier第6个元素的输出。
for param in model.features.parameters():
`param.requires_grad = False
import torch.nn as nn
n_inputs = model.classifier[6].in_features #4096
last_layer = nn.Linear(n_inputs, len(classes))
model.classifier[6] = last_layer
model.to(device)
print(model)
AlexNet(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(11, 11), stride=(4, 4), padding=(2, 2))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(7): ReLU(inplace=True)
(8): Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(9): ReLU(inplace=True)
(10): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(6, 6))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(1): Linear(in_features=9216, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(4): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
)
- 训练和测试模型
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
epochs = 5
losses = []
accuracy = []
val_losses = []
val_accuracies = []
for e in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0.0
running_accuracy = 0.0
val_loss = 0.0
val_accuracy = 0.0
for images, labels in training_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
running_accuracy += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
running_loss += loss.item()
#不必为验证集执行梯度
with torch.no_grad():
for val_images, val_labels in validation_loader:
val_images = val_images.to(device)
val_labels = val_labels.to(device)
val_outputs = model(val_images)
val_loss = criterion(val_outputs, val_labels)
_, val_preds = torch.max(val_outputs, 1)
val_accuracy += torch.sum(val_preds == val_labels.data)
val_loss += val_loss.item()
# metrics for training data
epoch_loss = running_loss/len(training_loader.dataset)
epoch_accuracy = running_accuracy.float()/len(training_loader.dataset)
losses.append(epoch_loss)
accuracy.append(epoch_accuracy)
# metrics for validation data
val_epoch_loss = val_loss/len(validation_loader.dataset)
val_epoch_accuracy = val_accuracy.float()/len(validation_loader.dataset)
val_losses.append(val_epoch_loss)
val_accuracies.append(val_epoch_accuracy)
#print the training and validation metrics
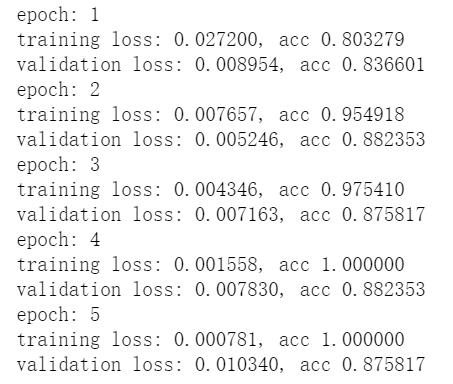
print("epoch:", e+1)
print('training loss: {:.6f}, acc {:.6f}'.format(epoch_loss, epoch_accuracy.item()))
print('validation loss: {:.6f}, acc {:.6f}'.format(val_epoch_loss, val_epoch_accuracy.item()))
plt.plot(losses, label='training loss')
plt.plot(val_losses, label='validation loss&以上是关于小白学习PyTorch教程十三迁移学习:微调Alexnet实现ant和bee图像分类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章