Linux 动态链接库(.so)的使用
Posted 旭东的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux 动态链接库(.so)的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 背景
库:就是已经编写好的,后续可以直接使用的代码。
c++静态库:会合入到最终生成的程序,使得结果文件比较大。优点是不再有任何依赖。
c++动态库:动态库,一个文件可以多个代码同时使用内存中只有一份,节省内存,可以随主代码一起编译。缺点是需要头文件。
网友说:库就是除了main函数之外的其他代码,都可以组成库。
2. 只介绍动态库(工作中主要用动态库)
C++使用动态库比C语言使用动态库稍微麻烦点。
因为C++支持函数重载(参数变量个数不同、参数类型不同、类型修饰符不同const/not const等),都会使得C++对函数名进行重写,不方便根据函数名查找对应函数。
C++中可以使用extern关键字修饰对应的函数,表示函数名按照C言语分隔编译,不进行改写。(extern关键字另一个关键字修饰变量,表示变量在其他文件中已经定义。通常见于修饰全局变量)
3. 使用so文件需要的api
头文件 #include <dlfcn.h>
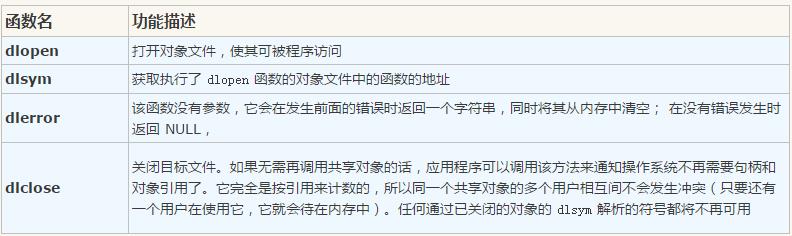
dlopen以指定的模式打开共享链接库。使用可以参考: http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/dlopen.3.html
4. C++使用动态链接库实例
4.1 test.h
1 class Test{ 2 public: 3 virtual int get(); 4 virtual void set(const int num); 5 };
4.2 test.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "test.h" 3 4 int g_num = 0; ///全局变量 5 6 int Test::get() { return g_num; } 7 void Test::set(const int num){ g_num = num; } 8 9 #ifdef __cplusplus 10 extern "C" { 11 #endif 12 13 Test* create(){ return new Test; } 14 15 #ifdef __cplusplus 16 } 17 #endif
4.3 main.cpp
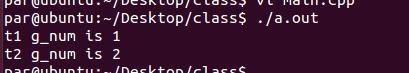
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <dlfcn.h> 3 #include "test.h" 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //声明函数指针 7 typedef Test* (*so_init)(); 8 9 //定义插件类来封装,句柄用完后需要释放 10 struct Plugin{ 11 void *handle; 12 Test *t; 13 14 Plugin():handle(NULL), t(NULL) { } 15 ~Plugin(){ 16 if(t) { delete t; } 17 if (handle) { dlclose(handle); } 18 } 19 }; 20 21 int create_instance(const char *so_file, Plugin &p){ 22 //根据特定的模式打开so文件, 获取so文件句柄 23 //RTLD_NOW:需要在dlopen返回前,解析出所有未定义符号 24 //RTLD_DEEPBIND:在搜索全局符号前先搜索库内的符号,避免同名符号的冲突 25 p.handle = dlopen(so_file, RTLD_NOW | RTLD_DEEPBIND); 26 if (!p.handle) { 27 cout << "Cannot open library: " << dlerror() << endl; 28 return -1; 29 } 30 31 //根据字符串"create"读取库中对应到函数, 并返回函数地址,可以理解为一种间接的“反射机制” 32 so_init create_fun = (so_init) dlsym(p.handle, "create"); 33 if (!create_fun) { 34 cout << "Cannot load symbol" << endl; 35 dlclose(p.handle); 36 return -1; 37 } 38 39 //调用方法, 获取类实例 40 p.t = create_fun(); 41 42 return 0; 43 } 44 45 int main(){ 46 Plugin p1; 47 Plugin p2; 48 49 if (0 != create_instance("./libtest_1.so", p1) 50 || 0 != create_instance("./libtest_2.so", p2)){ 51 cout << "create_instance failed" << endl; 52 return 0; 53 } 54 55 p1.t->set(1); //对库1中到全局变量进行设置 56 p2.t->set(2); //对库2中到全局变量进行设置 57 58 //输出两个库中的全局变量 59 cout << "t1 g_num is " << p1.t->get() << endl; 60 cout << "t2 g_num is " << p2.t->get() << endl; 61 return 0; 62 }
执行:
g++ -fPIC -shared test.cpp -o libtest_1.so
g++ -fPIC -shared test.cpp -o libtest_2.so
g++ -g -Wl,--no-as-needed -ldl main.cpp -rdynamic
以上是关于Linux 动态链接库(.so)的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章