C++中的继承
Posted 别碰我的宏定义
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++中的继承相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
前言
提示:C++与C语言相比,增加了后者没有的继承和多态以及封装。今天先了解继承,本博主所写内容全部是在VS2013(32位操作系统)环境下调试得到的
一、什么是继承?
继承在我们的生活中就是权力或者财产的转接,从父辈或者师傅手中继承来某样东西,C++也是这个意思,只不过他继承来的是父类的成员变量和方法。二、继承的几种方式
1.公有继承
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
}
int _a;
};
class Thrived : public Base //class 类名:继承方式 基类类名
{
public:
Thrived(int a, int d)
:_d(d)
{}
void display()
{
cout << this->_a << " "<< this->_d << endl;
}
private:
int _d;
};
int main()
{
Thrived s(1, 2);
s.print();
s.display();
return 0;
}
公有继承拥有父类或者是基类的非私有方法和成员变量并且可以显示调用。
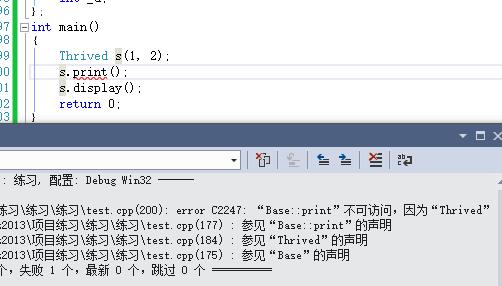
2.私有继承
私有继承则不能调用父类或者说基类的成员函数和变量,因为他对于子类来说是不可见的。你通过调用子类的构造函数来构造父类的对象时,也是不可操作的。
代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
}
int _a;
};
class Thrived : private Base
{
public:
Thrived(int a, int d)
:_d(d)
{}
void display()
{
cout << this->_a << " "<< this->_d << endl;
}
private:
int _d;
};
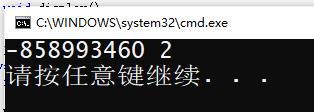
int main()
{
Thrived s(1, 2);
//s.print();
s.display();
return 0;
}
3.保护继承
保护继承和私有继承的性质是差不多一致的。也是不可调用父类的函数和变量。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
}
int _a;
};
class Thrived : protected Base
{
public:
Thrived(int a, int d)
:_d(d)
{}
void display()
{
cout << this->_a << " "<< this->_d << endl;
}
private:
int _d;
};
int main()
{
Thrived s(1, 2);
s.print();
s.display();
return 0;
}
三、基类和派生类对象赋值转换
1.赋值规则
1、派生对象可以赋值给基类的对象,指针或者引用,就像是大的,将其剪成和小的大小差不多的形状,赋给小的。
2、基类对象不能赋值给派生类对象
3、基类的指针可以通过强制类型转化赋值给派生类的指针。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Pet
{
public:
string name;
string sex;
};
class Dog : public Pet
{
public:
string color;
};
int main()
{
Dog d;
Pet p = d; //子类对象可以直接赋值给基类对象
Pet* pp = &d; //子类对象可以直接赋值给基类对象的指针
Pet& ppp = d; //子类对象可以直接赋值给基类对象的引用
d = p; //子类对象不能赋值给派生类的指针
return 0;
}
2.对象模型
对象模型:对象在内存中的存储方式,一个对象中成员变量在内存中的布局方式。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string _name;
char _sex;
int _age;
void Print()
{
cout << this->_name << " " << this->_sex << " " << this->_age << endl;
}
};
class Student : public Person
{
public:
string Stuid;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
Person p;
return 0;
}
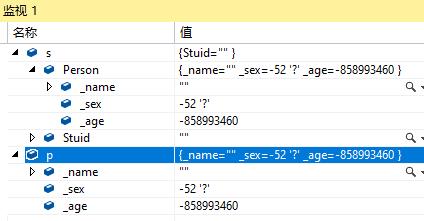
由此可以看出子类在继承父类或者基类的成员变量之后新添加了自己的变量,所以用子类对象赋值给父类对象的时候是可以的,但是用父类给子类赋值的时候就会出现错误。
3.继承的作用域
1、在继承体系中,基类和派生类都有独立的作用域。
2、子类和父类中有同名成员时,子类成员将屏蔽父类对成员的直接访问,称为同名隐藏。也叫重定义,如果需要访问父类的该成员,则可以使用基类:: 基类成员,显示访问。
3、如果是成员函数的隐藏,则只需要函数名相同就会发生同名隐藏。
4、继承体系中最好不要定义同名的成员,构成歧义。
5、友元关系不能继承,基类的友元是不能访问子类的私有和保护成员。
四、派生类默认成员函数
派生类构造成员的规则:
1、派生类构造成员在初始化基类的时候必须调用基类的构造函数,如果基类没有构造函数,则必须在派生类构造函数的初始化列表阶段显示调用。
2、派生类的拷贝构造函数必须要调用基类的拷贝构造函数来完成基类的拷贝构造初始化。
3、派生类对象的初始化先调用基类的构造,再调用派生类的构造。
4、派生类对象析构先调用派生类析构再调用基类的析构函数。
//在基类不声明构造函数的情况下子类必须显示的调用基类的构造函数来初始化基类的对象。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string _name;
string _sex;
int _age;
public:
Person(string name ="Peter" ,string sex = "man" ,int age = 10)
:_name(name)
, _sex(sex)
, _age(age)
{
cout << "Person Class Constructed" << endl;
}
Person(const Person& p)
:_name(p._name)
, _age(p._age)
, _sex(p._sex)
{}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person Class Destroy" << endl;
}
};
class Student : public Person
{
public:
Student(Person p,string s = "Hello World")
:Person(p)
, Stuid(s)
{
cout << "Student Class Constructed" << endl;
}
~Student()
{
cout << "Student Class Destroy" << endl;
}
string Stuid;
};
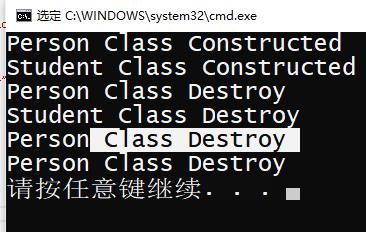
int main()
{
Person p;
Student s(p);
return 0;
}
五、继承与静态成员变量
1.单继承
只继承了一个基类
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int _a;
};
class B : public A
{
public:
int _b;
void print()
{
cout << this->_a << this->_b << endl;
}
};
2.多继承
1、继承于好几个基类
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int _a;
};
class A1
{
public:
int _a1;
};
class B : public A,public A1
{
public:
int _b;
void print()
{
cout << this->_a << this->_b <<this->_a1<< endl;
}
};
2、菱形继承
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int _a;
};
class B1 : public A
{
public:
int _b1;
};
class B2 : public A
{
public:
int _b2;
};
class C :public B1, public B2
{
public:
int _c;
void print()
{
cout << this->_a << this->_b1 << this->_b2 << this->_c << endl;//在访问_a的时候就会出现二义性,从而编译出错。
}
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}
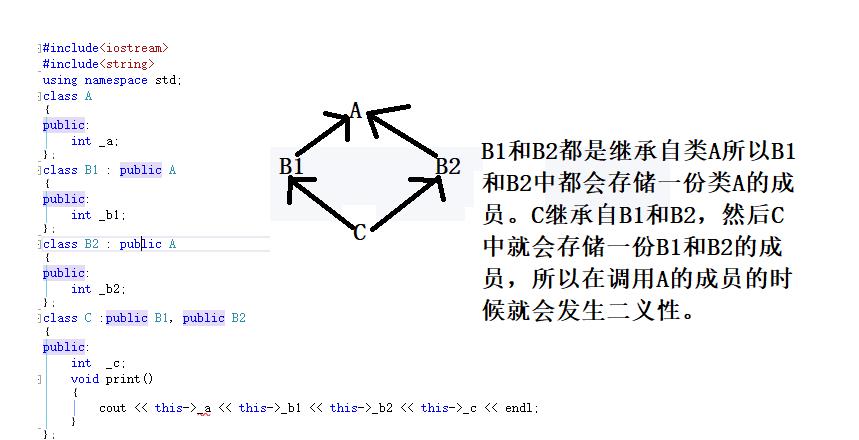
解决菱形继承的方法,虚拟继承
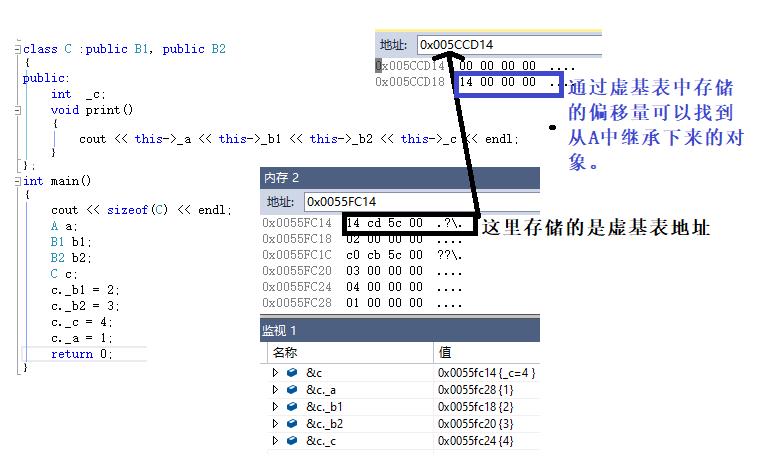
只讲A中的数据在C中存储一份,通过虚基表和偏移量来确定,从而获取A中数据的值。
总结
努力总会有收获的。
以上是关于C++中的继承的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章