netty源码之业务逻辑处理
Posted better_hui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了netty源码之业务逻辑处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言

红色的部分就是我们这次分析的核心

pipeline , 本质上是一个双向的链接,请注意是双向 , 它有head、tail , 中间有很多Context , 每个context 包含了需要执行的handler ,我们可以正向或者反向的查找下一个要执行的handler。
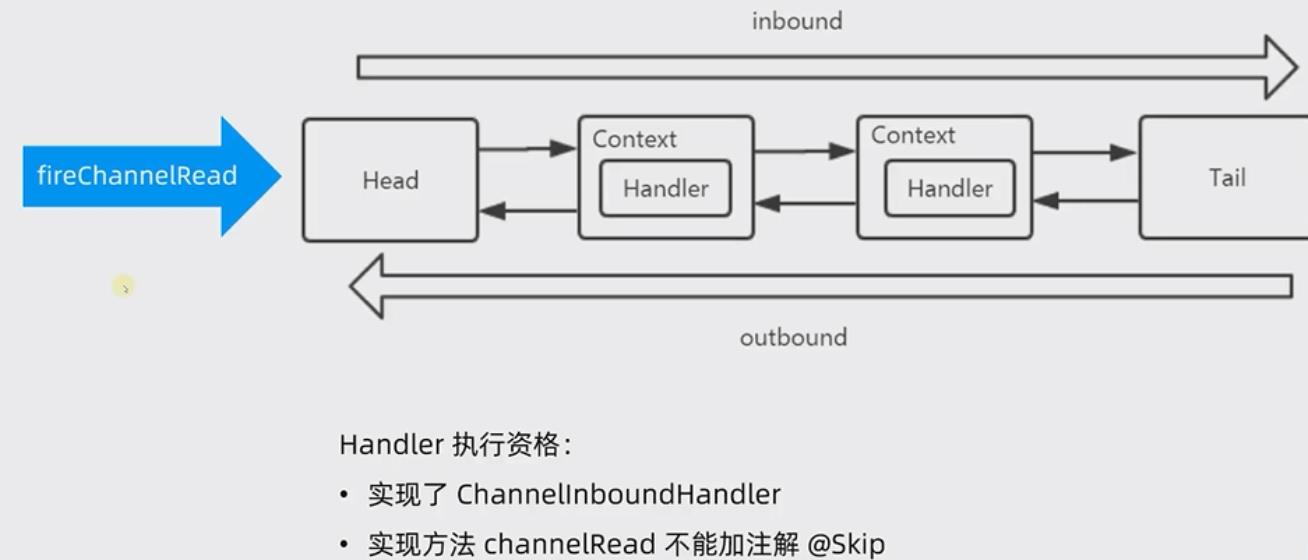
流程
1、业务逻辑的入口,read
业务逻辑的切入点,可以很明确的确认是在读数据的流程中的,所以我们打开NioEventLoop对象。
在这个读的逻辑里 , 处理数据是从这里开始的 pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf).
@Override
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 内存分配器
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
// 接收数据测handler
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 分配内存是自适应的
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// 开始读取数据
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {// 读取失败
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);//读取一次数据
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);// 将读到的数据传递出去
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());//继续读取
// 通过当前
allocHandle.readComplete();//计算下一次的需要分配的空间
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();// 将完成读取的事件传递出去
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
2、从pipeline的链表上依次执行
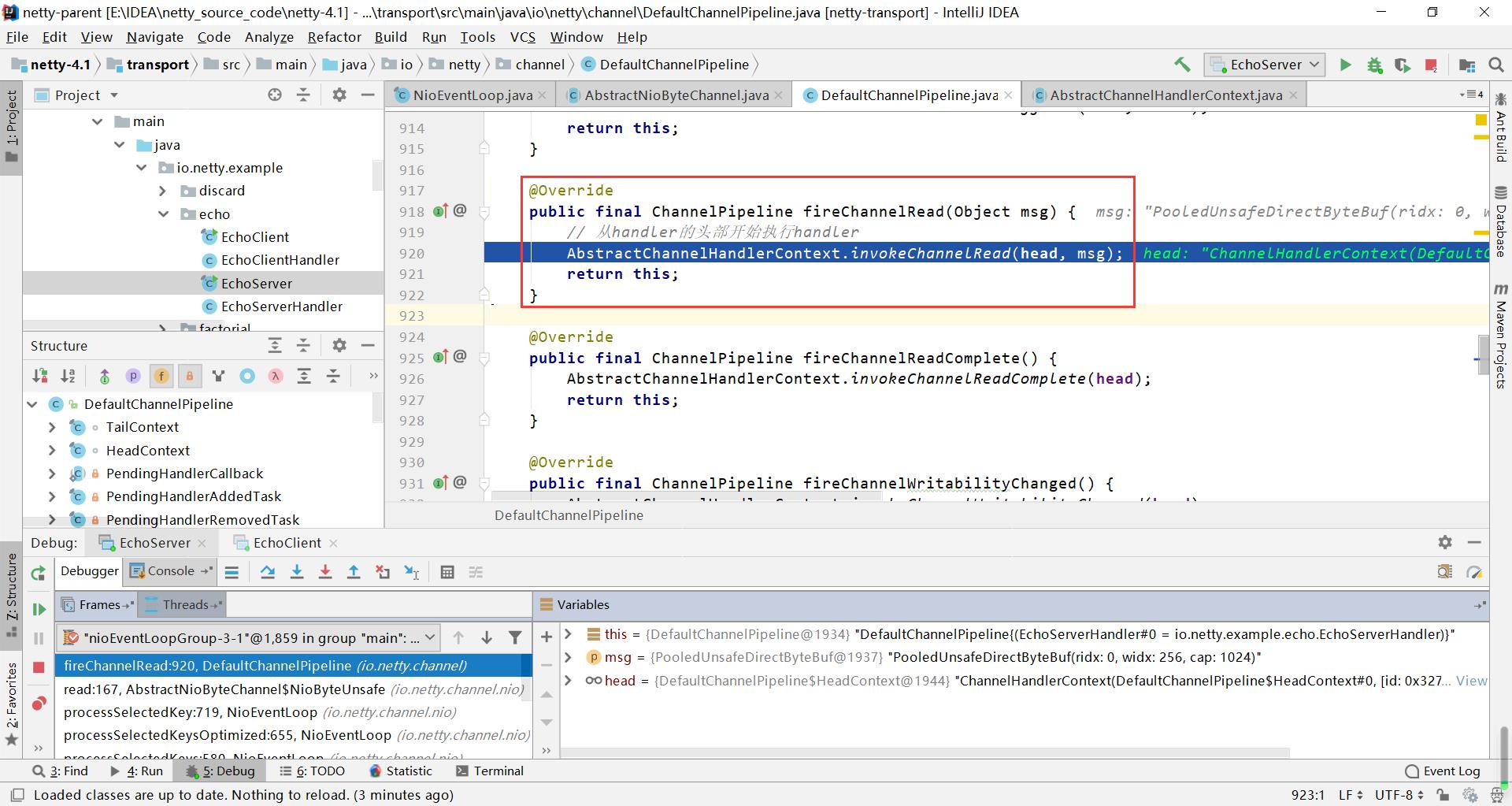
pipeline上的节点 是handlerContext , 所以执行的过程就是pipeline上找到context节点 , 然后处理节点内的handler
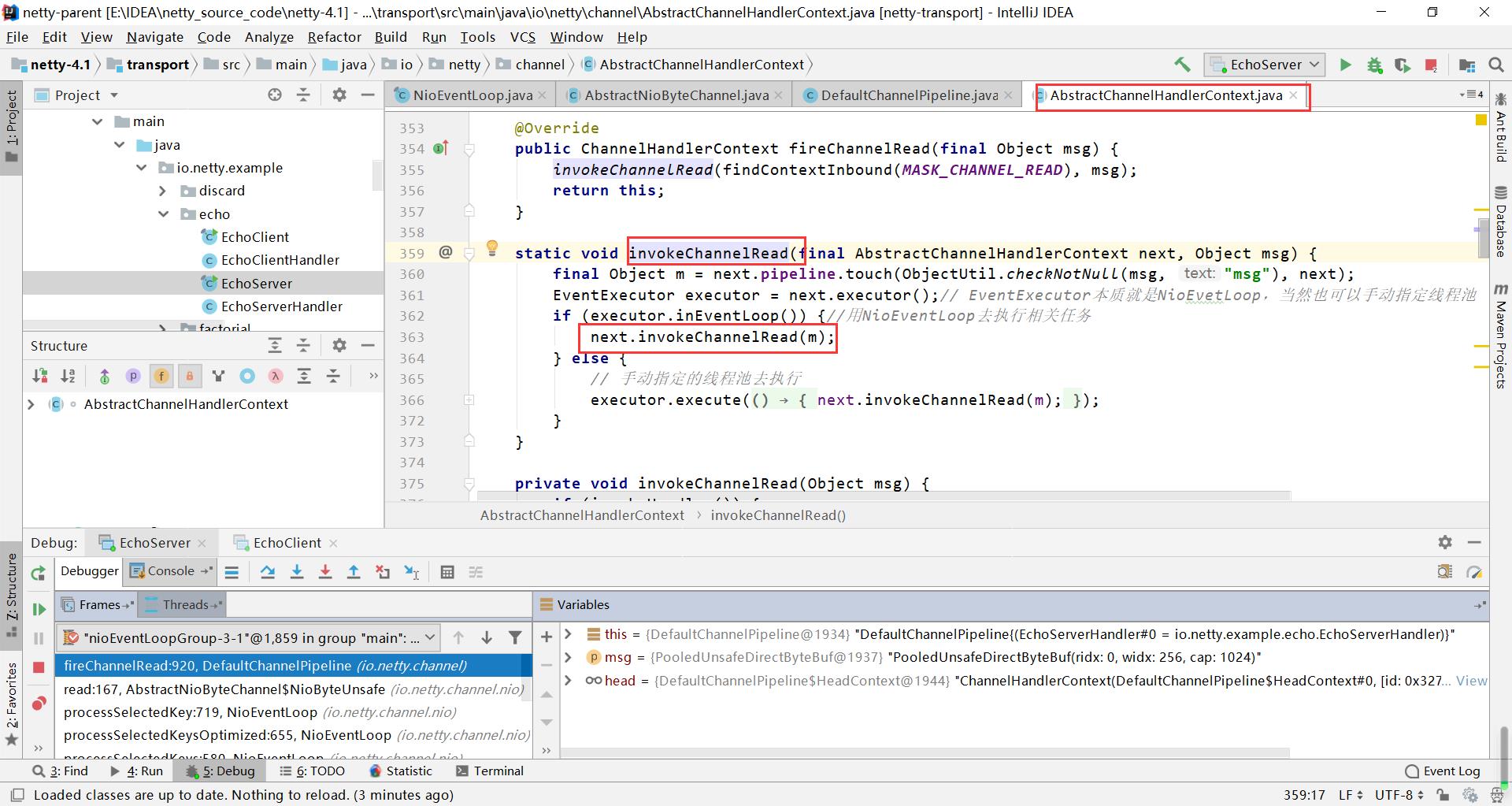
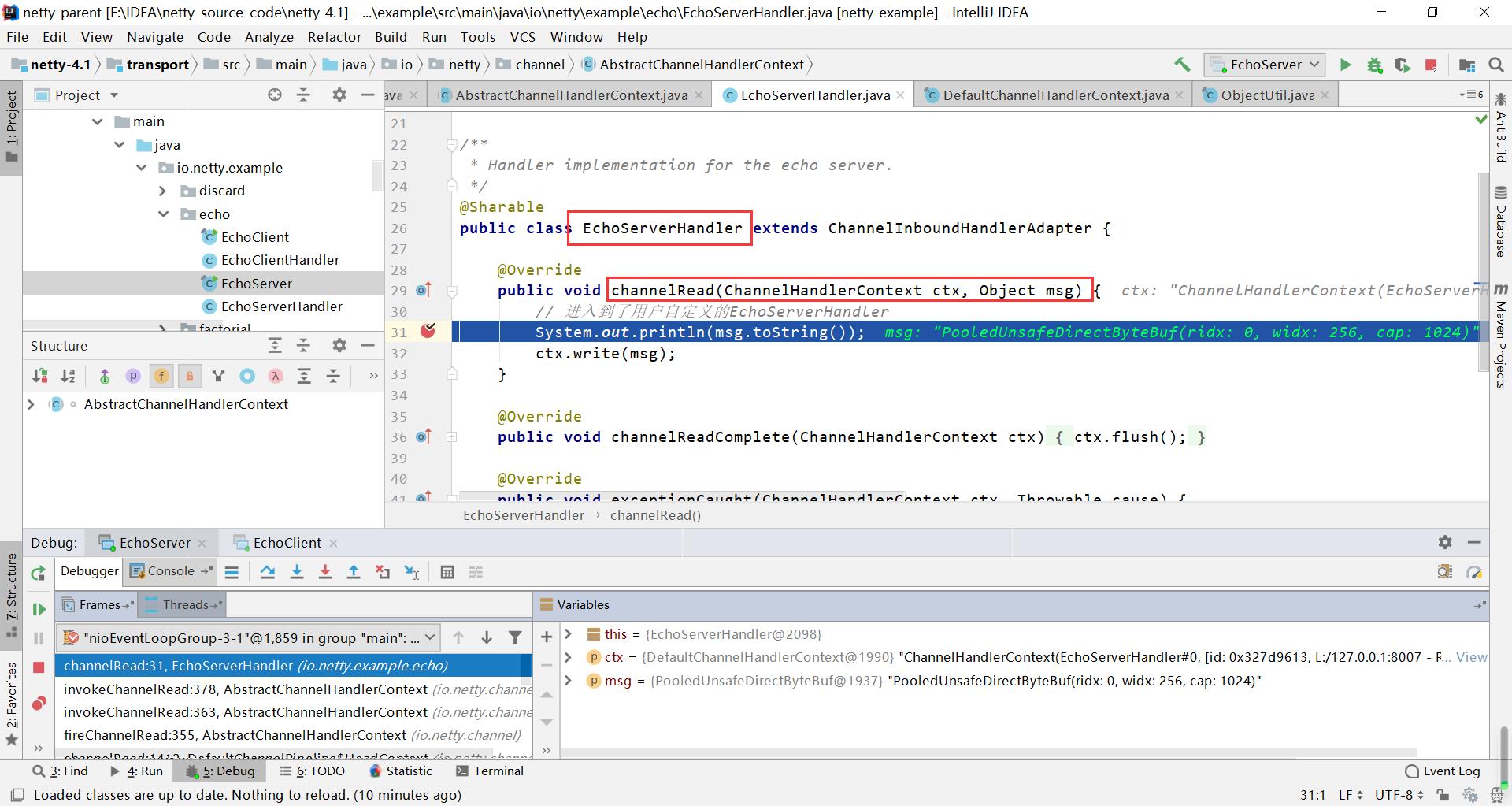
最终会走到我们自定义的handler里
以上是关于netty源码之业务逻辑处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章