链表1:单向链表的基本操作
Posted 纵横千里,捭阖四方
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了链表1:单向链表的基本操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
从这一节开始第三个专题:链表。链表也属于线性表,应用也非常广泛。我们大约用15篇文章来梳理相关的问题。
链表有单向,双向,循环等多种类型,其中单向是考察最多的。而双向和循环链表在实际应用中更多,双向链表+Hash可以实现LRU,这也是一个重要的考察点。leetcode中也有大量的算法都以其为基础。
链表的基本操作也都是创建+增删改查,不过每种根据其结构的不同,实现也有差异,我们重点看单向链表。
对于链表,插入和删除到底怎么操作一定要清清楚楚,画图也好,测试也罢,不然链表的面试题一定搞不定。
一.创建单向链表
单向链表包含多个结点,每个结点有一个指向后继元素的next指针。表中最后一个元素的next指向null。图示为:
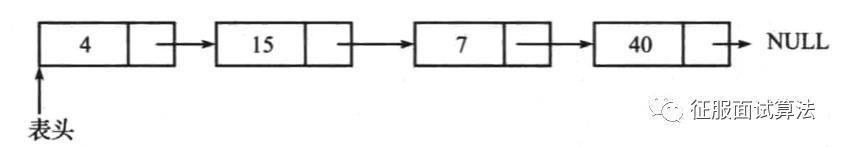
创建链表的方式可以很简单,在类里添加一个与类相同类型的next变量就行:
public class ListNode {private int data;private ListNode next;public ListNode(int data) {this.data = data;}public int getData() {return data;}public void setData(int data) {this.data = data;}public ListNode getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(ListNode next) {this.next = next;}}
在咕泡-兵兵的代码里,是定义一个内部静态类来表示节点,我感觉更好理解。方法如下,为了便于理解我们也添加一个获得链表长度的方法:
public class LinkedListBasicUse {static class Node {int data;Node next;public Node(int data) {this.data = data;}}public static int getListLength(Node head) {int length = 0;Node node = head;while (node != null) {length++;node = node.next;}return length;}}
接下来我们就用后面这种方式来实现增删改查等操作。
二.遍历链表
单链表必须知道表头的地址,然后沿着指针向前走,当next的值为null时停止。
我们看一下统计链表长度的实现方法:
/*** 获取链表长度** @param head 链表头节点* @return 链表长度*/public static int getListLength(Node head) {int length = 0;Node node = head;while (node != null) {length++;node = node.next;}return length;}
别看这个方法很简单,加上一些条件可以拓展出很多考题。
三.单向链表的插入
单向链表的插入有三个位置,表头,表尾和中间位置,都需要单独处理一下。
操作单链表一定要记住两条:必须明确知道表头在哪里,链表一定是能接上的。
(1)如果是在表头插入一个新结点,只需要修改一下next指针,然后更新表头指针。更新表头是特别容易遗忘的地方,而且到了复杂的场景更容易晕。
这个其实不用太多的文字,我们看图就知道了:
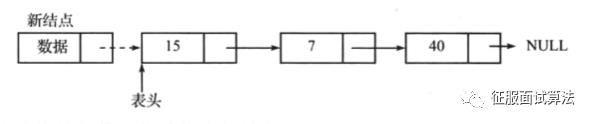
新的结点node要将next指向原来的表头head位置是吧,然后链表的表头不就是node吗?这时候将head换成node不就行了吗?
(2)在单向链表的表尾插入结点
表尾要容易很多,但是要记住必须保留表头,不用跟着一起跑到表尾了。
(3)在单向链表的中间插入结点
假设给定插入的元素,此时需要将链表断开,将新的结点接上去,脑子里始终有这个图:
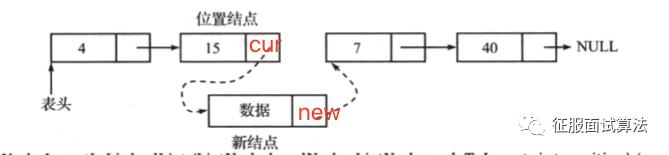
如果要你说该怎么接?如上图所示,要先遍历到15的位置cur,然后将new结点指向7的位置是不?之后将15指向new就行了。
如果不这么做会怎么样,比如先15指向new,那接下来new怎么指向7的位置呢?除非你再用一个变量记下来,否则就无法进行了?
所以完整的插入代码是:
/*** 链表插入** @param head 链表头节点* @param nodeInsert 待插入节点* @param position 待插入位置,取值从2开始* @return 插入后得到的链表头节点*/public static Node insertList(Node head, Node nodeInsert, int position) {// 需要判空,否则后面可能会有空指针异常if (head == null) {return nodeInsert;}int size = getListLength(head);if (position > size + 1 || position < 1) {System.out.println("位置参数越界");return head;}//在链表开头插入if (position == 1) {nodeInsert.next = head;return nodeInsert;} else {Node pNode = head;int count = 1;while (count < position - 1) {pNode = pNode.next;count++;}nodeInsert.next = pNode.next;pNode.next = nodeInsert;}return head;}
四.链表结点的删除
链表的删除也是删除头部,删除尾部和中间位置三种情况。
我们依次看一下。
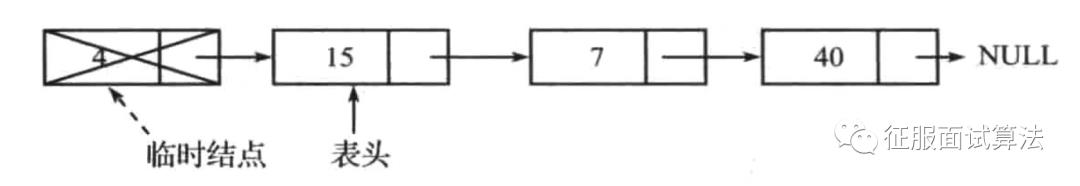
(1)删除表头元素
如下图,最容易晕的是遍历游标cur从4到15之后,head一定要指向cur,也就是要有head=cur的操作。废话不多说,看着这个图想明白就行了。
(2)删除表尾元素
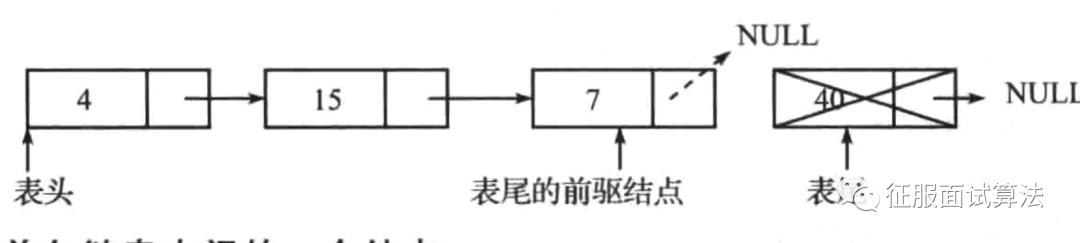
核心思想是找到尾结点时,需要将其前驱的next设置为null。如果只用一个遍历游标,可以判断遍历游标的cur.next.next是否为空,因为cur.next.next为null时,就说明cur.next是尾结点了,此时只要将cur.next设置为null就行了,如下图:
cur为7的时,cur.next是40,是尾结点,因为cur.next.next=null。此时只要设置7的next指针为null,结点40就脱离链表了。之后结点40会在某个时刻被jvm回收。
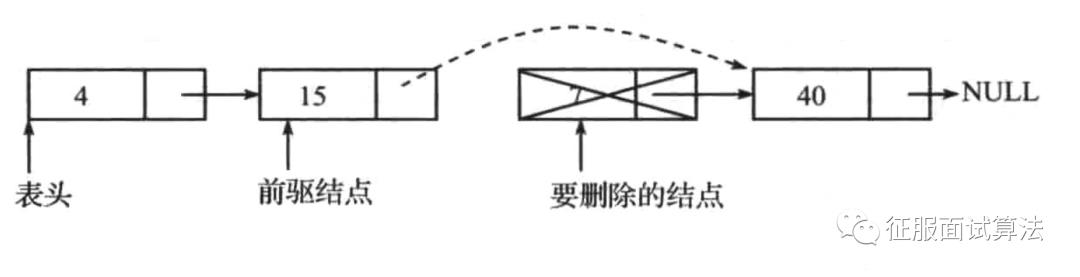
(3)删除中间元素
删除的元素在中间时,如下图,如果删除7。因为链表是单向的,此时必须提前知道结点15的地址,否则就无法将15连接到40上。
/*** 删除节点** @param head 链表头节点* @param position 删除节点位置,取值从1开始* @return 删除后的链表头节点*/public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {if (head == null) {return null;}int size = getListLength(head);if (position > size || position <= 0) {System.out.println("输入的参数有误");return head;}if (position == 1) {//curNode就是链表的新headreturn head.next;} else {Node preNode = head;int count = 1;while (count < position) {preNode = preNode.next;count++;}Node curNode = preNode.next;preNode.next = curNode.next;}return head;}
最后我们再补充一个打印链表方法:
/*** 链表打印** @param head 头结点*/public static String toString(Node head) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();while (head != null) {sb.append(head.data).append("\\t");head = head.next;}return sb.toString();}
然后测试方法就可以这样写了:
public static void main(String[] args) {// 头部添加节点1LinkedListBasicUse.Node head = new Node(1);System.out.println("头部添加节点1:" + LinkedListBasicUse.toString(head));// 尾部添加节点2head = LinkedListBasicUse.insertList(head, new Node(2), 2);System.out.println("尾部添加节点2:" + LinkedListBasicUse.toString(head));// 中间添加节点3head = LinkedListBasicUse.insertList(head, new Node(3), 2);System.out.println("中间添加节点3:" + LinkedListBasicUse.toString(head));// 删除中间节点2head = LinkedListBasicUse.deleteNode(head, 2);System.out.println("删除中间节点2:" + LinkedListBasicUse.toString(head));// 删除头部节点1head = LinkedListBasicUse.deleteNode(head, 1);System.out.println("删除头部节点1:" + LinkedListBasicUse.toString(head));}
以上是关于链表1:单向链表的基本操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章