2021深圳杯东三省建模
Posted weixin_43292788
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2021深圳杯东三省建模相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
火星探测器着陆控制方案
本题聚焦于探测器从火星同步轨道出发到探测器在火星地表上
方悬停的过程(以下简称着陆过程),要求参赛队收集有关天问一号
探测器的音像和文字等公开资料,建立数学模型,研究如下问题:
- 确定探测器着陆过程时间最短的操控方案(包括环绕器与着
陆巡视器分离、阻尼伞打开、发动机系统点火等时间,以及
发动机系统运行方案); - 对给定的着陆过程时间,确定消耗能量最少的操控方案;
- 如果希望探测器着陆过程与公开的音像和文字资料尽量一致,
如何设计操控方案
相关数据及数据分析
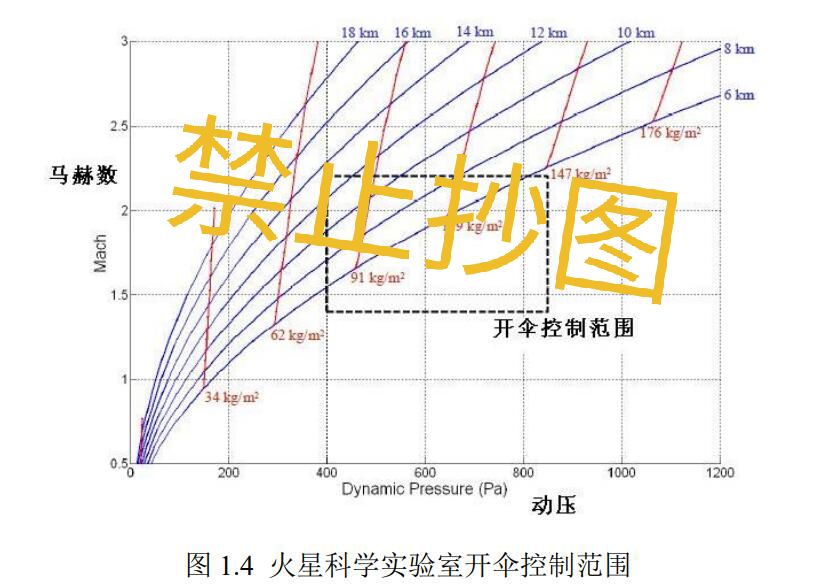
火星着陆器开伞条件均为超声速开伞,但为了确保降落伞的开伞可靠,
一般都控制开伞马赫数不大于 2.2;
由于大气密度小,开伞动压较小,一般采用弹伞筒直接弹伞和一次开伞
技术;
大部分火星着陆器均使用了盘缝带伞。其中在着陆前没有姿态控制的着
陆器均采用了火星探路者类型及其改进型的盘缝带伞(降落伞的稳定性高),在着陆前进行姿态控制的着陆器均采用海盗号类型的盘缝带伞(降落伞的阻力系数大);
最小弹射分离速度的确定方法
对于降落伞系统而言,确定弹射分离速度非常关键。该弹射分离速度取得过小,将可能导致降落伞无法越过回收物的尾流或无法正常拉直;该弹射分离速度取得过大,由于弹射分离推力一般与该速度的二次方成正比,过大的弹射分离推力将导致弹伞载荷偏大,并对回收物的结构设计、降落伞连接分离机构的结构设计带来影响,从而导致更大的结构重量。选取合适的弹射分离速度,首先需要得到所需的最小弹射分离速度。


受力分析


import java.util.*;
public class test9 {
private static String Time[] = { "0", "20", "50", "100", "150", "200",
"240", "290", "320", "400", "450", "490" };
private static int verticalspeed[] = { 1400, 1600, 1550, 1300, 1700, 1000, 1100, 800, 700, 40,
200, 400 };
private static int horizonspeed[] = { 0, 10, 15, 10, 5, 3, 0, -20, -30, -32, -35, -32, -21,
-11, 0 };
private static int b2[] = { 98, 78, 63, 50, 40, 33 };
private static int thrust[] = { 7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500,7500 };
private static int angle[] = { 85, 85, 84, 82, 80, 78, 77, 75, 74, 72, 68, 65 };
private int timeNum = Time.length;
private int popSize = 50;
private int maxgens = 10000;
private double pxover = 0.8;
private double pmultation = 0.05;
private long[][] distance = new long[timeNum][timeNum];
private int range = 2000;
private class genotype {
int city[] = new int[timeNum];
long fitness;
double selectP;
double exceptp;
int isSelected;
}
private genotype[] citys = new genotype[popSize];
/**
* 构造函数,初始化种群
*/
public test9() {
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) {
citys[i] = new genotype();
int[] num = new int[timeNum];
for (int j = 0; j < timeNum; j++)
num[j] = j;
int temp = timeNum;
for (int j = 0; j < timeNum; j++) {
int r = (int) (Math.random() * temp);
citys[i].city[j] = num[r];
num[r] = num[temp - 1];
temp--;
}
citys[i].fitness = 0;
citys[i].selectP = 0;
citys[i].exceptp = 0;
citys[i].isSelected = 0;
}
initDistance();
}
/**
* 计算每个种群每个基因个体的适应度,选择概率,期望概率,和是否被选择。
*/
public void CalAll() {
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) {
citys[i].fitness = 0;
citys[i].selectP = 0;
citys[i].exceptp = 0;
citys[i].isSelected = 0;
}
CalFitness();
CalSelectP();
CalExceptP();
CalIsSelected();
}
/**
* 填充,将多选的填充到未选的个体当中
*/
public void pad() {
int best = 0;
int bad = 0;
while (true) {
while (citys[best].isSelected <= 1 && best < popSize - 1)
best++;
while (citys[bad].isSelected != 0 && bad < popSize - 1)
bad++;
for (int i = 0; i < timeNum; i++)
citys[bad].city[i] = citys[best].city[i];
citys[best].isSelected--;
citys[bad].isSelected++;
bad++;
if (best == popSize || bad == popSize)
break;
}
}
/**
* 交叉主体函数
*/
public void crossover() {
int x;
int y;
int pop = (int) (popSize * pxover / 2);
while (pop > 0) {
x = (int) (Math.random() * popSize);
y = (int) (Math.random() * popSize);
executeCrossover(x, y);// x y 两个体执行交叉
pop--;
}
}
/**
* 执行交叉函数
*
* @param 个体x
* @param 个体y
* 对个体x和个体y执行佳点集的交叉
*/
private void executeCrossover(int x, int y) {
int dimension = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < timeNum; i++)
if (citys[x].city[i] != citys[y].city[i]) {
dimension++;
}
int diffItem = 0;
double[] diff = new double[dimension];
for (int i = 0; i < timeNum; i++) {
if (citys[x].city[i] != citys[y].city[i]) {
diff[diffItem] = citys[x].city[i];
citys[x].city[i] = -1;
citys[y].city[i] = -1;
diffItem++;
}
}
Arrays.sort(diff);
double[] temp = new double[dimension];
temp = gp(x, dimension);
for (int k = 0; k < dimension; k++)
for (int j = 0; j < dimension; j++)
if (temp[j] == k) {
double item = temp[k];
temp[k] = temp[j];
temp[j] = item;
item = diff[k];
diff[k] = diff[j];
diff[j] = item;
}
int tempDimension = dimension;
int tempi = 0;
while (tempDimension > 0) {
if (citys[x].city[tempi] == -1) {
citys[x].city[tempi] = (int) diff[dimension - tempDimension];
tempDimension--;
}
tempi++;
}
Arrays.sort(diff);
temp = gp(y, dimension);
for (int k = 0; k < dimension; k++)
for (int j = 0; j < dimension; j++)
if (temp[j] == k) {
double item = temp[k];
temp[k] = temp[j];
temp[j] = item;
item = diff[k];
diff[k] = diff[j];
diff[j] = item;
}
tempDimension = dimension;
tempi = 0;
while (tempDimension > 0) {
if (citys[y].city[tempi] == -1) {
citys[y].city[tempi] = (int) diff[dimension - tempDimension];
tempDimension--;
}
tempi++;
}
}
/**
* @param individual
* 个体
* @param dimension
* 维数
* @return 佳点集 (用于交叉函数的交叉点) 在executeCrossover()函数中使用
*/
private double[] gp(int individual, int dimension) {
double[] temp = new double[dimension];
double[] temp1 = new double[dimension];
int p = 2 * dimension + 3;
while (!isSushu(p))
p++;
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; i++) {
temp[i] = 2 * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * (i + 1) / p)
* (individual + 1);
temp[i] = temp[i] - (int) temp[i];
if (temp[i] < 0)
temp[i] = 1 + temp[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; i++)
temp1[i] = temp[i];
Arrays.sort(temp1);
// 排序
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < dimension; j++)
if (temp[j] == temp1[i])
temp[j] = i;
return temp;
}
/**
* 变异
*/
public void mutate() {
double random;
int temp;
int temp1;
int temp2;
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) {
random = Math.random();
if (random <= pmultation) {
temp1 = (int) (Math.random() * (timeNum));
temp2 = (int) (Math.random() * (timeNum));
temp = citys[i].city[temp1];
citys[i].city[temp1] = citys[i].city[temp2];
citys[i].city[temp2] = temp;
}
}
}
/**
* 初始化各状态之间的距离
*/
private void initDistance() {
for (int i = 0; i < timeNum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < timeNum; j++) {
distance[i][j] = Math.abs(i - j);
}
}
}
/**
* 计算所有状态序列的适应度
*/
private void CalFitness() {
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < timeNum - 1; j++)
citys[i].fitness += distance[citys[i].city[j]][citys[i].city[j + 1]];
citys[i].fitness += distance[citys[i].city[0]][citys[i].city[timeNum - 1]];
}
}
/**
* 计算选择概率
*/
private void CalSelectP() {
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++)
sum += citys[i].fitness;
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++)
citys[i].selectP = (double) citys[i].fitness / sum;
}
/**
* 计算期望概率
*/
private void CalExceptP() {
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++)
citys[i].exceptp = (double) citys[i].selectP * popSize;
}
/**
* 计算该状态序列是否较优,较优则被选择,进入下一代
*/
private void CalIsSelected() {
int needSelecte = popSize;
for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++)
if (citys[i]