初识Spring源码 -- 属性填充populateBean | 静态属性注入
Posted 做猪呢,最重要的是开森啦
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了初识Spring源码 -- 属性填充populateBean | 静态属性注入相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
0. 举个栗子:
@Component
public class SetterBean {
@Autowired
private BeanService beanService;
@Autowired
public void setBean() {
BeanServiceImpl bean = new BeanServiceImpl();
bean.setName("WTF");
beanService = bean;
}
}
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationBean {
@Bean
public BeanService beanService() {
BeanServiceImpl beanService = new BeanServiceImpl();
beanService.setName("zhangsan");
return beanService;
}
}
2. populateBean:
主要源码入口:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
至此,doCreateBean经历以下步骤:
- 实例化bean
- applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors进行属性和方法的预解析
- addSingletonFactory引入三级缓存
- populateBean属性填充
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
... ... ...
// 这块是提前暴露bean,引入三级缓存,解决循环依赖的,这里不做叙述
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 属性填充方法populateBean,进行依赖注入等
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
... ... ...
}
以下是属性注入方法populateBean整个方法的概览,下文会逐步介绍重点代码。
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
// 这块主要是成立bw == null的异常情况的,感觉没什么用,封装的实例bw不太会为null
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
return;
}
}
// mbd.isSynthetic()默认是false,也不懂什么情况是true,不必理会
// 同时有实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的Bean,则继续往下,正常这个条件都是成立的
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 返回false,这个属性就不继续注入,2.1中会说明一下这里
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
// 暂时不懂什么情况hasPropertyValues有值,难道是xml配置的时候的?
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// 采用注解的时候resolvedAutowireMode=0
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
// 这里是针对xml配置的bean,下文2.2会说明
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
// 是否有实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors的bean,到这都是会有的
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
// 是否需要依赖检查,默认false
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 这个是重点,postProcessProperties在这进行属性的注入,
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 兼容老版本的注入
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 依赖检查,对应depends-on属性
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 将所有PropertyValues中的属性填充到bean中
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
2.1. postProcessAfterInstantiation:
这块代码是作为扩展用的,比如有一个实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的bean,重写方法
·
在实例化SetterBean后,在属性注入之前给个机会修改bean或者放弃属性注入
·
比如此处不进行属性beanService注入,返回false;此时SetterBean对象内部属性全为空
·
除非扩展,不然正常都返回true,像AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class BeanInstantiaitionAwareImpl implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("setterBean"){
SetterBean setterBean = (SetterBean) bean;
setterBean.setXXX("XXX");
return false;
}
//默认返回true,什么也不做,继续下一步 初始化
return true;
}
2.1. resolvedAutowireMode:
这一块对resolvedAutowireMode判断逻辑代码,是针对xml配置的,可参考链接
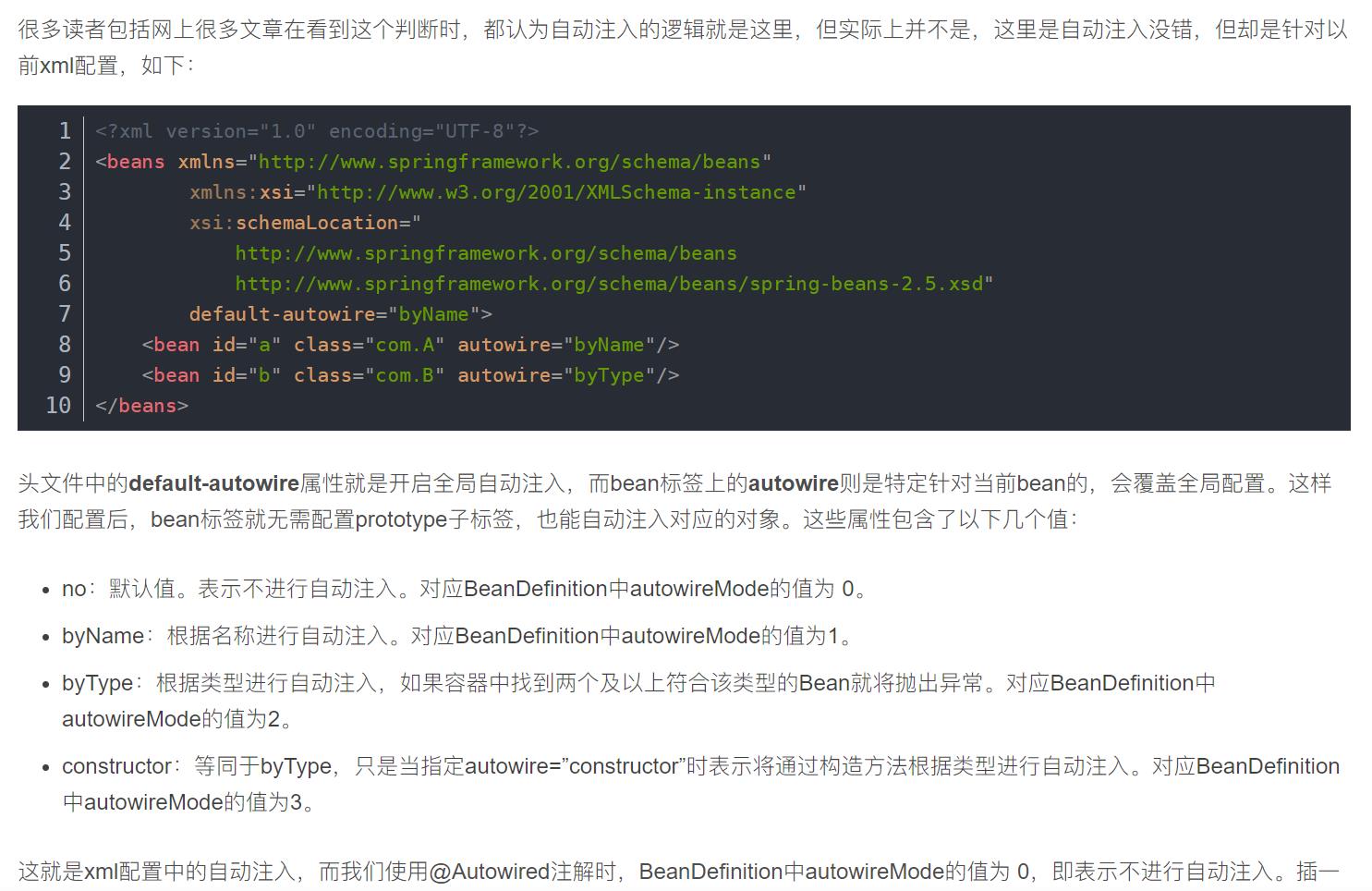
2.3. postProcessProperties:
这个是重点,对于@Autowired注入,此处调用的是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个后置处理器的方法
·
findAutowiringMetadata方法中,会从缓存中获取到InjectionMetadata,可见链接
·
再根据属性方法元数据metadata,进行注入
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 根据属性方法元数据metadata,进行注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
2.4. metadata.inject:
属性元数据封装到AutowiredFieldElement,方法元数据封装到AutowiredMethodElement,最后都封装到InjectionMetadata
`
二者都是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类,继承InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement
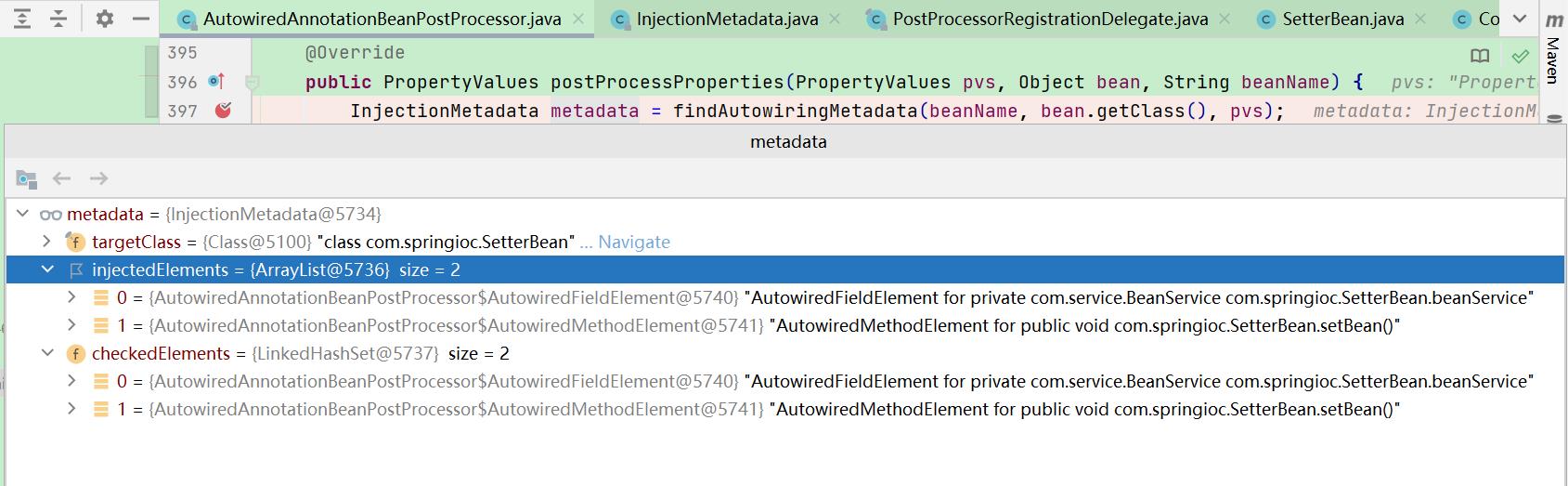
循环遍历属性、方法元数据进行注入;封装的对象都是继承InjectedElement的
·
会先进行属性注入,再进行方法注入,所以属性注入会存在被覆盖的可能,本栗子中,最后注入的beanService的name为WTF
·
根据这个特性,可以对static修饰的对象,进行方法注入,达到属性注入的效果
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
// 遍历属性/方法元数据
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
// 进行注入
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
2.5. element.inject :
resolveDependency方法来获取依赖的属性bean,这里的详细细节后面再介绍。
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// 就是类属性,反射中的field
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
// 有缓存就通过缓存获取注入的属性bean
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
// 构建DependencyDescriptor,required除非显示指定非必须@Autowired(required = false),默认是true
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// 这是重点,通过resolveDependency来解析出依赖的属性bean对象
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
// 这里是添加缓存的一些逻辑
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
// value就是依赖的属性bean,通过反射修改bean,实现属性注入
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
2.6. 小结:
通过postProcessAfterInstantiation方法,给后置处理器个机会在属性注入之前修改bean或者放弃属性注入,扩展用的
·
接下来会针对xml配置的bean进行byType / byName处理,注解的bean是不处理的
·
通过postProcessProperties方法进行属性注入
- 从预解析的缓存中获取封装了属性、方法元数据的对象InjectionMetadata
- 循环遍历各元数据,进行注入;先进行属性,再进行方法注入,属性注入会存在被覆盖的可能
- 通过resolveDependency来解析出依赖的属性bean对象
- 最后通过反射修改bean,实现属性注入
【参考】:
你所不知道的Spring的@Autowired实现细节
Spring源码分析衍生篇五:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
以上是关于初识Spring源码 -- 属性填充populateBean | 静态属性注入的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章