从零到一搭建React组件库
Posted 记得要微笑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从零到一搭建React组件库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近一直在捣鼓如何搭建React组件库,至于为什么会产生这个想法,主要是因为组件库对于前端生态来说究极重要,每一个着眼于长远发展、看重开发效率的的互联网公司基本上都会量身定制自己的组件库,它的好处不用多说。对于前端工程师而言,去理解以及掌握它,可以让我们在今后的工作中以及应聘过程中多出一项特殊技能,并且对自身的纵向发展也就是很有利的。下面是我记录我在搭建组件库的过程。
初始化工程
搭建工程不打算采用create-react-app脚手架来搭建,因为脚手架封装好了很多东西,而有些东西对于组件库并不适用,用来搭建组件库过于臃肿,因此我不打算借助任何脚手架来搭建工程。
首先,先创建一个工程文件夹pony-react-ui,在该文件夹下执行如下命令:
npm init // 生成package.json
tsc --init // 生成tsconfig.json然后,按照如下目录结构初始化工程:
pony-react-ui
├── src
├── assets
├── components
├── Button
├── Button.tsx
└── index.ts
└── Dialog
├── Dialog.tsx
└── index.ts
├── styles
├── _button.scss
├── _dialog.scss
├── _mixins.scss
├── _variables.scss
└── pony.scss
└── index.ts // 打包的入口文件,引入pony.scss,抛出每一个组件
├── index.js // 主文件入口,package.json中main字段指定的文件
├── package.json
├── tsconfig.json // 指定了用来编译这个项目的根文件和编译选项
├── webpack.config.js
└── README.md编写一个Button组件
Button组件应该满足一下需求:
- 不同尺寸
- 不同类型
- 不同颜色
- 禁用状态
- 点击事件
Button.tsx
import React from \'react\';
import classNames from \'classnames\';
export interface IButtonProps {
onClick?: React.MouseEventHandler;
// 类型
primary?: boolean;
secondary?: boolean;
outline?: boolean;
dashed?: boolean;
link?: boolean;
text?: boolean;
// 尺寸
xLarge?: boolean;
large?: boolean;
small?: boolean;
xSmall?: boolean;
xxSmall?: boolean;
// 颜色
success?: boolean;
warn?: boolean;
danger?: boolean;
// 禁用状态
disabled?: boolean;
className?: string;
style?: React.CSSProperties;
children?: React.ReactNode;
}
export const Button = (props: IButtonProps) => {
const {
className: tempClassName,
style,
onClick,
children,
primary,
secondary,
outline,
dashed,
link,
text,
xLarge,
large,
small,
xSmall,
xxSmall,
success,
danger,
warn,
disabled,
} = props;
const className = classNames(
{
\'pony-button\': true,
\'pony-button-primary\': primary,
\'pony-button-secondary\': secondary && !text,
\'pony-button-outline\': outline,
\'pony-button-dashed\': dashed,
\'pony-button-link\': link,
\'pony-button-text\': text && !secondary,
\'pony-button-text-secondary\': secondary && text,
\'pony-button-round\': round,
\'pony-button-rectangle\': noRadius,
\'pony-button-fat\': fat,
\'pony-button-xl\': xLarge,
\'pony-button-lg\': large,
\'pony-button-sm\': small,
\'pony-button-xs\': xSmall,
\'pony-button-xxs\': xxSmall,
\'pony-button-long\': long,
\'pony-button-short\': short,
\'pony-button-success\': success,
\'pony-button-warn\': warn,
\'pony-button-danger\': danger,
\'pony-button-disabled\': disabled,
},
tempClassName
);
return (
<button
type="button"
className={className}
style={style}
onClick={onClick}
disabled={disabled}>
<span className="pony-button__content">{children}</span>
</button>
);
}在Button/index.ts文件中抛出Button组件以及定义的类型
export * from \'./Button\';这样,一个示例组件就基本完成了,有同学肯定会有这么一个疑问,为什么在Button.tsx中没有引入它的样式文件_button.scss,而是在使用时引入全局样式或者单独引入_button.scss呢?
// 单独引入组件样式
import { Button } from \'pony-react-ui\';
import \'pony-react-ui/lib/styles/button.scss\';
// 全局引入组件样式,打包时抽离出来的样式
import \'pony-react-ui/lib/styles/index.scss\';这跟样式的权重有关,通过import引入的样式权重会低于JSX中className定义的样式,因此才可以在组件外部修改内部的样式。
举个实例:
import { Button } from \'pony-react-ui\';
import \'pony-react-ui/lib/styles/button.scss\';
import styles from \'./index.module.scss\';
const Demo = () => (
<div className={styles.btnBox}>
<Button onClick={submit}>submit</Button>
</div>
)引入组件库中的Button.scss和本地的index.module.scss在打包后会以<style></style>标签注入到页面中,而且顺序是:
<style type="text/css">
// Button.scss的样式
</style>
<style type="text/css">
// index.module.scss的样式
</style>因此,index.module.scss中的样式权重是高于Button.scss中的样式,可以在index.module.scss中修改Button.scss的样式
编写样式
├── styles
├── _button.scss
├── _dialog.scss
├── _mixins.scss
├── _variables.scss
└── pony.scss我在style文件下存放所有的样式文件,与_button.scss、_dialog.scss类型的样式文件属于组件的样式文件,_mixins.scss用于存放mixin指令,提高样式逻辑复用
// _mixins.scss
@mixin colors($text, $border, $background) {
color: $text;
background-color: $background;
border-color: $border;
}
// 设置按钮大小
@mixin button-size($padding-x, $height, $font-size) {
height: $height;
padding: 0 $padding-x;
font-size: $font-size;
line-height: ($height - 2);
}
比如,在_button.scss中使用
$values: #ff0000, #00ff00, #0000ff;
.primary {
@include colors($values...);
}node-sass会将其编译成
.primary {
color: #ff0000;
background-color: #00ff00;
border-color: #0000ff;
}_variables.scss用于存放一些样式常量,比如定义不同尺寸按钮的字体大小:
$button-font-size: 14px !default;
$button-xl-font-size: 16px !default;
$button-lg-font-size: 16px !default;
$button-sm-font-size: 12px !default;pony.scss会引入所有的样式文件,_mixins.scss、_variables.scss这类工具类样式文件需要置前引入,因为后面的组件样式文件可能依赖它们
@import \'variables\';
@import \'mixins\';
@import \'button\';
@import \'dialog\';
...
在对样式文件构建处理时,我没有使用css modules去避免样式重名,而是使用BEM规范书写样式规避这一问题。为什么我要这么做呢?
rules: [
{
test: /\\.(sa|sc|c)ss$/,
use: [
loader: \'css-loader\',
options: {
modules: false // 禁止css modules
}
]
}
]因为使用css modules导致无法从组件外部修改组件内部样式。通常,从外部修改组件样式一般会这样写:
<Button className="btn">按钮</Button>
// 修改Button内部样式,假如组件内部样式有个样式类名为pony-button-promary
.btn {
:global {
.pony-button-promary {
color: #da2227;
}
}
}但是,采用了css modules后,pony-button-promary类名后面会多出一串hash值,而且在每次修改Button组件后,生成的hash都会不同,这将导致在深度遍历查找过程中找不到类名
.btn {
:global {
// 下次修改Button组件构建后,生成的hash不一定为sadf6756
.pony-button-promary-sadf6756 {
color: #da2227;
}
}
}构建
打包入口文件
src/index.ts为webpack构建入口文件
import \'./styles/pony.scss\';
export * from \'./components/Button\';
export * from \'./components/Dialog\';这里会引入全局样式文件,在构建时MiniCssExtractPlugin会对样式进行抽离压缩,然后分离输出JS脚本和CSS脚本
打包输出UMD规范
在构建之前,我们必须明确组件库的使用场景。现在常见会通过es module以及CommonJS引入,有些场景下会直接使用 <script> 在 html 中引入,还有些极少数场景使用AMD(require.js)、CMD(sea.js)引入。作为组件库,应该兼容这些使用场景。组件库应该保持中立,不应该限定于某种使用方式。
为了支持多种使用场景,我们需要选择合适的打包格式。webpack提供多种打包输出方式,如下:
MyLibrary是由output.library 定义的变量名
libraryTarget: \'var\':当library加载完成,入口起点的返回值将分配给一个变量var MyLibrary = _entry_return_; // 在一个单独的 script... MyLibrary.doSomething();libraryTarget: \'this\':入口起点的返回值将分配给this的一个属性,this的含义取决于你this[\'MyLibrary\'] = _entry_return_; // 在一个单独的 script... this.MyLibrary.doSomething(); MyLibrary.doSomething(); // 如果 this 是 windowlibraryTarget: \'window\':入口起点的返回值分配给window对象的这个属性下window[\'MyLibrary\'] = _entry_return_; window.MyLibrary.doSomething();libraryTarget: \'global\':入口起点的返回值分配给global对象的这个属性下global[\'MyLibrary\'] = _entry_return_; global.MyLibrary.doSomething();libraryTarget: \'commonjs\':入口起点的返回值分配给exports对象。这个名称也意味着,模块用于CommonJS环境exports[\'MyLibrary\'] = _entry_return_; require(\'MyLibrary\').doSomething();libraryTarget: \'module\':输出ES模块,需要注意的是,该功能还未完全支持libraryTarget: \'commonjs2\':入口起点的返回值将分配给module.exports对象。这个名称也意味着模块用于CommonJS环境module.exports = _entry_return_; require(\'MyLibrary\').doSomething();libraryTarget: \'amd\':将你的library暴露为AMD模块。AMD模块要求入口chunk(例如使用标签加载的第一个脚本)通过特定的属性定义,例如define和require,它们通常由RequireJS或任何兼容的模块加载器提供(例如almond)。否则,直接加载生成的AMD bundle将导致报错,如define is not definedmodule.exports = { //... output: { library: \'MyLibrary\', libraryTarget: \'amd\', }, };生成的
output名称将被定义为"MyLibrary":define(\'MyLibrary\', [], function () { return _entry_return_; });可以在
script标签中,将bundle作为一个模块整体引入,并且可以像这样调用bundle:require([\'MyLibrary\'], function (MyLibrary) { // Do something with the library... });如果
output.library未定义,将会生成以下内容。define([], function () { return _entry_return_; });libraryTarget: \'umd\':将你的library暴露为所有的模块定义下都可运行的方式。它将在CommonJS, AMD环境下运行,或将模块导出到global下的变量module.exports = { //... output: { library: \'MyLibrary\', libraryTarget: \'umd\', }, };最终的输出结果为:
(function webpackUniversalModuleDefinition(root, factory) { if (typeof exports === \'object\' && typeof module === \'object\') module.exports = factory(); else if (typeof define === \'function\' && define.amd) define([], factory); else if (typeof exports === \'object\') exports[\'MyLibrary\'] = factory(); else root[\'MyLibrary\'] = factory(); })(typeof self !== \'undefined\' ? self : this, function () { return _entry_return_; });
根据上面描述,将libraryTarget="umd"设置umd打包格式。webpack处理脚本、样式以及字体文件的具体配置如下:
const path = require(\'path\');
const webpack = require(\'webpack\');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require(\'mini-css-extract-plugin\');
// const UglifyJsPlugin = require(\'uglifyjs-webpack-plugin\');
const TerserJSPlugin = require(\'terser-webpack-plugin\');
const OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin = require(\'optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin\');
// const SpeedMeasurePlugin = require(\'speed-measure-webpack-plugin\')
// const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require(\'clean-webpack-plugin\');
// const LoadablePlugin = require(\'@loadable/webpack-plugin\')
// const smp = new SpeedMeasurePlugin() // 测量构建速度
const devMode = process.env.NODE_ENV !== \'production\';
const pkg = require(\'./package.json\');
module.exports = ({
mode: devMode ? \'development\' : \'production\',
devtool: devMode ? \'inline-source-map\' : \'hidden-source-map\',
entry: path.resolve(__dirname, \'./src/index.ts\'),
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, \'./dist\'),
filename: devMode ? \'pony.js\' : \'pony.min.js\',
library: \'pony\',
libraryTarget: \'umd\'
},
resolve: {
// Add `.ts` and `.tsx` as a resolvable extension.
extensions: [\'.ts\', \'.tsx\', \'.js\'],
alias: {
}
},
module: {
rules: [
// all files with a `.ts` or `.tsx` extension will be handled by `ts-loader`
{
test: /\\.tsx?$/,
use: [
\'babel-loader?cacheDirectory\',
{
loader: \'ts-loader\',
options: {
configFile: \'tsconfig.json\'
}
}
]
},
{
test: /\\.(sa|sc|c)ss$/,
use: [
{
loader: MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader // 抽取样式文件,将css样式文件用link标签引入,使用此loader就不需要用style-loader,即使用了也不会有效果
},
{
loader: \'css-loader\',
options: {
modules: {
auto: true,
localIdentName: \'[path][name]__[local]\'
},
importLoaders: 2, // 一个css中引入了另一个css,也会执行之前两个loader,即postcss-loader和sass-loader
}
},
{
// 使用 postcss 为 css 加上浏览器前缀
loader: \'postcss-loader\',
options: {
// options has an unknown property \'plugins\';
postcssOptions: {
// PostCSS plugin autoprefixer requires PostCSS 8.将autoprefixer降到8.0.0版本
plugins: [require(\'autoprefixer\')]
}
}
},
{
loader: \'sass-loader\' // 使用 sass-loader 将 scss 转为 css
}
]
},
{
test: /(\\.(eot|ttf|woff|woff2)|font)$/,
loader: \'file-loader\',
options: { outputPath: \'fonts/\' }
},
{
test: /\\.(png|jpg|gif|svg|jpeg)$/,
loader: \'file-loader\',
options: { outputPath: \'images/\' }
}
]
},
plugins: [
// new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
// new LoadablePlugin(),
// 该插件能够使得指定目录被忽略,从而使得打包变快,文件变小;下面忽略了包含’./locale/\'该字段路径的文件目录,但是也使得我们使用的时候不能显示中文语言了,所以这个时候可以手动引入中文语言的目录
new webpack.IgnorePlugin(/\\.\\/locale/, /moment/),
// 主要用于对打包好的js文件的最开始处添加版权声明
new webpack.BannerPlugin(`pony ${pkg.version}`),
// 将CSS提取到单独的文件中
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
// Options similar to the same options in webpackOptions.output
// both options are optional
filename: devMode ? \'pony.css\' : \'pony.min.css\',
chunkFilename: \'[id].css\'
})
// devMode ? new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin() : null
],
optimization: {
minimizer: devMode
? []
: [
// 压缩js代码
// new UglifyJsPlugin({
// cache: true, // 启用文件缓存并设置缓存目录的路径
// parallel: true, // 使用多进程并行运行
// sourceMap: true // set to true if you want JS source maps
// }),
// webpack v5 使用内置的TerserJSPlugin替代UglifyJsPlugin,因为UglifyJsPlugin不支持ES6
new TerserJSPlugin({
// cache: true, // 启用文件缓存并设置缓存目录的路径
parallel: true, // 使用多进程并行运行
// sourceMap: true // set to true if you want JS source maps
}),
// 用于优化或者压缩CSS资源
new OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin({
assetNameRegExp: /\\.css$/g,
cssProcessor: require(\'cssnano\'), // 用于优化\\最小化 CSS 的 CSS 处理器,默认为 cssnano
cssProcessorOptions: { safe: true, discardComments: { removeAll: true } }, // 传递给 cssProcesso
canPrint: true // 布尔值,指示插件是否可以将消息打印到控制台,默认为 true
})
],
sideEffects: false
}
});
这里对上述配置做一个说明:
- 在将
scss转化成css后,使用postcss对样式做了一些加工,利用autoprefixer插件为样式加上浏览器前缀,防止有一些样式存在兼容性问题 - 使用
webpack内置插件BannerPlugin给构建后的文件开头加上版本号 - 工程使用
webpack 5.x版本进行构建,使用内置TerserJSPlugin对JS进行压缩;样式压缩采用OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin插件。另外为了生成压缩和非压缩两个版本,通过cross-env插件在执行构建命令时注入环境变量控制是否压缩优化
配置如下构建命令:
"scripts": {
"build:dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack",
"build:prod": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack",
"build": "npm run build:prod && npm run build:dev"
},当执行yarn build时,在dist目录下生成压缩和非压缩两个版本的脚本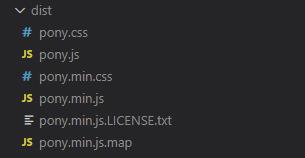
src/index.js为指向模块的入口程序,在开发环境引入的是dist/pony.js,在生产环境下引入的是dist/pony.min.js
if (!process.env.NODE_ENV || process.env.NODE_ENV === \'development\') {
module.exports = require(\'./dist/pony.js\');
} else {
module.exports = require(\'./dist/pony.min.js\');
}
打包输出es module规范
webpack 5.x还未完全支持es module打包方式,处于实验室试用阶段。tsc编译器可以完成这件事,只需要按如下配置好编译选项,主要module属性为"ES6"或 "ES2015"
// tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2015", // 指定ECMAScript目标版本 "ES3"(默认), "ES5", "ES6"/ "ES2015", "ES2016", "ES2017"或 "ESNext"
"lib": [ // 编译过程中需要引入的库文件的列表
"dom",
"esnext"
],
"module": "es2015", // 指定生成哪个模块系统代码:"None", "CommonJS", "AMD", "System", "UMD", "ES6"或 "ES2015"
"allowJs": true, // 指定是否允许编译JS文件,默认false,即不编译JS文件
"skipLibCheck": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"strict": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"moduleResolution": "node",
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"isolatedModules": true,
"noEmit": false, // 不生成输出文件
"jsx": "react", // 在 .tsx文件里支持JSX
"newLine": "lf", // 当生成文件时指定行结束符: "crlf"(windows)或 "lf"(unix)
},
"include": [
"src/**/*.ts",
"src/**/*.tsx"
],
"exclude": [
"node_modules"
]
}
在typescript项目中还需要生成类型声明文件,我在根目录下新建tsconfig.build.json,继承tsconfig.json中的配置
// tsconfig.build.json
{
"extends": "./tsconfig",
"compilerOptions": {
"declaration": true, // 指定是否在编译的时候生成相应的d.ts声明文件,如果设为true,编译每个ts文件之后会生成一个js文件和一个声明文件,但是declaration和allowJs不能同时设为true
"declarationMap": false, // 指定编译时是否生成.map文件
"sourceMap": true, // 编译时是否生成.map文件
},
"include": [
"src/**/*.ts",
"src/**/*.tsx"
],
"exclude": [
"node_modules"
]
}在scripts命令中增加
"scripts": {
"build:dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack",
"build:prod": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack",
// 生成es module编译命令
"build:tsc": "tsc -p tsconfig.build.json --target ES5 --outDir lib",
"build": "npm run build:prod && npm run build:dev"
},当执行yarn build:tsc会编译生成es module规范脚本,如下所示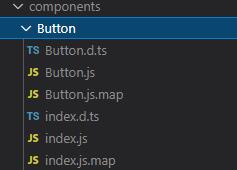
有同学肯定会问为什么不直接在tsconfig.json新增编译选项呢?
还记得构建脚本中编译tsx的配置项吗?
module: {
rules: [
// all files with a `.ts` or `.tsx` extension will be handled by `ts-loader`
{
test: /\\.tsx?$/,
use: [
\'babel-loader?cacheDirectory\',
{
loader: \'ts-loader\',
options: {
configFile: \'tsconfig.json\'
}
}
]
},
]
} 在使用webpack构建生成umd规范的脚本时不需要生成类型声明文件,在tsc编译生成es module规范脚本时需要生成,因此做了区分
生成es module规范脚本的同时,也做到了组件的按需加载,因为按需加载依赖es module
上面只生成了es module规范的Js脚本和类型声明文件,没有对于样式文件、静态资源文件没有做处理,这部分该怎么处理呢?
我没有对其做特殊处理,只是将assets、styles目录及其子目录copy到lib文件夹,先安装以下几个库:
yarn add rimraf make-dir-cli cpr --save-devnpm script 中涉及到的文件系统操作包括文件和目录的创建、删除、移动、复制等操作,而社区为这些基本操作也提供了跨平台兼容的包,列举如下:
rimraf或del-cli,用来删除文件和目录,实现类似于rm -rf的功能;cpr,用于拷贝、复制文件和目录,实现类似于cp -r的功能;make-dir-cli,用于创建目录,实现类似于mkdir -p的功能;
配置一下scripts命令:
"scripts": {
"build:dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack",
"build:prod": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack",
"clean": "rimraf dist && rimraf lib",
"build:tsc": "tsc -p tsconfig.build.json --target ES5 --outDir lib",
"build:es": "cpr src/styles lib/styles -o && cpr src/assets lib/assets -o",
"build": "npm run clean && npm run build:prod && npm run build:dev && npm run build:tsc && npm run build:es"
},当执行yarn build后会生成两种规范的脚本目录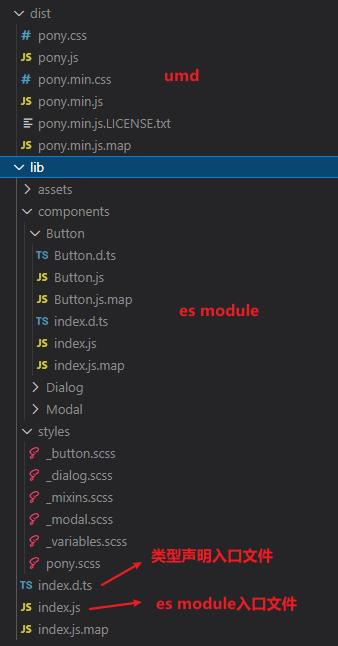
package.json配置
最后完善一下package.json的配置:
{
"name": "pony-react-ui",
"version": "1.0.2",
"description": "React组件库",
"main": "index.js", // 配置一个文件名指向模块的入口程序
"module": "lib/index.js",
"types": "lib/index.d.ts",
"author": "zhousheng_zuel@163.com",
"license": "MIT",
"homepage": "",
"keywords": [
"react",
"component"
],
"scripts": {
"build:dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack",
"build:prod": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack",
"clean": "rimraf dist && rimraf lib",
"build:tsc": "tsc -p tsconfig.build.json --target ES5 --outDir lib",
"build:es": "cpr src/styles lib/styles -o && cpr src/assets lib/assets -o",
"build": "npm run clean && npm run build:prod && npm run build:dev && npm run build:tsc && npm run build:es"
},
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/Revelation2019/pony-react-ui/issues",
"email": "zhousheng_zuel@163.com"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https://github.com/Revelation2019/pony-react-ui.git"
},
"files": [
"dist/*",
"lib",
"index.js",
"package.json",
"README.md"
],
...
}
main:定义commonjs规范的入口文件module:定义es module规范的入口文件types:定义类型声明入口文件files:指定这个包被install时候有哪些文件homepage:项目官网的url
docz生成组件使用文档
有了团队的 UI 组件库就少不了使用文档,毕竟文档还是比口口相传要靠谱的多。这里介绍一个可以快速创建 React UI 组件库使用、演示文档的项目: Docz 。 Docz 的特色是零配置、简单、快速,它使用 Markdown 语法的扩展 MDX (在 Markdown 里引入 React 组件并渲染出组件)来书写文档,对于熟悉 Markdown 的开发者是可以直接上手的。
!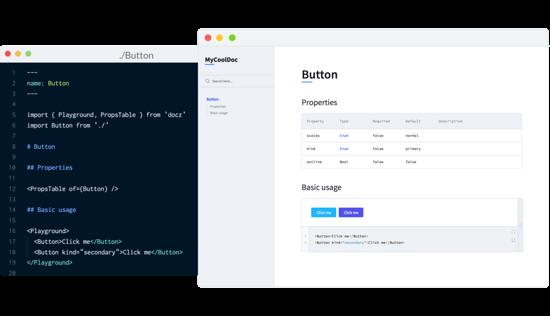
左边是创建的 MDX 文档,右边是 Docz 渲染出的组件及组件代码。
是不是很方便?那下面简单介绍一下使用步骤
- 在你的项目里安装
Docz
yarn add docz --dev 或者 npm install docz --save-dev- 在根目录下创建
docs文件夹存放mdx文件
编写
mdx文件
需要注意的是mdx中不能使用react hooks写法--- name: Button menu: Components --- import { Playground, Props } from "docz"; import { Button } from "../src/components/Button"; import "../src/styles/_button.scss"; # 按钮 ## Properties <Props of={Button} /> ## 基础用法 <Playground> <Button primary> primary button </Button> </Playground> ## 多种用法 <Playground> <Button secondary> danger button </Button> </Playground>在根目录下创建配置文件
doczrc.js,并写入如下配置:export default { title: \'pony-ui\', // 网站的标题 typescript: true, // 如果需要在.mdx文件中引入Typescript组件,则使用此选项 dest: \'build-docs\', // 指定docz构建的输出目录 files: \'docs/*.mdx\', // Glob模式用于查找文件。默认情况下,Docz会在源文件夹中找到所有扩展名为.mdx的文件。 ignore: [\'README.md\', \'CHANGELOG.md\'] // 用于忽略由docz解析的文件的选项 };docz使用gatsby来搭建静态站点展示组件说明文档,需要安装gatsby-plugin-sass使站点支持scss。在根目录下新建gatsby-config.js,添加如下配置:module.exports = { plugins: [\'gatsby-plugin-sass\'] };如果执行
docz dev报如下错误:
这是因为gatsby-plugin-sass默认情况下,使用Dart实现的Sass(sass)。 要使用用Node(node-sass)编写的实现,您可以安装node-sass而不是sass并将其作为实现传递到选项中。yarn add node-sass --save-dev修改配置
module.exports = { plugins: [ { resolve: `gatsby-plugin-sass`, options: { implementation: require("node-sass"), }, } ], }配置
scripts命令
当执行docz dev后,会构建mdx文件,并且创建静态站点展示组件说明文档(这一过程会加载gatsby-config.js配置选项,使站点支持sass)"scripts": { "docz:dev": "docz dev", "docz:build": "docz build", "docz:serve": "docz build && docz serve", "build:dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack", "build:prod": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack", "clean": "rimraf dist && rimraf lib", "build:tsc": "tsc -p tsconfig.build.json --target ES5 --outDir lib", "build:es": "cpr src/styles lib/styles -o && cpr src/assets lib/assets -o", "build": "npm run clean && npm run build:prod && npm run build:dev && npm run build:tsc && npm run build:es" },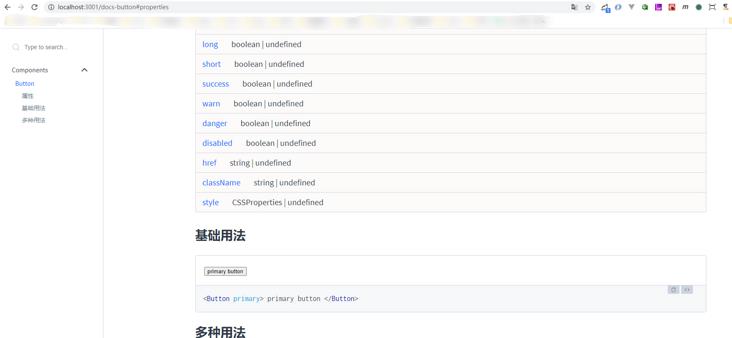
发布到npm仓库
首先登录npm,在终端输入npm login,跟着提示输入账户名、密码以及邮箱,如果报了如下错误:
npm ERR! 409 Conflict - PUT http://npm.dev.casstime.com/-/user/org.couchdb.user:xxx - user registration disabled这是因为镜像源使用的不是http://registry.npmjs.org/,我这里使用的公司的镜像源,要改成http://registry.npmjs.org/,执行如下命令即可,然后重新登录,构建后执行yarn publish即可(跟npm publish有些区别,这里不多讲)
npm config set registry=http://registry.npmjs.org/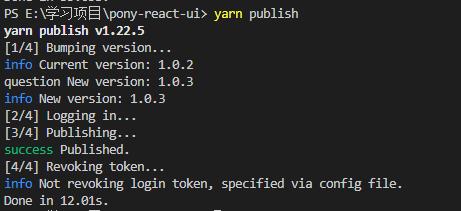
部署
我们公司并没有将构建好的目录部署到服务器上,而是通过nginx代理去拉取gitlab上的静态文件,详细流程如下:
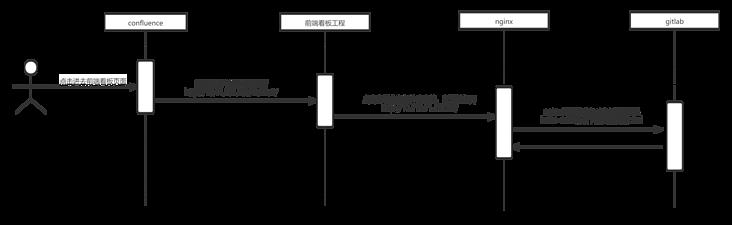
nginx配置:
server {
listen 83;
server_name 10.118.71.232;
location / {
root /opt/web/gitweb/inquiry-bre-component/build-docs;
index index.html index.htm;
if ( $request_uri !~* \\. ) {
rewrite ^/([\\w/]+).*/? /index.html break;
}
}
}
server {
listen 82;
server_name 10.118.71.232;
location / {
root /opt/web/gitweb/bre-components/build-docs;
index index.html index.htm;
if ( $request_uri !~* \\. ) {
rewrite ^/([\\w/]+).*/? /index.html break;
}
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name 10.118.71.232;
location ~ ^/v {
root /opt/web/gitweb/bricks-docs;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location / {
root /opt/web/gitweb/bricks-docs;
index index.html index.htm;
if ( $request_uri !~* \\. ) {
rewrite ^/([\\w/]+).*/? /index.html break;
}
}
} 最后附上仓库地址:https://github.com/Revelation...
以上是关于从零到一搭建React组件库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章