多任务学习——ICML 2018GradNorm
Posted 卓寿杰SoulJoy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多任务学习——ICML 2018GradNorm相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.02257.pdf
之前讲过了多任务学习,如简单的shared bottom,都存在一个问题:多个任务的loss如何融合?简单的方式,就是将多个任务的loss直接相加:
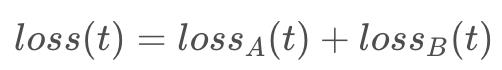
但实际情况是,不同任务loss梯度的量级不同,造成有的task在梯度反向传播中占主导地位,模型过分学习该任务而忽视其它任务。此外,不同任务收敛速度不一致的,可能导致有些任务还处于欠拟合,可有些任务已经过拟合了。当然,我们可以人工的设置超参数,如:
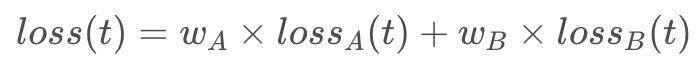
由于各任务在训练过程中自己的梯度量级和收敛速度也是动态变化的,所以很显然这样定值的w做并没有很好的解决问题。作者提出了一种可以动态调整loss的w的算法——GradNorm:
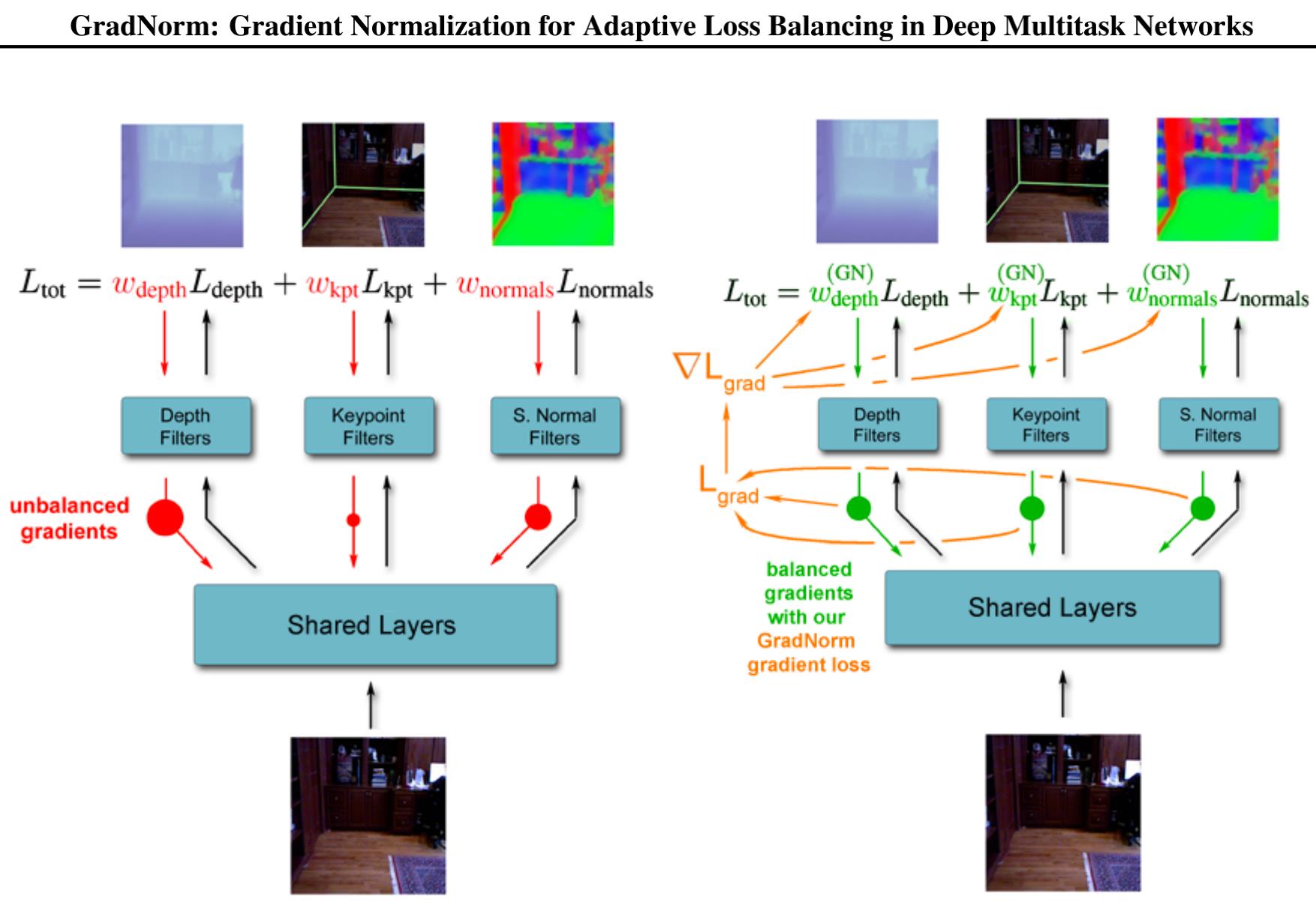
从上图可知,GradNorm 是以平衡的梯度作为目标,优化Grad Loss,从而动态调整各个任务的w。
那下面我们就来看看Grad Loss是怎么样的:
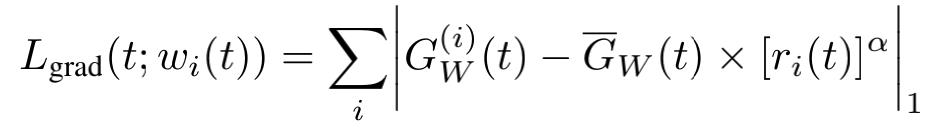
要注意的是,上式中,减号后面的项,是基于当轮各任务的梯度所计算出来的常量。其中:


G调节着梯度的量级。r调节着任务收敛速度:收敛速度越快,
r
i
r_i
ri就越小,从而
G
w
(
i
)
(
t
)
G^{(i)}_w(t)
Gw(i)(t)应该被优化的变小。
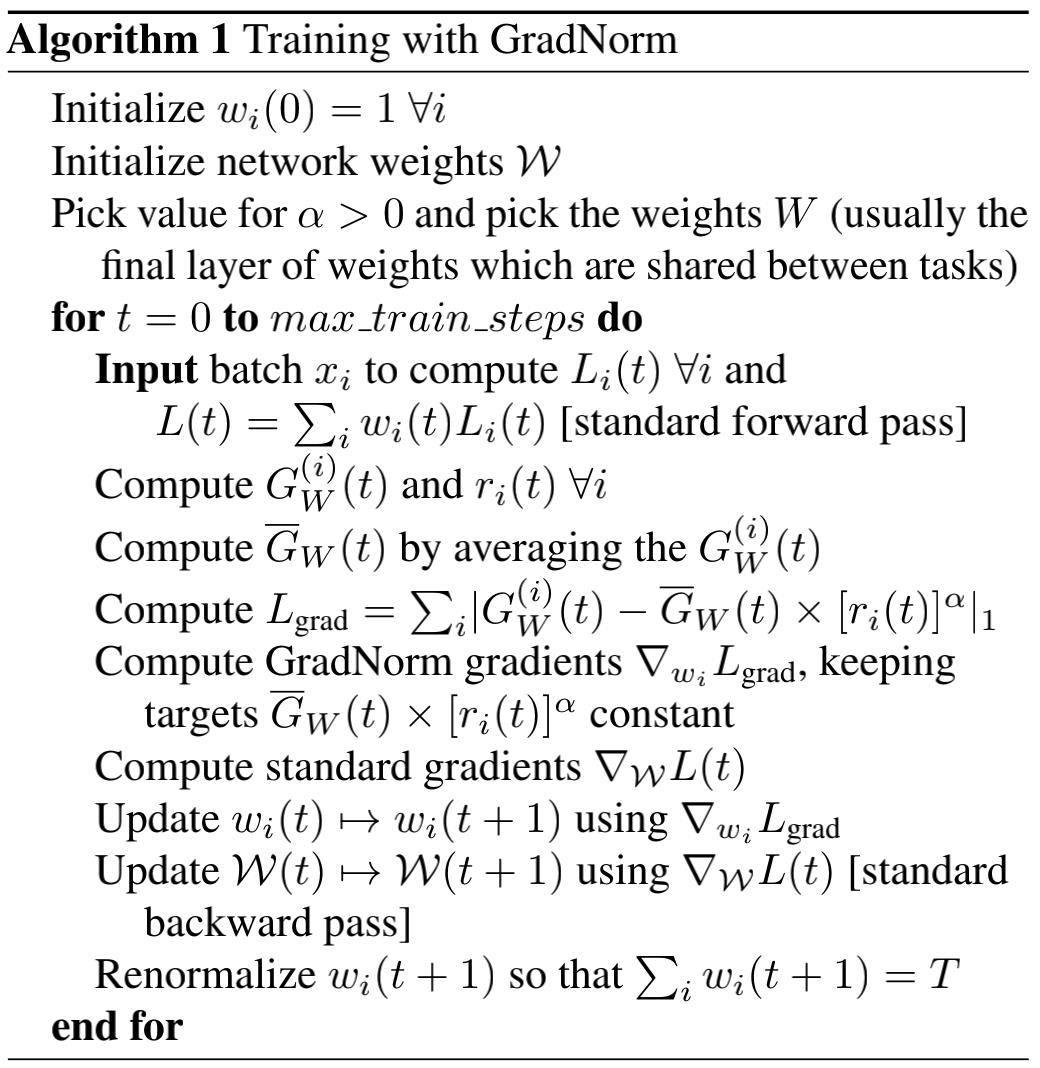
算法步骤如下:
实现如下(引自 GitHub):
# switch for each weighting algorithm:
# --> grad norm
if args.mode == 'grad_norm':
# get layer of shared weights
W = model.get_last_shared_layer()
# get the gradient norms for each of the tasks
# G^{(i)}_w(t)
norms = []
for i in range(len(task_loss)):
# get the gradient of this task loss with respect to the shared parameters
gygw = torch.autograd.grad(task_loss[i], W.parameters(), retain_graph=True)
# compute the norm
norms.append(torch.norm(torch.mul(model.weights[i], gygw[0])))
norms = torch.stack(norms)
#print('G_w(t): {}'.format(norms))
# compute the inverse training rate r_i(t)
# \\curl{L}_i
if torch.cuda.is_available():
loss_ratio = task_loss.data.cpu().numpy() / initial_task_loss
else:
loss_ratio = task_loss.data.numpy() / initial_task_loss
# r_i(t)
inverse_train_rate = loss_ratio / np.mean(loss_ratio)
#print('r_i(t): {}'.format(inverse_train_rate))
# compute the mean norm \\tilde{G}_w(t)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
mean_norm = np.mean(norms.data.cpu().numpy())
else:
mean_norm = np.mean(norms.data.numpy())
#print('tilde G_w(t): {}'.format(mean_norm))
# compute the GradNorm loss
# this term has to remain constant
constant_term = torch.tensor(mean_norm * (inverse_train_rate ** args.alpha), requires_grad=False)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
constant_term = constant_term.cuda()
#print('Constant term: {}'.format(constant_term))
# this is the GradNorm loss itself
grad_norm_loss = torch.tensor(torch.sum(torch.abs(norms - constant_term)))
#print('GradNorm loss {}'.format(grad_norm_loss))
# compute the gradient for the weights
model.weights.grad = torch.autograd.grad(grad_norm_loss, model.weights)[0]
以上是关于多任务学习——ICML 2018GradNorm的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章