Java集合与数据结构 栈和队列
Posted 头发都哪去了
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合与数据结构 栈和队列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java集合与数据结构 栈和队列
栈(Stack)
概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶
基本方法
示例代码如下:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
//stack.peek() 拿到栈顶元素
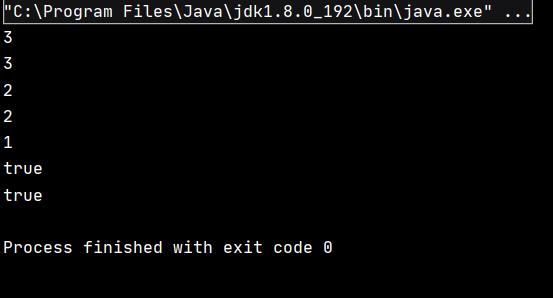
System.out.println(stack.peek());//3
//弹出栈顶元素
System.out.println(stack.pop());//3
System.out.println(stack.peek());//2
System.out.println(stack.pop());//2
System.out.println(stack.pop());//1
System.out.println(stack.empty());//t
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());//t
}
}
该代码的执行结果如下:
栈的习题
出栈顺序不可能
一个栈的入栈序列是a,b,c,d,e则栈的不可能的输出序列是:()
A edcba B decba C dceab D abcde
解答:
栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出,对于A选项是可以作为栈的输出序列的,进a ,进b,进c,进d,进e,出e,出d,出c,出b,出a,所以出栈顺序为edbca;对于B选项是可以作为栈的输出序列的,进a,进b,进c,进d,出d,进e,出e,出c,出b,出a,所以出栈顺序为decba;对于D选项也是可以作为栈的输出序列的,进a,出a,进b,出b,进c,出c,进d,出d,进e,出e,所以出栈顺序为abcde;而C选项的出栈顺序可能为dceba,绝不可能为dceab。
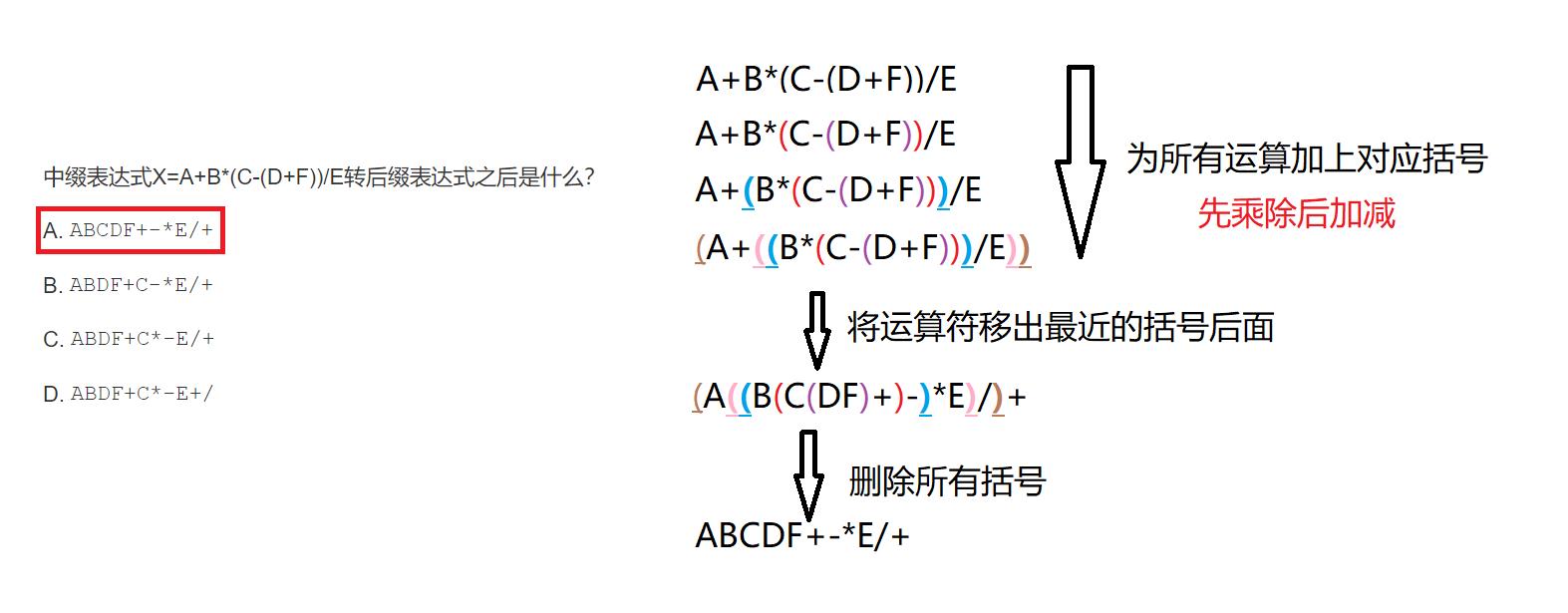
中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰式)

中缀表达式转后缀表达式的方法:
1.遇到操作数:直接输出(添加到后缀表达式中)
2.栈为空时,遇到运算符,直接入栈
3.遇到左括号:将其入栈
4.遇到右括号:执行出栈操作,并将出栈的元素输出,直到弹出栈的是左括号,左括号不输出。
5.遇到其他运算符:加减乘除:弹出所有优先级大于或者等于该运算符的栈顶元素,然后将该运算符入栈。
6.最终将栈中的元素依次出栈,输出。
这里我们再介绍一种简单方法:
手动实现栈
public class MyStack {
private int[] elem;
private int top;//既可以代表下标:这个位置就是当前可以存放数据的下标
// 也可以代表当前有多少个元素
public MyStack() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.top == this.elem.length;
}
public int push(int item) {
if(isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈为满");
}
this.elem[this.top] = item;
this.top++;
return this.elem[this.top-1];
}
/*
* 弹出栈顶元素 并且删除
* @return
*/
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
//return -1;
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");
}
this.top--;
return this.elem[this.top];
}
/*
* 拿到栈顶元素不删除
* @return
*/
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
//return -1;
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");
}
return this.elem[this.top-1];
}
public boolean empty() {
return this.top == 0;
//return size() == 0;
}
public int size() {
return this.top;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(12);
myStack.push(23);
myStack.push(34);
myStack.push(45);
myStack.push(56);
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
System.out.println(myStack.empty());
}
}
该代码执行效果如下:

队列(Queue)
概念
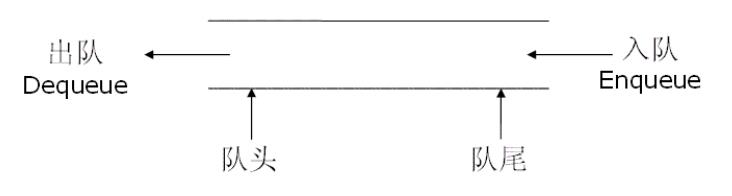
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear)
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)
基本方法

示例代码如下:
public class QueueTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//普通的队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//此时调用的add方法,默认从队尾入队
queue.add(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
//得到队头元素,不删除
System.out.println(queue.peek());
//拿出队头元素
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
此代码的执行结果如下:

链表实现队列
class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyQueueByLinkedList {
public Node first;//队头
public Node last;//队尾
public boolean offer(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
//判断是否第一次插入
if (this.first == null) {
this.first = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
this.last.next = node;
this.last = node;
}
return true;
}
/*
* 拿出队头元素
*/
public int poll() throws RuntimeErrorException{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空~");
}
int ret = this.first.val;
this.first = this.first.next;
return ret;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.last == null && this.first == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
* 得到队头元素不删除
*/
public int peek() throws RuntimeErrorException{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空~");
}
int ret = this.first.val;
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueueByLinkedList myQueue = new MyQueueByLinkedList();
myQueue.offer(1);
myQueue.offer(2);
myQueue.offer(3);
myQueue.offer(4);
//得到队头元素,不删除
System.out.println(myQueue.peek());
//拿出队头元素
System.out.println(myQueue.poll());
System.out.println(myQueue.peek());
}
}
该代码的执行结果为:

循环队列
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
手动实现循环队列手动实现循环队列力扣链接
public class MyCircularQueue {
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] elem;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
}
/*
* 判断队列是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.front == this.rear;
}
/*
* 判断队列是否已满
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return (this.rear + 1) % this.elem.length == this.front;
}
/*
* 入队
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
//放到数组的rear下标
this.elem[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
/*
* 出队
* @return
*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
/*
* 得到队头元素
* @return
*/
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = this.elem[this.front];
return ret;
}
/*
* 得到队尾元素
* @return
*/
public int Rear() {
int index;
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
if (this.rear == 0) {
index = this.elem.length - 1;
} else {
index = this.rear-1;
}
return this.elem[index];
}
}
该代码执行通过。
用队列实现栈
题目描述:
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
private Queue<Integer> qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
} else if (!qu2.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
} else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for(int i=0;i<size-1;i++){
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
}
return qu1.poll();
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for(int i=0;i<size-1;i++){
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
int cur = -1;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cur = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(cur);
}
return cur;
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
int cur = -1;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cur = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(cur);
}
return cur;
}
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
该代码执行通过。

用栈实现队列
题目描述:
仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(以上是关于Java集合与数据结构 栈和队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章