Service的生命周期
Posted lgz0921
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Service的生命周期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
谷歌官网的一张Service的生命周期图:

在Service的生命周期里,常用的方法有:
- 6个内部自动调用的方法
| 内部自动调用的方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| onCreat() | 创建服务 |
| onStartCommand() | 开始服务 |
| onBind() | 绑定服务 |
| onUnbind() | 解绑服务 |
| onRebind() | 解绑后重新绑定服务 |
| onDestroy() | 销毁服务 |
上面6种内部自动调用的生命周期方法
class ExampleService : Service() {
private var startMode: Int = 0 // indicates how to behave if the service is killed
private var binder: IBinder? = null // interface for clients that bind
private var allowRebind: Boolean = false // indicates whether onRebind should be used
override fun onCreate() {
// The service is being created
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
// The service is starting, due to a call to startService()
return mStartMode
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent): IBinder? {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService()
return mBinder
}
override fun onUnbind(intent: Intent): Boolean {
// All clients have unbound with unbindService()
return mAllowRebind
}
override fun onRebind(intent: Intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService(),
// after onUnbind() has already been called
}
override fun onDestroy() {
// The service is no longer used and is being destroyed
}
}对其中的四个进行说明(引用的谷歌官网原话)
onStartCommand()当另一个组件(如 Activity)请求启动服务时,系统会通过调用 startService() 来调用此方法。执行此方法时,服务即会启动并可在后台无限期运行。如果您实现此方法,则在服务工作完成后,您需负责通过调用 stopSelf() 或 stopService() 来停止服务。(如果您只想提供绑定,则无需实现此方法。)
onBind()
当另一个组件想要与服务绑定(例如执行 RPC)时,系统会通过调用 bindService() 来调用此方法。在此方法的实现中,您必须通过返回 IBinder 提供一个接口,以供客户端用来与服务进行通信。请务必实现此方法;但是,如果您并不希望允许绑定,则应返回 null。
onCreate()
首次创建服务时,系统会(在调用 onStartCommand() 或 onBind() 之前)调用此方法来执行一次性设置程序。如果服务已在运行,则不会调用此方法。
onDestroy()
当不再使用服务且准备将其销毁时,系统会调用此方法。服务应通过实现此方法来清理任何资源,如线程、注册的侦听器、接收器等。这是服务接收的最后一个调用。
- 4个手动调用的方法
| 手动调用方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| startService() | 启动服务 |
| stopService() | 关闭服务 |
| bindService() | 绑定服务 |
| unbindService() | 解绑服务 |
注意:
- startService()和stopService()只能开启和关闭Service,无法操作Service; bindService()和unbindService()可以操作Service
- startService()开启的Service,调用者退出后Service仍然存在; bindService()开启的Service,调用者退出后,Service随着调用者销毁。
解释上面两句话:
如果组件通过调用 startService() 启动服务(这会引起对 onStartCommand() 的调用),则服务会一直运行,直到其使用 stopself() 自行停止运行,或由其他组件通过调用 stopService() 将其停止为止。
如果组件通过调用 bindService() 来创建服务,且未调用 onStartCommand() ,则服务只会在该组件与其绑定时运行。当该服务与其所有组件取消绑定后,系统便会将其销毁。
上面4种手动调用方法的具体生命周期流程
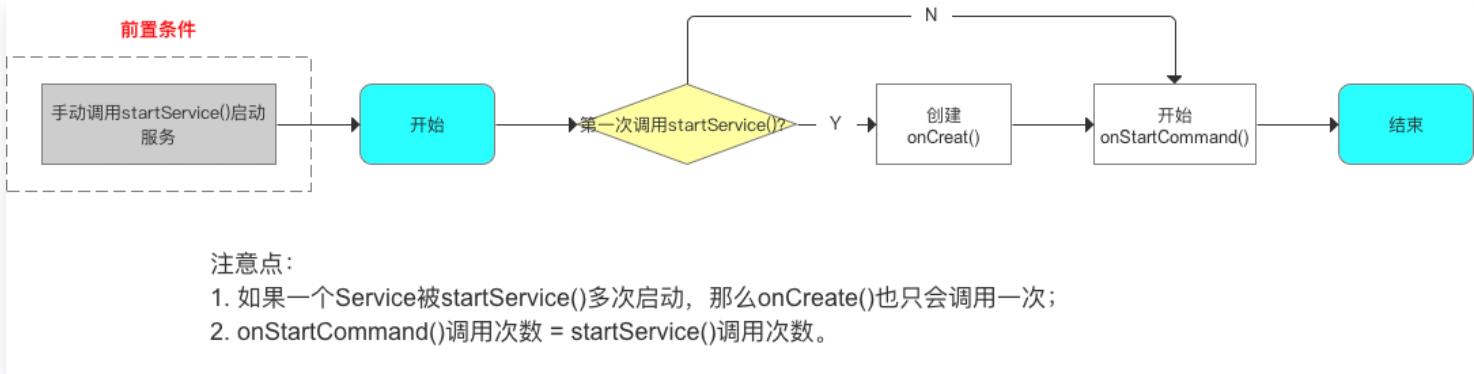
1)startService()
- 作用:启动Service服务
- 手动调用startService()后,自动调用内部方法:onCreate()、onStartCommand()
- 调用流程图如下:
2) stopService()
- 作用:关闭Service服务
- 手动调用stopService()后,自动调用内部方法:onDestory()
- 调用的流程图如下:

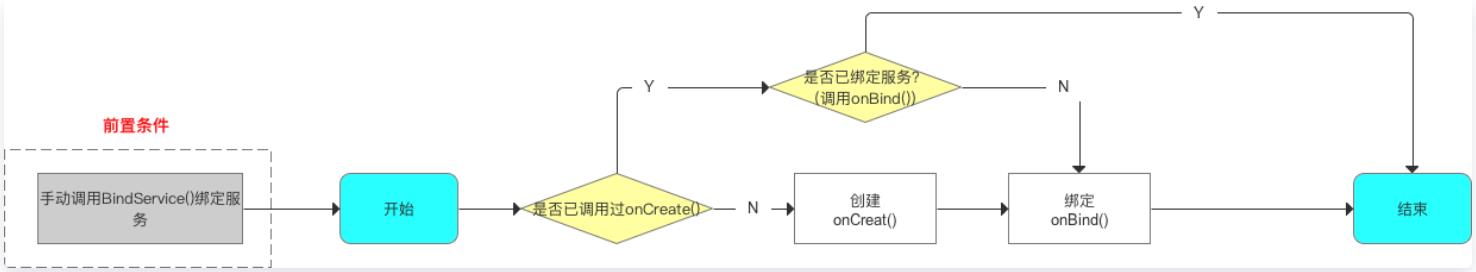
3)bindService()
- 作用:绑定Service服务
- 手动调用bindService()后,自动调用内部方法:onCreate()、onBind()
- 调用的逻辑:
4)unbindService()
- 作用:解绑Service服务
- 手动调用unbindService()后,自动调用内部方法:onUnbind()、onDestory()
- 调用的逻辑:

介绍一下三种调用Service的生命周期情况
1)只使用startService()启动服务的生命周期

2)只使用bindService()绑定服务的生命周期

3)同时使用startService()启动服务、bindService()绑定服务的生命周期

以上是关于Service的生命周期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章