Java SSM 项目实战 day08 方法级别的权限操作 服务器端的权限控制(JSR-250注解)(支持表达式的注解)(@Secured)以及页面端的权限控制
Posted 蓝盒子bluebox
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java SSM 项目实战 day08 方法级别的权限操作 服务器端的权限控制(JSR-250注解)(支持表达式的注解)(@Secured)以及页面端的权限控制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、服务器端方法级权限控制
在服务器端我们可以通过Spring security提供的注解对方法来进行权限控制。Spring Security在方法的权限控制上
支持三种类型的注解,JSR-250注解、@Secured注解和支持表达式的注解,这三种注解默认都是没有启用的,需要
单独通过global-method-security元素的对应属性进行启用
1、开启注解使用
配置文件
<security:global-method-security jsr250-annotations="enabled"/>
<security:global-method-security secured-annotations="enabled"/>
<security:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="disabled"/>
注解开启
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity :Spring Security默认是禁用注解的,要想开启注解,需要在继承
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的类上加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解,并在该类中将
AuthenticationManager定义为Bean。
2、JSR-250注解
@RolesAllowed表示访问对应方法时所应该具有的角色
示例:
@RolesAllowed({"USER", "ADMIN"}) 该方法只要具有"USER", "ADMIN"任意一种权限就可以访问。
这里可以省略前缀ROLE_,实际的权限可能是ROLE_ADMIN。
@PermitAll表示允许所有的角色进行访问,也就是说不进行权限控制
@DenyAll是和PermitAll相反的,表示无论什么角色都不能访问
3、注解的使用
这里的配置在之前已经配置过


//查询全部产品
@RequestMapping("/findAll.do")
@RolesAllowed("ADMIN")
public ModelAndView findAll() throws Exception {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
List<Product> ps = productService.findAll();
mv.addObject("productList",ps);
mv.setViewName("product-list");
return mv;
}
4、运行测试
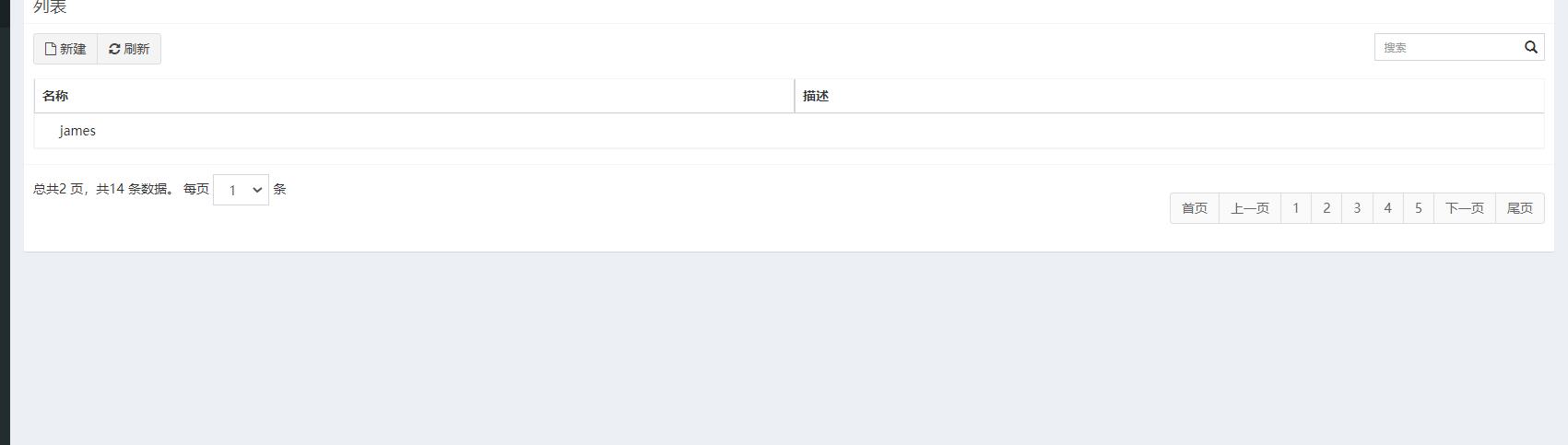
(1)查看james用户的权限:没有ADMIN角色的权限
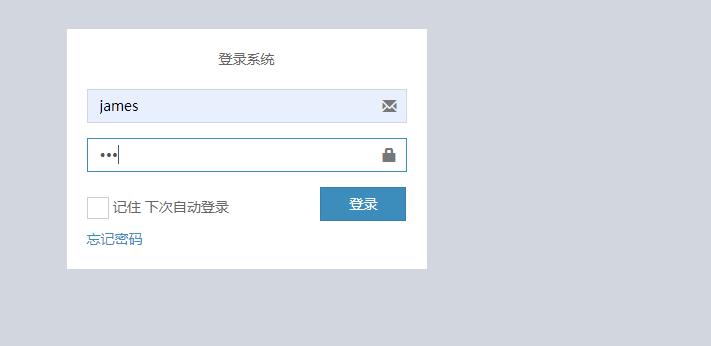
(2)登出当前用户,并登录james用户



(3)设置不显示403,修改web.xml

<error-page>
<error-code>403</error-code>
<location>/403.jsp</location>
</error-page>
(4)创建403.jsp

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 页面meta -->
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<title>权限</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>权限不足</h1>
</body>
</html>
(5)再次运行测试


5、方法级权限控制-@Secured注解的使用
@Secured注解标注的方法进行权限控制的支持,其值默认为disabled。
示例:
@Secured("IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY")
public Account readAccount(Long id);
@Secured("ROLE_TELLER")
(1)修改spring-security.xml文件

(2)修改OrdersController当中findAll方法添加@Secured("ADMIN")

(3)从新运行并测试
a、先让james登录


发现权限不足

a、后让tom登录:tom拥有ADMIN权限
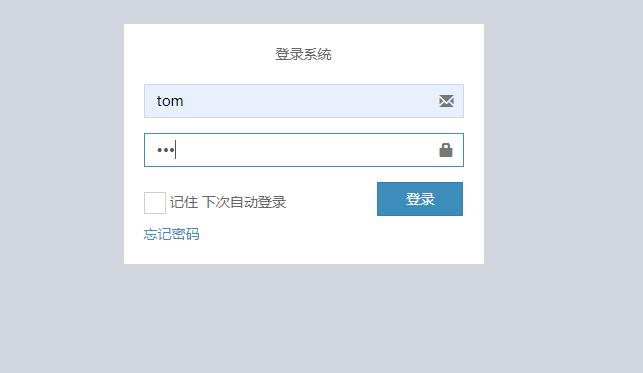
依旧权限不足

(4)上面执行的流程不对(修改OrdersController当中的findAll方法) @Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")

为啥要这样因为
在这里配置权限拦截规则的时候是这样盘配置的
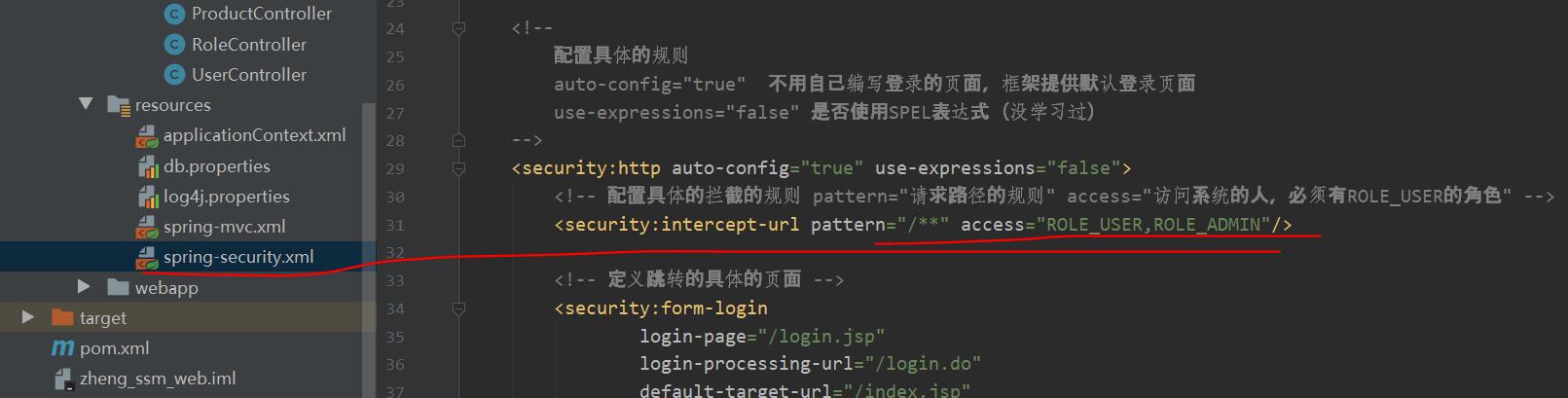
(5)注意
在使用JSR250的注解的时候,可以省略ROLE_前缀
而我们现在使用的@Secured注解是不能省略前缀的
(6)从新运行
a、tom登录



b、james登录



6、支持表达式的注解
@PreAuthorize 在方法调用之前,基于表达式的计算结果来限制对方法的访问
示例:
@PreAuthorize("#userId == authentication.principal.userId or hasAuthority(‘ADMIN’)")
void changePassword(@ P("userId") long userId ){
}
这里表示在changePassword方法执行之前,
判断方法参数userId的值是否等于principal中保存的当前用户的userId
或者当前用户是否具有ROLE_ADMIN权限,两种符合其一,就可以访问该方法。
@PostAuthorize 允许方法调用,但是如果表达式计算结果为false,将抛出一个安全性异常
示例:
@PostAuthorize
User getUser("returnObject.userId == authentication.principal.userId orhasPermission(returnObject, 'ADMIN')");
@PostFilter 允许方法调用,但必须按照表达式来过滤方法的结果
@PreFilter 允许方法调用,但必须在进入方法之前过滤输入值
(1)第一步:开启使用:修改spring-security.xml文件


<security:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled" jsr250-annotations="enabled" secured-annotations="enabled" >
</security:global-method-security>
(2)第二步:修改UserController当中的save方法和findAll方法
指定只有tom用户可以执行save操作
只有ADMIN用户可以执行findAll方法
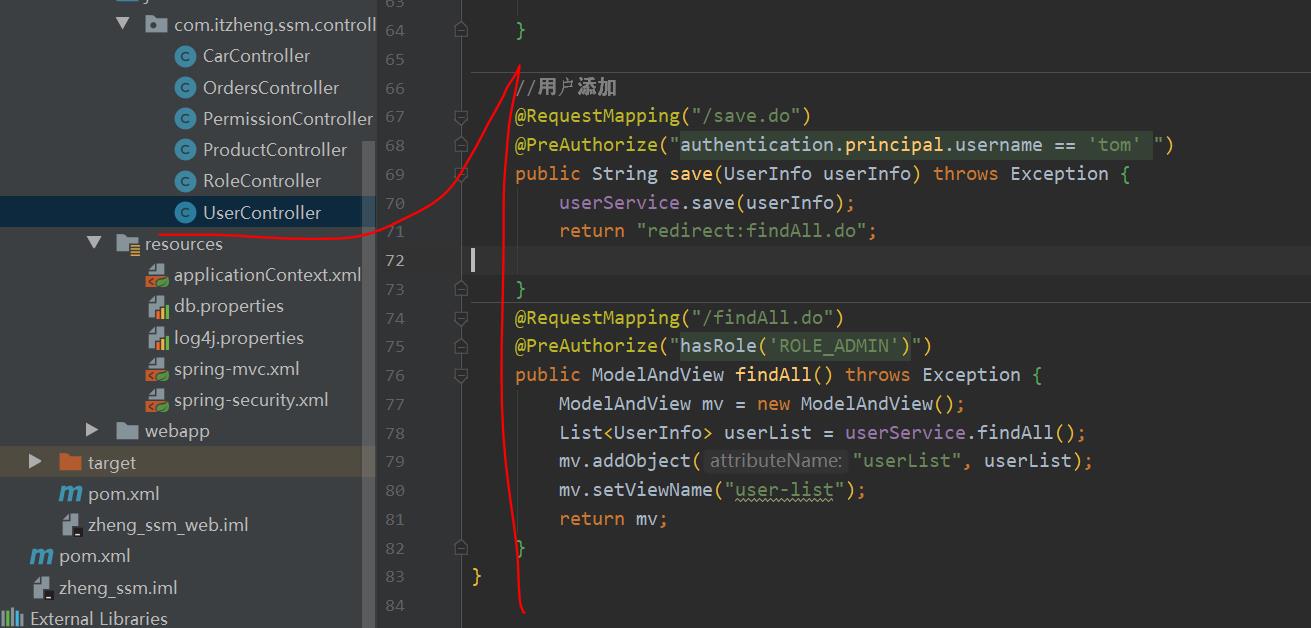
//用户添加
@RequestMapping("/save.do")
@PreAuthorize("authentication.principal.username == 'tom' ")
public String save(UserInfo userInfo) throws Exception {
userService.save(userInfo);
return "redirect:findAll.do";
}
@RequestMapping("/findAll.do")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public ModelAndView findAll() throws Exception {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
List<UserInfo> userList = userService.findAll();
mv.addObject("userList", userList);
mv.setViewName("user-list");
return mv;
}

(3)运行测试



fox1用户登录。fox1拥有ADMIN角色


点击新建用户


点击保存,发现权限不足,因为在上面设置了只有tom用户才可以添加用户

切换到tom用户



保存成功

二、页面端的权限控制

1、导入配置
(1)在maven当中的pom.xml文件当中导入

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-taglibs</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
(2)JSP页面导入
a、header.jsp页面当中

<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" prefix="security"%>
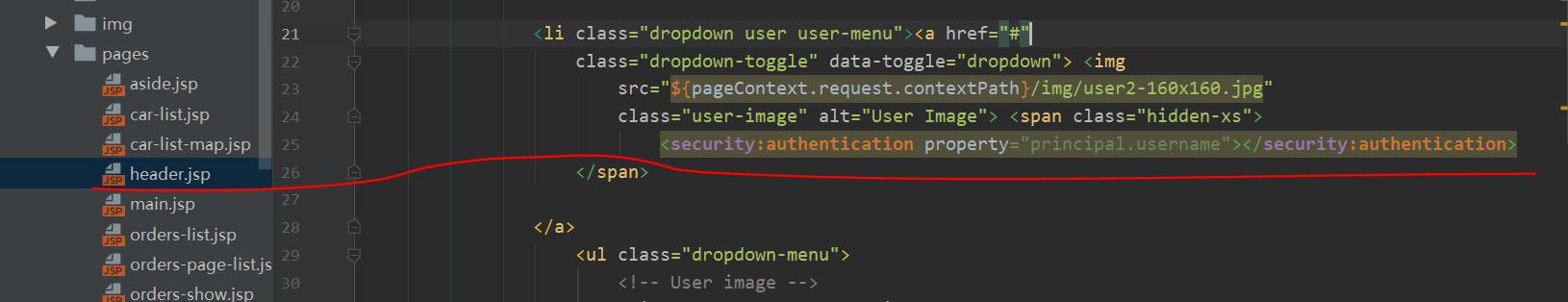
<security:authentication property="principal.username"></security:authentication>
b、aside.jsp页面当中

<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" prefix="security"%>

<p>
<security:authentication property="principal.username"></security:authentication>
</p>
c、重新运行项目


2、设置当前用户如果没有ADMIN就不能看到用户管理的选项
(1)修改aside.jsp

<security:authorize access="hasRole('ADMIN')" >
<li id="system-setting">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/findAll.do">
<i class="fa fa-circle-o"></i> 用户管理
</a>
</li>
</security:authorize>
(2)修改spring-security.xml

<security:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<!-- 配置具体的拦截的规则 pattern="请求路径的规则" access="访问系统的人,必须有ROLE_USER的角色" -->
<security:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER','ROLE_ADMIN') "/>
(3)运行项目
登录james
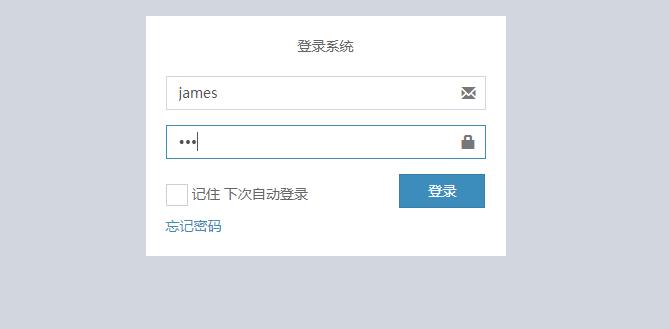
用户管理的选项消失了

登录tom,tom拥有ADMIN角色
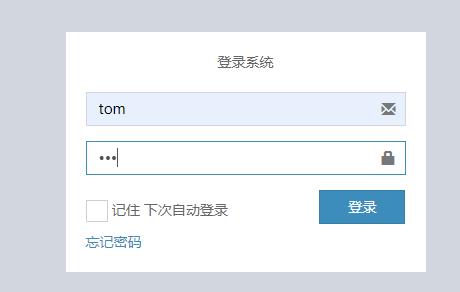
用户管理依旧在

3、常用标签
在jsp中我们可以使用以下三种标签,其中authentication代表的是当前认证对象,可以获取当前认证对象信息,例
如用户名。其它两个标签我们可以用于权限控制
(1) authentication
<security:authentication property="" htmlEscape="" scope="" var=""/>
property: 只允许指定Authentication所拥有的属性,可以进行属性的级联获取,如“principle.username”,
不允许直接通过方法进行调用。
htmlEscape:表示是否需要将html进行转义。默认为true。
scope:与var属性一起使用,用于指定存放获取的结果的属性名的作用范围,默认我pageContext。Jsp中拥
有的作用范围都进行进行指定。
var: 用于指定一个属性名,这样当获取到了authentication的相关信息后会将其以var指定的属性名进行存放,默认是存放在pageConext中
(2) authorize
authorize
是用来判断普通权限的,通过判断用户是否具有对应的权限而控制其所包含内容的显示
<security:authorize access="" method="" url="" var=""></security:authorize>
access:
需要使用表达式来判断权限,当表达式的返回结果为true时表示拥有对应的权限
method:
method属性是配合url属性一起使用的,表示用户应当具有指定url指定method访问的权限,
method的默认值为GET,可选值为http请求的7种方法
url:
url表示如果用户拥有访问指定url的权限即表示可以显示authorize标签包含的内容
var:
用于指定将权限鉴定的结果存放在pageContext的哪个属性中
(3) accesscontrollist
accesscontrollist标签是用于鉴定ACL权限的。
其一共定义了三个属性:hasPermission、domainObject和var,其中前两个是必须指定的
<security:accesscontrollist hasPermission="" domainObject="" var=""></security:accesscontrollist>
hasPermission:
hasPermission属性用于指定以逗号分隔的权限列表
domainObject:
domainObject用于指定对应的域对象
var:
var则是用以将鉴定的结果以指定的属性名存入pageContext中,以供同一页面的其它地方使用
以上是关于Java SSM 项目实战 day08 方法级别的权限操作 服务器端的权限控制(JSR-250注解)(支持表达式的注解)(@Secured)以及页面端的权限控制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章